Recommendations for muscle growth
Let's consider the basic rules that every athlete who wants to increase muscle mass must adhere to.
- Burn carbohydrates with exercise. Consuming 20% more than your daily calorie intake each day will ensure active muscle growth. To minimize the deposition of fat under the skin, take carbohydrate cocktails 2 hours before. before training and after 1.5 hours. after her.
- Remember the fat-testosterone relationship. Excluding animal triglycerides from an athlete’s menu will inevitably lead to a decrease in the production of male sex hormone, which will negatively affect the development of muscle mass. In addition, a lack of fat reduces the endurance of an athlete by 10% and the performance of an athlete by 12%. It also causes a drop in lactic acid during strength exercises, which is the main sign of ineffective metabolic processes in the body: an increase in the proportion of harmful cholesterol, loss and inability to absorb vitamins and microelements. The daily intake of triglycerides for intensive development of muscle mass is 80-100g. Exceeding this indicator several times leads to the launch of the mechanism of subcutaneous fat deposition. Therefore, effective nutrition for muscle development prohibits the consumption of excessively fatty foods (salty snacks, chips, margarine, mayonnaise, crackers, smoked meats, spreads).
- Reduce cardio loads. To maintain endurance and strengthen the heart, it is enough to limit yourself to cycling training or 1-2 jogs per week for 30 minutes each. Neglecting this condition can lead to “burning” of muscles.
- Reduce the number of repetitions per exercise. The training program for gaining muscle mass is designed for no more than 50 minutes. At the same time, it is important to perform up to 12 repetitions in one exercise. The number of approaches should not exceed 5 times.
- Balanced nutrition (vitamins, minerals, amino acids, dietary supplements). Ideal nutrient ratio for muscle gain:
- fats (polyunsaturated fatty acids) – 10-20% of the daily diet;
carbohydrates (slow or complex) – 50-60%;
- proteins – 30-35%.
- Not to starve. You need to eat 1.5-2 hours before. before classes, preferably carbohydrate foods and after 1 hour. after physical activity. Otherwise, training on an empty stomach will lead to the body starting to intensively burn protein reserves necessary for muscle growth to replenish energy loss. When refreshing yourself, it is important to control the amount of food you eat - do not overeat. After training, you cannot remain hungry; you need to nourish your body with foods rich in minerals and vitamins. A banana, nuts, cottage cheese, protein shake, bun with milk, kefir, gainer, protein, sandwich with jam are suitable as a light snack. And after 1.5 hours. you need to eat well, preferably protein foods, to restore and increase muscles, otherwise exhaustion of the body cannot be avoided.
- Drink plenty of fluids. The daily volume of water consumed during intense training should be 2.5-3 liters. Lack of fluid leads to dehydration, a decrease in muscle strength by 20% and slower muscle growth.
- Rest. The growth of muscle mass does not occur during periods of intense exercise, but during the rest of the body. Stretching and muscle growth occurs within 3-7 days. During this period, it is worth following a diet and alternating between exercise and rest. For beginners, the period of muscle recovery after strength exercises is 72 hours, for trainees – 36 hours. Healthy sleep should be at least 8 hours. in a day. It is important to avoid stress, since nervousness leads to an increase in cortisol levels in the body, which causes fat deposits and muscle loss. Failure to comply with the rest and nutrition regime helps to pump up muscles without increasing volume.
- Change the training program periodically (every two months). For example, introduce new exercises, take additional weight, change the number of repetitions.
- Go towards your goal. Don't walk around the gym doing nothing. To achieve the desired result, you need to concentrate as much as possible on performing the exercise.
The lack of the required amount of useful organic substances in the diet leads to the fact that the body has nowhere to get the required amount of energy to build muscles. An athlete's daily diet for muscle growth should consist of three full meals and two or three light snacks (fruits, nuts, protein shakes).
Following the above key rules for gaining lean muscle mass is an effective path to a healthy, pumped-up body.
If you are overweight, it is important to lose excess fat before performing strength training exercises to increase muscle mass. To do this, you need to take a weight loss course. This is due to the fact that, contrary to popular belief, it is physiologically impossible to “pump” fat into muscles. The protein diet of Dukan and Maggi will help solve this problem.
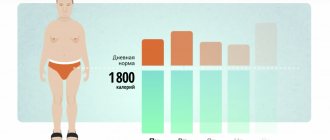
How many calories do you need to gain weight?
In this article, I will tell you how many calories you need to gain weight (pump muscles).
In bodybuilding, at least 70% of success depends on nutrition (in my opinion). For those who don’t know, at the stage of gaining muscle mass there should be an EXCESS OF CALORIES (this is when you eat more carbohydrates (energy) than you expend (expend)), and this is actually what causes an increase in body weight.
If there is no excess calories, it is impossible to build muscle.
To calculate the required number of calories to gain muscle mass, use the formula:
WEIGHT (in kg) X 30 = ....Kcal
For example, if your weight is now 73 kg, then 73x30 = 2190 kcal per day.
However, this resulting figure will tell you the approximate number of calories to maintain your body weight the same. I REPEAT, UNCHANGEABLE. Because our goal is to gain muscle mass, we need a lot of energy, because we need to receive more than we spend (so that excess calories come out), so we need to add at least another 500 calories per day to the resulting kcal per day, so in our example, 2190 + 500 = 2690 kcal . You do the calculation according to your weight.
It’s also worth taking into account your body type. There are 3 of them (ectomorph, endomorph, mesomorph), see photo:
My advice is this: if you are an ectomorph or a mesomorph, you can safely add not 500, but 1000 kcal at once or even more (see and decide for yourself), I would add 500, and then adjust (gradually) upward, because this is the most correct solution . But I do not recommend for an ENDOMORPH (FAT MAN) to exceed the 500 kcal level, because you will gain fat (due to too many calories).
I also recommend reading: “Ectomorph Nutrition”, “Erdomorph Nutrition”, “Mesomorph Nutrition”.
You should also know that as your body weight increases, you will need to increase your caloric intake (otherwise there will be no muscle growth). Those. if at the beginning of your journey you weighed 73 kilograms, and you need 73x30 = 2190 + 500 = 2690 kcal per day, and then you gained from 73 to 75, then now 75x30 = 2250 + 500 = 2750 kcal. Do you see?
WEIGHT INCREASED = INCREASE CALORIES!!!
Once you have figured out the number of calories, you need to start planning your diet. The optimal ratio of nutrients for a healthy diet, including for weight gain, should have the following percentage of fat, protein and carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates - 50-60%
- proteins – 20-30%
- fats – 10-20%
Based on this data, you need to select the required number of the right products, for each category (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), in the right quantities (according to your calorie content).
For example, I was doing calculations for a person who ordered a consultation from me. He needs to gain 2690 kcal for the mass to begin to grow. For CARBOHYDRATES, he uses (eats) either BUCKWHEAT or RICE. Protein products include only chicken breast and cottage cheese. Based on this, I made calculations for him:
I opened the table (B+F+U+KKAL) and found the necessary products there (for example, RICE).
I started doing the calculations: I look in the last column (where the calories are, there is the number 345), I take this number and multiply it by the desired number of grams (I chose 600), therefore, 345x6 = 2070 kcal. Next, I calculated the number of carbohydrates from rice: I no longer look at the last column, but at the penultimate one (carbohydrates), there is a figure of 76.0, therefore, 76x6 = 456 grams. carbohydrates. Here, see photo below:
And so with any food product, I hope everyone understands?! ?
And so, what happened in the end for the client who needs to gain 2690 kcal:
CARBOHYDRATES (INDEPENDENTLY)
- Boiled rice = 600 gr. = 456 g carbohydrates = 2070 Kcal
OR
- Buckwheat = 600 gr. = 426 gr. carbohydrates = 2058 Kcal
Total: or 456 gr. CARBOHYDRATES (if rice) or 426 gr. carbohydrates (if buckwheat) = 2058/2070 Kcal. This is exactly about 50-60% CARBOHYDRATES.
PROTEIN
- Chicken breast = 500 g (ready weight) = 100 g protein = 600 Kcal
- Cottage cheese = 150 gr. = 27 g protein = 144 Kcal
Total: 127 g of protein = 744 Kcal (just about 20% protein).
TOTAL AMOUNT: 127 g of protein (744 kcal) + 456/426 g of carbohydrates (2058/2070 kcal) = 2802 kcal (and we needed 2690, we went a little too far, it’s okay if you’re bulky). And that's not even counting fruits and vegetables. Fats themselves come out 10%. This is how kcal calculations are done. Nothing difficult.
Read more in the article: “How to correctly count calories DRYING/MASS/KEEPING IN SHAPE.”
If you don't mind/feel sorry, please share the link to this article on social networks (social buttons are below). This is the best you can do, I will really, really appreciate it.
Best regards, administrator.
Thursday, July 18, 2019
The importance of water and proper nutrition for an athlete
The key to rapid muscle recovery after physical activity is proper nutrition. An unbalanced diet reduces the results of your workout to zero. The effectiveness of strength exercises depends on the literacy of the athlete’s menu.
Benefits of proper nutrition:
- rapid muscle growth;
- increased productivity;
- possibility of increasing the load during training;
- more endurance and energy;
- there is no glycogen deficiency in muscle tissue;
- improved concentration;
- constantly keeping the body in good shape;
- elimination of excess fat deposits;
- insurance against burning protein reserves required for muscle development;
- no need to take long breaks between workouts.
A properly designed nutrition program (see in detail p. Menu for gaining muscle mass) helps to squeeze out maximum energy and strength to perform even the most difficult strength exercises.
Do not underestimate the importance of water during training, since it makes up 75% of the muscles. During sports, an athlete loses a lot of fluid (up to 300 ml in 50 minutes), which leads to dehydration. In order to prevent a violation of the water-salt balance and, as a result, an ineffective workout, it is important to drink a glass of water before starting it, then take a few sips every 10 minutes.
The amount you drink directly depends on the season and the amount of sweat produced. The hotter it is outside and the more sweating, the higher the level of consumption of purified still water should be.
Signs of dehydration:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- apathy;
- irritability;
- dry mouth;
- chapped lips;
- lack of appetite;
- feeling of thirst.
If at least one of the above symptoms occurs, you should immediately start drinking fluids.
During training, it is allowed to drink freshly squeezed orange juice, diluted with water in a ratio of 50%-50%, or special protein shakes - BCAAs, gainers, which minimize the breakdown of muscle protein, promote energy generation, and speed up the start of the recovery process.
Drug options: MusclePharm Amino 1, BSN Amino X. Immediately after completing the workout, you are allowed to drink milk, green tea, or a protein shake.
Let's consider, using the example of an athletic man weighing 75 kg, the optimal ratio of BJU/calories per day required to increase muscle mass.
General points for gaining muscle mass
There are 2 difficult moments in gaining muscle mass. The first is related to the constitution (physique): ectomorphs have difficulty gaining weight, especially at a young age. The second point is that it is advisable to gain muscle mass, not fat. Therefore, ectomorphs (thin people) don’t have to be very picky about food - the main thing is to get an excess of calories, which will go towards weight gain. But for endomorphs (prone to being overweight), it is advisable to structure their diet more carefully, focusing on protein and reducing the amount of carbohydrates and fats.
1. Balanced nutrition
So, the first principle of gaining muscle mass is proper nutrition. Taking into account your body type, lifestyle, type of activity and training regimen. For an ectomorph, a fairly high percentage of fats in the daily diet is allowed (15-20%) and a lot of carbohydrates (55-60%), but the emphasis still needs to be placed on protein - it requires at least 25%. Moreover, it is desirable that the main part of the protein is of animal origin - due to the fact that plant protein has an amino acid composition less suitable for an athlete.
The ectomorph's metabolism is very fast, so the number of meals should be increased - up to 6-7 times a day. This is difficult because ectomorphs often suffer from a lack of appetite and a tendency to skip meals. You need to fight this habit if you are serious about gaining weight. If you are not able to eat and properly digest the required amount of regular food, use sports nutrition - protein shakes and gainers. You can also take digestive enzymes, which will help you successfully digest more food. To get body weight off the ground, an ectomorph sometimes needs to increase the calorie intake by 100%.
An abundance of protein foods requires a large amount of water - try to drink 2-2.5 and even 3 liters per day, especially during training.
Mandatory rest for recovery
The next principle is necessary rest. Muscles grow during rest, more precisely during the period of supercompensation, when the body has completely restored damaged muscle fibers and prepared for a new load. Most often, supercompensation occurs 3-5 days after training, so give your muscles a rest. Not only the one who trains 2-3 times a month will not grow, but also the one who runs to the gym every other day, tirelessly “killing” the same muscle groups. In order to train more effectively, especially if you have already passed the initial stage, use the split method - performing exercises on different muscle groups on different training days. For example, Monday - chest, arms (biceps), Wednesday - shoulders, back, Friday - legs, arms (triceps). In this case, even with 3 workouts per week, each muscle group will have almost a week to rest.
The right training program
Another key point is a well-designed training program. It should take into account not only the characteristics of your body, but also your level of preparedness, goals, etc. Here we can advise you to use the services of a professional trainer, from whom you can take several individual lessons and ask for help in drawing up a training program, as well as in establishing the correct technique.
In addition, you can take into account a number of other principles to make your training more effective and overcome the training plateau if you have already reached it. The most important point is that the body adapts to its usual regime. Therefore, one of the main training principles is that training should periodically “shock” the muscles, preventing them from getting used to the load and thus forcing them to grow. This principle is sometimes called confusion (“confusion”).
The principle of isolation aims to better load a specific muscle by isolating it from others that can take on part of the load. Isolation exercises become relevant for athletes who have already passed the initial level, for whom multi-joint basic exercises no longer provide the necessary growth.
The principle of the pyramid is that the load increases from approach to approach (for example, the weight starts from 50% of the worker in the first approach to 100% in the third or fourth), and then, in further approaches, it decreases again. A method based on this principle does not always work due to excessive muscle fatigue.
The principle of priority allows you to use more energy to work less developed muscles. It is recommended to do exercises for lagging muscles at the beginning of the workout, so that the fatigue that accumulates towards the end of the workout does not prevent them from being fully worked out.
The principle of combined sets is to increase the number of exercises per muscle group. The use of this principle is available to sufficiently trained athletes.
The principle of peak contraction requires the greatest tension in the muscle at the moment of greatest contraction. Sometimes (for example, when bench pressing, when lifting a barbell or dumbbells for biceps, etc.) the working muscle experiences minimal tension at the end of the working movement. Therefore, such exercises must be supplemented with others in which muscle tension remains constant - for example, in exercises on block simulators.
There are a number of other principles that can be applied to make your training more effective and varied. But no matter how far you go along the path of your development, do not forget about the basic exercises, about the fact that it is necessary to develop supporting and stabilizing muscles, which develop in the process of working with free weights, as well as with your own weight (push-ups, pull-ups, bar, etc.).
Daily calorie intake
For muscle growth, it is important to meet the body's need for the required amount of energy. To do this, you need to calculate your daily calorie intake using the Lyle MacDonald formula or use a specially designed nutrition calculator available on the Internet. In this case, the obtained value should be multiplied by the energy reserve coefficient - 1.2, necessary for muscle development.
Daily calorie intake = Weight, kg * K, kcal/per 1 kg of weight
The K coefficient depends on gender and the intensity of metabolic processes.
| Floor | Metabolism level | Indicator K, kcal |
| Female | slow | 31 |
| Female | fast | 33 |
| Male | slow | 33 |
| Male | fast | 35 |
In our case, the calculation will look like this:
Daily calorie intake = 75kg * 35kcal = 2625kcal
Taking into account the energy reserve correction factor = 2625 kcal * 1.2 = 3150 kcal
Thus, when performing strength exercises, the diet for muscle development in a man weighing 75 kg should be 3150 kcal. Daily caloric intake in this volume, on average, will provide an increase in muscle mass by 2 kg. per month.
Lack of weight indicates a lack of energy and the need to include an additional 400-500 kcal in the daily diet. If your weight gain exceeds 3 kg in 30 days, you should reduce the amount of calories you eat by 300-400 kcal.
As you can see, an athlete’s nutrition schedule depends on the individual characteristics of the body and is subject to constant analysis and adjustment.
Nutrition chart for gaining muscle mass
| Slender body weight, kg | Number of calories consumed, kcal |
| 55 | 2455 |
| 58 | 2634 |
| 63,5 | 2813 |
| 68 | 3037 |
| 70 | 3136 |
| 72,5 | 3260 |
| 77 | 3440 |
| 82 | 3663 |
| 86 | 3885 |
| 91 | 4064 |
| 95 | 4244 |
| 100 | 4467 |
| 104 | 4646 |
| 109 | 4868 |
| 113,5 | 5091 |
| 118 | 5270 |
| 122,5 | 5494 |
Body weight is taken into account without fat mass. For example, the “clean kilograms” of an athlete with 95 kg and 12% body fat are 95-95 * 0.12 = 83.6 kg.
After determining the calorie content of the daily diet, we will consider the correct ratio of nutritional supplements, which make up a sports nutrition complex for muscle development.
The daily intake of carbohydrates is 5g/kg – 4kcal/g, protein – 2g/kg – 4kcal/g, fat – remaining, 1g/kg – 9kcal/g.
For a man weighing 75 kg:
- proteins – 150g. – 600kcal;
- carbohydrates – 375g. – 1500kcal;
- fats – 115g. – 1050kcal.
How many calories should you consume daily to gain muscle mass?
- Optimal calorie surplus for MEN: 250 calories per day.
- Optimal calorie surplus for WOMEN: 125 calories per day.
Let's take a closer look...
- Men: 250 extra calories per day For example, if you are a man with a maintenance calorie level of 2000, you should consume 2250 calories daily to gain muscle mass. Regardless of your maintenance level, you need to add 250 calories daily.
- Women: 125 extra calories per day For example, if you are a girl with a maintenance calorie level of 2000, then you need to consume 2125 calories daily to grow muscle mass. At any maintenance calorie level, you need to add 125 calories.
Determine your maintenance calorie level and calculate how much of a calorie surplus you need to create. Have you already done this? Great. This is exactly the amount of calories you need to consume daily!
Make sure you write down this number.
The additional calories you consume above this amount will only add additional weight, less calories will not give you positive results.
Therefore, this number represents a caloric surplus that will help you achieve muscle growth most quickly and effectively and minimize the possibility of gaining excess weight.
Of course, the main reason for creating a calorie surplus is uniform weight gain .
You ask, is there a norm for increasing muscle mass?
Here she is…
Daily protein intake
The most important building material for muscle growth is protein. When doing strength exercises, it is important to ensure that a sufficient amount of protein enters the body every day, based on the calculation of 1.5-2 g/kg of weight. Slow muscle growth indicates a lack of protein, in which case the norm should be increased to 2.5 g/kg.
The athlete's diet should consist of egg whites, cottage cheese with a fat content of 0-9%, fish, lean meats - beef, chicken breast, seafood. You can replenish the required amount of protein in the body of a bodybuilder who does not consume animal products by introducing plant ingredients into the daily menu. Namely, soy milk, legumes (beans, lentils, peas), seeds, nut butters, nuts (almonds, peanuts, hazelnuts, cashews, walnuts, pine, Brazilian, coconut, macadamia, pistachios). However, it is important to consider that a vegetarian diet slows down the process of muscle building due to the lack of animal protein in the diet.
To get the maximum effect, you should drink a protein shake immediately after training, since this is when the body absorbs nutrients best.
As a result of intense exercise, micro-tears of muscle tissue often occur; their healing occurs with the participation of amino acids and protein foods.
The optimal solution for rapid muscle gain is a combination of animal and plant proteins.
Despite the fact that the main building material of muscles is protein, its consumption in excess of the calculated norm leads to an increase in fat deposition in the liver, increased excitability of the endocrine glands, the central nervous system, increased decay processes in the intestines, and an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system. Protein in excess amounts will not be absorbed by the body and will not have an effect on muscle growth.
It is recommended to divide the daily protein intake into 4 meals during the day, which will ensure uniform “feeding” of the muscles throughout the day.
Table of products for the athlete
| Name | Protein content, g |
| Meat and poultry | |
| Beef liver | 17,4 |
| Chicken liver | 20,4 |
| Chicken (breast, drumstick) | 23,09-26,8 |
| Egg | 12.7 (6-7g per 1 piece) |
| Pork | 11,4-16,4 |
| Veal | 19,7 |
| Fish and seafood | |
| Herring | 18 |
| Squid | 18 |
| Cod | 17,5 |
| Tuna | 22,7 |
| Salmon | 20,8 |
| Trout | 22 |
| Crab | 16 |
| Shrimp | 18 |
| Pollock | 15,9 |
| Halibut | 18,9 |
| Milk, dairy products | |
| Cheese 17% | 29 |
| Cheese 45% | 25 |
| Milk 0.5% | 2 |
| Milk 3.2% | 2,8 |
| Cottage cheese 0% (dry in a pack) | 18 |
| Legumes | |
| Beans | 22,3 |
| Lentils | 24,8 |
| Peas | 23 |
| Chickpeas | 20,1 |
| Nuts and seeds | |
| Peanut | 26,3 |
| sunflower seed | 20,7 |
| Walnut | 13,8 |
| Hazelnut | 16,1 |
| Almond | 18,6 |
Protein nutrition not only increases muscle volume, reduces fat deposits, but also makes the body of women and men more prominent.
Daily fat intake
Currently, most athletes are wary of triglycerides. However, there is no need to be afraid of fats; if they are consumed correctly (compliance with the daily norm), they do not transform into adipose tissue. On the contrary, they will have a beneficial effect on muscle growth.
Namely, fats take an active part in the production of hormones, which, in turn, are involved in building muscles. For testosterone production, it is important that the daily intake of triglycerides in the body is at least 15% of the total diet.
The following types of fats are distinguished:
- healthy (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated);
- harmful (saturated).
Monounsaturated triglycerides include: avocados, olives, chicken, olive and peanut meat. These products are a storehouse of healthy Omega 9 fatty acids, which speed up metabolism, stabilize blood sugar levels, and protect the heart from the harmful effects of blood pressure fluctuations.
Sources of polyunsaturated triglycerides (Omega-3.6) are: fish oil, cottonseed, soybean, corn, sunflower, flaxseed, rapeseed oil, as well as seeds and nuts. Fatty acids in this category improve the anabolic response of protein and insulin, increase performance, and increase performance, which is especially important during heavy strength exercises.
Sports nutrition while gaining muscle mass excludes the consumption of saturated triglycerides found in butter, palm, coconut, cocoa butter, lard, red meat, and confectionery products.
This is due to the fact that the molecule of harmful fat is completely saturated with hydrogen and contains “bad” cholesterol, which means it can provoke the development of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Therefore, the main sources of healthy triglycerides in an athlete’s menu are fatty fish, vegetable oils, and nuts. It is allowed to include in the diet milk 3.2%, cottage cheese, cheese 9%.
Daily carbohydrate intake
The main source of energy is carbohydrates.
Nutrition for gaining muscle mass involves taking 5g daily. organic compounds containing hydroxyl and carbonyl groups per 1 kg of own body weight. The role of carbohydrates is to increase insulin/hormone levels in the body and help repair tissue after exercise. In addition, they serve to transport nutrients directly to muscle cells.
A lack of carbohydrates in an athlete’s diet causes apathy, weakness, decreased performance, and reluctance to continue training. Muscle development is impossible without consuming carbohydrates.
Depending on the rate of splitting, they are:
- fast (simple), it is preferable to consume them an hour before, immediately after sports, as they are perfect for quickly restoring spent energy reserves;
- slow (complex), they should be eaten 2 hours before physical activity.
Products containing 50g. fast carbohydrates per 100g ingredient: jam, cookies, sugar, candy, halva, condensed milk, raisins, figs, honey, chocolate, dates, pineapple, cakes, crackers, pasta, white bread, waffles, gingerbread, semolina, rolls.
Ingredients containing complex organic compounds more than 50g. per 100g: beans, chickpeas, lentils, peas, buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, bread, pasta.
Slow carbohydrates should be included in the daily menu for gaining muscle mass for girls and boys, since they are the main source of energy not only for the muscles, but also for the brain.
Products containing simple organic compounds in moderate quantities - 20g per 100g: all sweet berries, fruits (most in persimmons, bananas, grapes, less in citrus fruits, apples), boiled potatoes, carbonated drinks (lemonade, Coca-Cola, Sprite, Fanta, Burn, Schweppes, Pepsi, Fruktime). The latter, in turn, should be avoided, since such drinks do not contain useful substances and do not satisfy hunger.
Products with a minimum carbohydrate content – 10g. per 100g: dairy products, fresh vegetables (eggplant, tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, carrots). In addition to enriching the body with healthy carbohydrates, they contain everything necessary (vitamins, minerals, fiber) to improve the digestion of food in large quantities.
Thus, in the process of selecting the optimal ratio of BJU, you should, first of all, focus on your own well-being. If during the period of strength training you experience a surge of energy by consuming more carbohydrates than the daily norm “allows”, the amount of fat can be reduced to 0.8 g/kg.
The key to a successful workout is the athlete’s well-being.
If apathy occurs during physical activity, fats should be increased to 2g/kg, and carbohydrates should be reduced in direct proportion. Adjusting your diet to suit your body’s individual characteristics will increase the effectiveness of your stay in the gym.
A rapid gain of muscle mass is possible only if the following conditions are met:
- natural balanced nutrition;
- healthy eight-hour sleep;
- a properly selected set of strength exercises.
Violation of at least one of them leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of training and a slowdown in muscle development.
Menu for gaining muscle mass
Building muscle is a long process that requires self-discipline in nutrition. Eating five meals a day every three hours is a reliable way to achieve the desired result.
The best nutrition for an athlete is fractional, it ensures the systematic intake of food into the body in small doses, which helps accelerate synthesis, improve protein absorption, metabolism, having a positive effect on muscle growth.
It is strictly forbidden to skip meals, go hungry or overeat. In the first case, separate nutrition will not bring the desired effect - the muscles will not increase in volume, in the second - it will lead to excess weight gain and the deposition of fat under the skin.
Sample daily menu for an athlete to increase muscle mass
Let's look at options for each meal. Choose any of them, focusing on taste preferences and individual characteristics of the body (ectomorph).
BREAKFAST
- Banana – 1 pc., black bread – 2 slices, omelette from two egg whites of one whole.
- Pear – 1 pc., cocoa, oatmeal – 150g, dark chocolate – 30g.
- Apple – 1 pc., milk, buckwheat porridge – 150g.
- Yogurt – 100g, rolled oats – 50g, cottage cheese 9% – 100g.
SNACK #1 (pre-workout)
- Kefir 0% or 1%, cheese – 50g, bread – 2 slices.
- Black tea, low-fat cottage cheese – 200g, raspberry jam or honey – 4 tsp.
- Unsweetened oatmeal – 150g, jam – 3 tsp, grapefruit – 1 pc.
- Apple – 1 pc., nuts (assorted) – 40g, prunes, raisins, dried apricots, prunes – 80g.
- Banana – 1 pc., protein – 1.5 scoops, rye bread – 3 slices, peanuts – 30g.
DINNER
- Avocado – 150g. (half), boiled turkey fillet – 100g, unpolished rice – 100g.
- Beef broth soup – 200ml, dried fruit compote, buckwheat – 100g, chicken – 150g, vegetable salad – 100g.
- Rice – 100g, milk 1%, turkey 150g or 2 whole eggs.
- Carrot or orange juice, banana – 1 piece, mashed potatoes – 100g, poultry meat – 150g.
- Green tea, honey – 2 tsp, vegetable puree soup – 200 ml, fish – 200 g, rice – 100 g, grapes – 200 g.
SNACK #2 (immediately after training)
- Gainer + nuts – 40g, dark chocolate – 50g.
- Black tea, raspberry jam or honey - 5 tsp, low-fat cottage cheese - 200g.
- Banana – 2 pcs., dark chocolate – 50g.
- Milk, oatmeal – 150g.
- Pineapple smoothie with chocolate pieces, bread - 2 slices.
- Apple – 1 pc., egg yolks – 2 pcs., whites – 4 pcs., almonds – 50g.
- Dried fruits – 100g, nuts – 40g.
DINNER
- Broccoli – 100g, boiled beef/chicken breast – 200g, rice – 100g.
- Berry fruit drink, egg whites – 5 pcs, vegetable salad – 150g.
- Fish – 200g, green tea, orange – 1 pc.
- Nuts – 50g, raspberry jam – 4 tsp, low-fat cottage cheese – 150g.
- Buckwheat – 100g, turkey – 200g, vegetable oil – 3 tbsp, cabbage and carrot salad – 100g.
- Mashed potatoes – 100g, veal – 150g, stewed vegetables – 100g, banana – 1 pc.
The presented variations serve as the basis for creating a menu for the week.
You can make changes to the nutrition plan: replace products with analogues according to BZHU. To supply the athlete with strength, in 1 hour. before the start of training, the menu (snack No. 1) consists of fast and slow carbohydrates. They act as the main sources of energy. At the same time, proteins and saccharides will help replenish wasted energy and ensure muscle growth after exercise (snack No. 2).
If the nutrition when gaining muscle mass is balanced and calculated correctly, the first results can be observed after 3 weeks.
If at the end of this period there is no weight gain, carbohydrate intake should be increased by 50g. after training, at breakfast.
An example of a diet (schedule) for a vegetarian athlete to increase muscle mass
BREAKFAST
- Green tea, tofu cheese – 100g. bread - 2 slices.
- Freshly squeezed juice from cucumber, green apple, cabbage, spinach, ginger, celery – 450 ml, protein shake from almond milk (1 glass), banana (1 pc.), soy protein (2 tbsp.) – 200 ml.
SNACK #1
- Carrot casserole or cheesecakes – 150g, mixed nuts – 40g/peanut butter – 1 tbsp.
- Pumpkin-almond oil - 2 tsp, oatmeal - 150g, tofu - 100g.
- Protein bar – 1 pc., apple-grapefruit cocktail.
DINNER
- Vegetable soup – 250ml, stewed zucchini, carrots, broccoli – 100g, soy meat – 150g, tempeh – 100g.
- Burger with avocado and cheese – 1 pc., cabbage salad with tomatoes – 150g, banana – 1 pc., broccoli and spinach cream soup – 200 ml., almond butter – 2 tsp.
- Kion rice – 100g, lentil and couscous salad – 100g, seitan – 50g, quinoa seeds – 1 tsp, olive oil – 1 tsp.
- Pea soup - 200ml, cheese - 100g, buckwheat porridge - 100g, tomato and spinach salad - 100g.
SNACK #2
- Kefir, pumpkin or sunflower seeds – 80g, fruit jam – 5 tsp, bread – 1 slice.
- Dried fruits – 100g, peanut butter – 1 tbsp.
- Protein shake made from banana, almond milk and hemp protein with dark chocolate pieces.
DINNER
- Flaxseed porridge – 100g, steamed pumpkin-carrot cutlets – 3 pcs, berry smoothie or jelly, cabbage salad, tomatoes, walnuts – 150g.
- Rice or mashed potatoes with cheese – 100g, boiled broccoli – 150g, avocado – 100g (half), tofu – 50g.
Vegetarian nutrition during the period of gaining muscle mass should be as balanced as possible. Animal proteins (fish, shellfish, eggs, meat) should be replaced with: tempeh, nuts, kefir 0%, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt 2.5%, Mozzarella, Riccotta cheeses, soy products, tofu, legumes. However, you should not overload your body with protein products. To increase muscle mass, the daily protein intake is 2g/kg, for maintenance – 1.5g.
For vegetarians, the ideal training regimen is intense but short (up to 30 minutes). This is due to the fact that prolonged exercise “uses up” a large supply of protein, which is problematic to accumulate on foods of plant origin.
Focus on the little things: how much protein do you need to gain muscle mass?
In organizing the nutrition process aimed at gaining muscle mass, there are certain nuances that promise additional benefits. However, often these nuances are given paramount importance to the detriment of the basics.
What comes first? Quantity, namely an adequate amount of protein for gaining muscle mass, as well as fat and carbohydrates, providing the body with the necessary plastic material and energy.
What's secondary? Meal frequency. Just because you eat 3 or 5 times, muscle growth will not change significantly. You can consume protein 3 times for 50 grams, or 5 times for 30 grams. Within a reasonable frequency of nutrition, these 150 grams of protein will provide the same benefit. Since “on the mass” you have to eat a lot, the number of meals will be limited by the capabilities of the digestive system. It is unlikely that she will cope with the daily calorie intake of 3000-4000 accepted at one time. This is not reasonable. And, if 150 grams of protein at one time is not so much for our gastrointestinal tract, then when you add 80 grams of fat and 400 carbohydrates to this amount, then there will be a war in the stomach.
- Type of protein. We have been taught that in the morning and after training we need fast proteins, and slow ones at night and during the day. Whey in the morning, casein before bed. Is there any logic to this? Undoubtedly. What would actually happen if whey and casein were swapped? Nothing will change, or rather muscle growth will not change. What if you eat meat instead of whey protein after a workout? Will muscles stop growing? No. No study has shown that manipulating the time travel of a particular type of protein provides a significant benefit. Although temporary changes are always recorded. For example, whey protein produces a greater increase in muscle protein synthesis, while casein has a greater inhibition of proteolysis (muscle breakdown). Both are important for hypertrophy. It is possible that under IDEAL conditions some scheme that distributes fast and slow proteins throughout the day will bring 10% more muscle mass in a month, but creating IDEAL conditions is not realistic. Nutrition in general, sleep, life stresses, the training process - all this also affects growth and all this can vary over the course of a month, sometimes not for the better. Therefore, no one has yet identified the best scheme, but it is certain that a chronic lack of protein (or energy) will lead to less results than is possible, even under ideal conditions.
PS But someone seriously believes that his muscles are not growing properly, because after training he drinks whey concentrate instead of a faster, but more expensive hydrolyzate.
— Timing your protein intake around your workout. The anabolic effect of protein foods lasts ~ 6 hours and scientific recommendations (for example, coming from ISSN), based on this circumstance, state that training should fall within this time interval. Then the increased protein synthesis in the muscles, induced by the load, will increase due to the synergistic effect of amino acids entering the cells. If the workout ends 6 hours after the previous meal, then in this case it will be useful not to put off post-workout protein intake. Under other circumstances, there is no urgent need to eat right in the gym locker room, although this is not prohibited, especially if it will help you gain your daily requirement.
In general, it is not a mistake to pay great attention to the little things, there is nothing wrong with choosing one or another type of protein for yourself, consuming it at one time or another, using any supplements. But when all this is the only thing that is controlled and taken into account in the diet, then this is not entirely correct. What good is it when you consume your protein if when you gain muscle mass you do not gain even a minimal energy surplus (point 1 again)?