Upper block pull
Actually, what is good about the pull of the upper block is that it is “creative”, i.e. variable exercise. The most common are the following rod options:
- Per head;
- in front of the chest;
The purpose of the lat pulldown is to work the back muscles . In essence, these are the same pull-ups on a bar, only in reverse: in this exercise, it is not you who are pulled up, but the bar (the handle of the exercise machine) “seeks” towards you. The lat pulldown would be a great addition to the deadlift .
If you still think that doing basic exercises is unfeminine or you want to, but are afraid, then the article “Do the basics, beauty, or everything about the squat, deadlift and press for the fair sex” is for you!
Seated wide grip technique
- Sit facing the machine, moving your body slightly forward.
- Place your hips under special support rollers. The angle between the thigh and shin should be approximately 90°.
- Place your feet firmly on the floor.
- Keep your body straight with a slight arch in your lower back.
- Take the bar of the machine with a wide grip (palms facing down).
- The forearms are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the floor, while the elbows are bent at an angle of 90°.
- As you exhale, begin to smoothly lower the bar behind your head to the back of your head.
- Touching the back of your neck with the bar, hold in this position, strongly contracting your shoulder blades.
- As you inhale, smoothly straighten your arms, returning them to their starting position.
Basic principle of execution
Video: how to properly perform overhead pull-downs
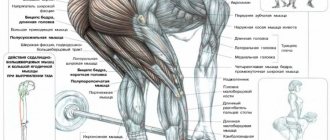
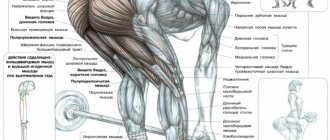
What muscles are involved?
The lat pulldown has as its main goal working the latissimus dorsi muscles , which are also called the wings. Secondary muscles are the biceps, shoulders and forearms. The long head of the triceps acts as a dynamic stabilizer.
A complete list of muscles involved in the movement and engaged by this exercise:
- brachialis/brachioradialis;
- biceps;
- large/small round;
- rear delta;
- cavity;
- diamond-shaped;
- levator scapula;
- trapezoidal (lower/middle parts);
- small pectoralis.
The head pull is a basic exercise, as it involves the work of several muscle groups and joints. Despite this, it is recommended to use it as an additional load after performing heavy exercises, usually, as already mentioned, after deadlifts.
IMPORTANT: When performed regularly and correctly combined with other exercises, lat pulldowns both behind the head and to the chest help strengthen muscles and get rid of chronic pain in the shoulders and lower back. However, if you know that you have back problems, you should not exercise without the permission of a (preferably sports) doctor.
How to take the right selfie or how to become a fit girl in 5 seconds?
What is the difference between behind the head and towards the chest?
Despite common misconception, the neck pulldown does not engage the lats better than the classic chest pulldown, but the former does pose an increased risk for shoulder injury. Muscle activity in these two options is almost the same, which cannot be said about the load on the shoulder joints and rotator cuff.
According to a study published in the Journal of Strength and Functional Training, when the shoulder joints are placed in a position of horizontal abduction in combination with external rotation (as we see with a lat pulldown), stress on the rotator cuff increases.
To stabilize the humeral head, the rotator cuff muscles have to work harder, leaving them vulnerable and increasing the risk of injury, particularly tendinitis and pain. In short, you can injure your shoulder.
Particularly zealous individuals, when zealously performing head pulls in the lower phase of the movement, can hit themselves with a bar on the cervical vertebrae, which can result in bruising and even fracture.
Bottom line: By performing chest rows, you not only get similar or better muscle activity, but you also reduce the risk of shoulder, neck, or nerve damage, so it's best not to take any chances. Although, again, with the correct technique and high-quality, thoughtful execution, you are unlikely to harm yourself.
Harmful exercises in the gym: never do them!
How to avoid getting injured
The vertical overhead row is suitable for athletes with mobile shoulder joints, as the movement occurs in a slightly unnatural plane.
The presence of injuries to the back, neck and shoulder joints is a reason to temporarily refuse to perform this exercise.
To prevent injury, the following requirements :
- Before lifting, warm up the muscles of the back, neck, and shoulder girdle.
- Work with a weight that you can control.
- Do not place the bar too far behind the head or lower it below the base of the skull.
- Do not perform jerky movements or throw the bar.
- Sit correctly on the exercise machine (as described above).
- Separate deadlifts and overhead pull-downs.
Common Mistakes
- The machine handles are lowered too low.
- The bar is not lowered low enough.
- Incorrect position (rounding or excessive arching) of the back.
- Full extension of the arms.
- Working with too much weight.
- Incorrect position on the machine.
You can include the exercise in your training program if you have developed muscles of the back and shoulder girdle, and master the upper wide row behind the head, starting with a small weight.
Lat rows or pull-ups?
Which exercise is better for the back: pull-ups or overhead rows? So, of course, pull-ups are better for back width, this is as obvious as the superiority of working with free weights over machines, but not every beginner can master at least 5 pull-ups. You understand that the amount of work that needs to be done to see the result is clearly greater.
So an excellent way out in this situation is to perform lat pull-downs , and then gradually switch to pull-ups on the horizontal bar. In this way, we develop the strength needed to pull our body up on the treasured horizontal bar. As an intermediate option (especially for girls), you can use pull-ups in a gravitron , and as strength develops, switch to a pull-up .
Pull-ups on the bar with rubber shock absorbers
A general tip when working with a lat pulldown machine is to include free weights in your training program.
Vertical block thrust
The seated lat pulldown (or lat pulldown) is a key exercise for developing back and upper body muscles. In terms of its mechanics, the block row is analogous to pull-ups on the bar, however, with an overhead row to the chest, the athlete can use a working weight that exceeds his own - which is impossible with conventional pull-ups.
At the same time, the correct technique for performing lat pulldowns involves exclusively pulling to the chest, and not behind the head. Despite the fact that the overhead pull-down can be used by professional athletes to target specific muscle groups, for beginners and intermediate athletes, such a variation can cause significantly more harm than good.
// Vertical block row (upper row) - correct technique and common mistakes
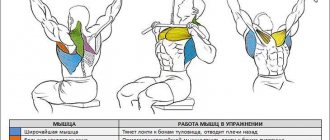
Upper row: what muscles work
The main muscle groups working when performing lat pulldowns are the latissimus dorsi and the shoulder girdle muscles - however, depending on the type of handle (regular bar or narrow parallel bar), as well as the immediate width of the grip, which secondary muscles take over significantly changes additional load.
If, when performing an overhead row to the chest, the palms are directed towards you, then the biceps are actively involved in the work. A wide stance increases the involvement of the latissimus and small rotator cuff muscles, and when using a parallel handle (palms facing each other), the pectoral muscles are also involved in the exercise.