Classic deadlifts are not for everyone. Firstly, this complex multi-joint exercise is not recommended for beginners, since the muscles are not yet ready for the traction technique, and secondly, physiologically the exercise causes pain, most often in the lumbar region, and the reason for this is not even diseases and injuries of the spine, but morphological features . And there is an alternative to such an exercise - this is its variation with dumbbells. Let's look at the benefits and disadvantages of the dumbbell deadlift, and whether it's worth replacing the barbell deadlift.
The benefits of dumbbell deadlifts
The classic version of the deadlift, as you know, is performed with a barbell, with the load being distributed to a greater extent on the back muscles, then on the quadriceps, and to a lesser extent on the buttocks and hamstrings. If for men this is most often a mandatory exercise, then for many girls it is not of particular significance or benefit.
It is the deadlift version with dumbbells that is more justified for the female body, since it does not overload the back and quadriceps, and to a greater extent develops the gluteal muscles and hamstrings.
In addition to aesthetic benefits, there are also anatomical ones. That is, for those who are contraindicated in deadlifting with a barbell due to the physiological characteristics of the body, pain and spinal injuries, the option with dumbbells will be more comfortable and safer.
Another morphological aspect is that not everyone is comfortable holding the barbell with an overhand grip, in which the hands are in a pronated position. When holding dumbbells, this moment is smoothed out, since the position of the shoulder joints can be controlled by holding the dumbbells with a parallel, neutral grip.
Execution options
- Front row with dumbbells . Not the most convenient option for long legs and large hips, but nevertheless it is performed as a backup. The athlete must activate the muscles of the back and buttocks, and perform the movement as a classic, with a barbell, bringing the dumbbells in front of the body. This movement is considered more accentuated on the back of the thighs.
- Lateral kettlebell row . This movement is also called a “suitcase” pull, although a suitcase is a different type of projectile and has a higher stall. In the corners, this movement is more reminiscent of a trap bar row, but with a full breakdown, and not as truncated as a dumbbell row;
- Single leg row . Sometimes this movement is called the King's deadlift with dumbbells, but this does not change the essence. The movement is that the weight is transferred to one leg, and the second is placed on the toe, or comes off. The athlete performs deadlifts at his maximum amplitude and performs an equal number of repetitions on each leg.
Deadlift. Deadlift with Straight Legs. Exercise for the Buttocks and Biceps Thighs.
Disadvantages and contraindications for deadlifting with dumbbells
The only disadvantages of the exercise include the requirement for flexibility and elasticity of the muscles and ligaments of the back surface of the body. If there is insufficient flexibility, with tight and shortened muscles, when performing deadlifts with dumbbells, the hamstrings are subjected to strong tension, which can cause serious injuries. Therefore, inflexible and previously injured muscles and tendons should not be subjected to such stress.
Contraindications include spinal injuries, hernias, displacements, protrusions, pinched nerves, and back pain. As well as injuries and inflammation in the muscles and ligaments of the back of the body.
Differences between classic and sumo deadlifts
The main difference between these types of deadlifts is the positioning of the legs. The distance between the legs affects the height of the lift - that is, the wider the athlete places his legs, the lower the height to which the barbell needs to be lifted. Accordingly, this also affects the amplitude of movement.
Let's look at biomechanical indicators to better understand the differences and similarities of deadlifts:
- The lifting time in the classic version of the deadlift and the sumo deadlift are approximately the same, and are about 2 seconds, so in this regard they are almost identical.
- The distance required for an athlete to lift the apparatus is reduced by approximately 19% in the sumo deadlift compared to the classic version of the exercise. So you will need less energy to lift the same weight.
- The transverse load on the 4th and 5th vertebrae in the classic deadlift is slightly greater than in the sumo deadlift.
- When performing a classic deadlift, the main load is placed on the back, while in a sumo deadlift, mainly the knees and hips are involved. This is due to the positioning of the legs - the hip and knee angles are wider.
- In the sumo deadlift, the implement is placed closer to the body, which reduces the lever distance and the moment of resistance.
- When performing deadlifts, the athlete encounters a so-called “stumbling point” when the barbell’s movement becomes most difficult. Both in the classical version and in the sumo deadlift, this moment is achieved in the second half of the exercise, but due to the physiological characteristics in the classical version it is easier to overcome it. Perhaps it is for this reason that many refuse to perform the sumo deadlift - the stumbling point becomes their barrier to the correct execution of the exercise.
- Both types of deadlifts must be performed using a weightlifting belt.
- The sumo deadlift showed greater EMG activity in the medial, tibialis lateralis, and tibialis anterior muscles. The load in the classic deadlift goes mainly to the head of the calf muscle. Both options are equally good for gaining muscle mass.
Also, we will briefly list the advantages of the sumo deadlift over the classic version, not related to biomechanics:
- During the sumo deadlift, the body position is more vertical;
- The range of knee extension at the bottom of the movement is greater;
- To perform sumo deadlifts well, great strength is required in the quadriceps and tibialis anterior muscles;
- The projectile is located closer to the body, which makes leverage more effective;
- The distance over which you need to transfer weight during the exercise is reduced.
With this we will finish the analysis of the theoretical part and move on to practice.
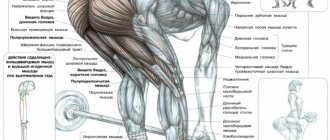
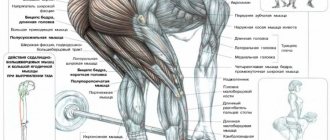
What muscles work
- Large gluteal muscles.
- Spinal erector muscle.
- Semitendinosus muscle.
- Biceps femoris muscle.
- Semimembranosus muscle.
- Abdominal muscles - perform a stabilizing function.
What muscles work when performing a deadlift?
First of all, the exercise is aimed at developing all the back muscles. These include the latissimus muscles, which span the upper back and resemble wings, as well as a group of extensor muscles, including the iliocostalis, longissimus and spinalis, which run along the spine. In addition, the work includes the rhomboid muscle, located in the middle part of the back and responsible for the formation of the natural curve of the spine. Finally, the trapezius muscle, located in the upper back and involved in the movements of the neck and shoulders, works.
The next area that is “pumped up” thanks to the deadlift is the quadriceps or quadriceps muscle. When extending the legs, several component groups of the quadriceps are involved, namely:
- the vastus lateralis muscle, located on the outer part of the thigh and extending the leg at the knee joint;
- vastus medialis (teardrop-shaped) - a small narrow muscle located in the lower anterior region of the thigh and also takes part in knee extension;
- the rectus muscle in the middle part of the thigh, responsible for flexion of the hip joint;
- The vastus intermedius muscle in the upper part of the thigh also performs flexion of the hip joint.
Deadlifts are excellent for developing your back muscles.
When performing a deadlift, the back of the thigh and gluteal muscles are actively involved in the work. These include: the biceps femoris and semitendinosus muscles, which run along the entire back of the thigh and flex the leg at the knee, as well as the semimembranosus and gluteus maximus muscles, which are involved in extension of the hip joint.
Performing deadlifts additionally strengthens the elbow and knee joints, increases hand grip strength, helps expand the chest, and increases overall strength and endurance of the body.
Taking into account the high risk of injury and complexity of the exercise, it is not recommended to do it if the following contraindications are present:
- rachiocampsis;
- diseases of joints and cartilage;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- respiratory system diseases;
- flat feet.
Technique for performing deadlifts with dumbbells
First of all, let's look at performing deadlifts with stronger knee flexion, which emphasizes the load on the gluteal muscles:
- Take dumbbells in your hands and place the weight on the sides of your hips. Throughout the exercise, the arms always remain straight.
- Place your feet hip-width apart, parallel to each other.
- Bend your knees as if you were squatting and move your pelvis back, while leaning your torso forward as if you were trying to lie on your thighs. Your back should be as straight as possible; under no circumstances should you round your spine.
- As you inhale, lower yourself to the lowest point, but do not lower the dumbbells to the floor, your pelvis should not fall too low, and your knees should not be sharp. Keep your hands in a neutral position along your shins.
- As you exhale, straighten your torso using your gluteal muscles, pushing off with your heels.
Option with emphasis on hamstrings
The second embodiment can be classified as a variation of the Romanian deadlift, in which the knees bend to a lesser extent, which significantly increases the load on the biceps femoris muscles. In this case, the predominant movement is a downward bend, with a slight bend of the knees. When tilting the torso, we move the pelvis back, and the center of gravity shifts to the heels. The spine remains as straight as possible, and the slope reaches parallel with the floor. We lower the dumbbells down with a neutral grip along the shin, without touching the floor.
Equipment in video format
Execution technique
And now the promised subtleties of execution, which, despite the similarity of the loads, differ for each variety. Let's look at them one by one.
Classic deadlift with dumbbells
- Take the initial position (IP) - straight back, legs less than shoulder-width apart with feet parallel to each other, look forward parallel to the floor, move your pelvis back.
- Take the projectile from the support, holding them along the body. Beginners can use hand straps and hooks to help support weight. In this case, you can not be distracted by the weight slipping out of your hands, but direct all your attention to the correct position of the body.
- As you inhale, bend forward (back straight), lower the dumbbells to the floor. Hands with weight are located along the body.
- Leaning forward a little, bend your knees into a small squat. Leg muscles are tense.
- Squat to the required level. The lowest point is when the thighs are parallel to the floor. But it’s not a fact that you will touch it with dumbbells. And don’t try to reach out, because this will round the lower back, and this should not be allowed. Choose an amplitude in which you are comfortable.
- Having reached the lowest possible position, immediately, exhaling, return to the original stance. Watch your back position.
The deadlift on straight legs with dumbbells, when the arms are lowered below the knee, maximally loads the back of the thighs, and athletes call this subtype of exercise the deadlift.
Romanian deadlift with dumbbells
- Take the starting position, as in the previous description, and take the dumbbells from the supports.
- Place the apparatus in front of you, arms along the body, move your buttocks as far back as your athletic form allows.
- As you inhale, go down, paying attention not to the downward movement (tilt), but to the abduction of the buttocks. Place the dumbbells closer to the body, without bringing them forward, so that the load is concentrated on the back extensors.
- Continue going down until you feel a slight burning sensation when the back of your thighs and buttocks begin to stretch. Those who do not feel any changes should perform additional fatigue (up to 4 approaches), bending while sitting or lying down. This develops neuromuscular connection with the thigh muscles and allows you to deeply feel the process of movement.
- As you exhale, return to the starting position while keeping your hamstrings tense. Do not straighten all the way to prevent the muscles from relaxing. Once you reach a point where your body is slightly tilted, repeat the approach. This improves efficiency.
An advanced variation of the Romanian deadlift is to perform all the steps described above while standing alternately on your right or left leg. The need to maintain balance requires the athlete to concentrate maximally on the processes in the tissues, enhancing the effectiveness of the practice.
Dumbbell sumo deadlift
Take the initial stance - legs slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, feet turned toes outward at an angle of 45°, back straight, gaze forward, collarbones pointing upward, pelvic area pulled back. Take the shell.
As you inhale, begin to move down, starting to tilt your back, then moving on to working your legs.
Watch the position of your knees and feet - they should be on the same line, not falling either in or out, to avoid injury.
The sensations are concentrated on the inner thighs. The downward movement continues until the dumbbells touch the floor or as far as your individual stretch and goal will allow. If you need to build muscle mass, you don’t need to lower the dumbbells completely. The opposite action leads to an increase in strength characteristics.
Having reached the bottom point, as you exhale, begin to return to IP, relying on the strength of your leg muscles. Straighten up completely. To develop strength, when you lower the dumbbells to the floor, you need to rise with acceleration, training the muscles at a speed-strength pace, which helps to quickly increase working weights.
Deadlift with dumbbells: recommendations for girls and men
In accordance with the techniques described above, you can place emphasis on certain muscle groups, which means:
- to emphasize the buttocks, follow the first option;
- on the hamstrings – the second.
For beginners in the gym, as well as for girls , it is recommended to perform the exercise with light weight, 15-20 repetitions, 3 sets. The light weight of the load will allow you to develop the correct technique without putting stress on the spine.
For men who are physically fit , it is worth choosing dumbbells of such a weight that it is not possible to perform more than 12 repetitions, so perform 3-4 sets.
Dumbbell deadlifts should be included on leg day; the exercise can be performed after barbell squats or leg presses. It can also be performed with supersets paired with hyperextension or leg curls in the simulator.
Benefit
If you regularly exercise with dumbbells, then your strength with a barbell will also increase.
By exercising with dumbbells, an athlete, as already mentioned, strengthens the core, which effectively prepares him for more difficult training in the future. The performance of exercises such as barbell squats, for example, improves.
Deadlifts with dumbbells allow you to work with not very heavy weights, while doing 12-15 repetitions, which makes it possible to better work out the technique, concentrating on the work of the muscles. This greatly strengthens both the legs and the back, giving the athlete's body an athletic shape. This option is ideal for girls, since the exercise is simplified as much as possible due to the low weight and the risk of injury is practically reduced to zero.
The range of movements is greater than when working with a barbell due to the small diameter of the dumbbell discs, and as a result, much more muscle fibers work - this is one of the advantages.
Contraindications and warnings
Any exercise (especially basic) has a number of contraindications, which forces many athletes to simply abandon them, both temporarily and permanently, if suddenly necessary. These are the following diseases:
- Lordosis.
- Scoliosis.
- Protrusions.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Kyphosis, etc.
You should avoid lifting too much weight—even dumbbells can be prohibitively heavy—because this will inevitably compromise your technique. Rounding the lower back in the lower phase of the exercise leads to an increase in the axial load on the spinal column.