To achieve a beautiful, stately and pumped up figure, most people regularly exercise. They visit training rooms, which are equipped with all kinds of equipment and equipment. Each fitness room has in its arsenal an “upper block” exercise machine. The exercises performed on it help to perfectly pump and comprehensively develop the back muscles. To do this, it is necessary to perform various types of thrusts from the bottom up. The lat pulldown is a basic exercise that is done behind the head, to the chest, to the lower back, and so on.
Description and features of the exercise
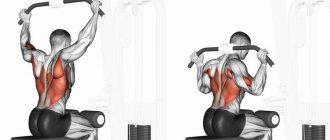
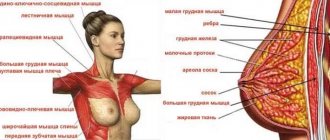
To pump up the back muscles, the athlete is required to concentrate and comply with the rules and regulations regarding the technique. In a block machine, vertical rows resemble regular pull-ups. The main anatomy is that at the time of execution, the biceps and the main muscle group - the broad back muscles - are involved. Therefore, it is important to perform deadlifts accurately and correctly, since this exercise is the best way to strengthen and maintain the muscular parts of the back.
Physical fitness, especially muscle development, must remain at the proper level, since exercise is characterized by the addition of weights. In this case, the mass of additional equipment can significantly exceed the person’s own body weight.
What muscles are involved?
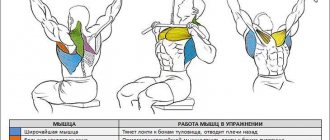
In addition to the “wings” of the back, lat pulldowns additionally load the muscles:
- torso – abdominal and erector discs of the vertebrae;
- forearms and shoulder rotators;
- diamond-shaped, jagged anterior, lower and middle trapezoidal;
- wrist flexors, biceps.
The simulator includes different types of bars. The muscle groups of the shoulder girdle, which take on the secondary load, change significantly depending on the width of the grip and its type. To pump up the back muscles, especially the broad muscles, the biceps should take on a minimal part of the load during the exercise.
The chest row activates the abdominal muscles of the trunk - stabilizers, if you perform small, as light as possible bends back without introducing a large load mass.
One-arm vertical row using the trapezius and head of the biceps muscles strengthens the anterior and middle part of the deltoid muscles, the clavicular part of the pectoral muscle.
Benefits of doing it
Vertical rows do not require much time from the athlete and provide a number of benefits:
- beautiful back muscles;
- narrow waist and straight posture;
- the torso becomes V-shaped when viewed in profile;
- availability of execution in any gym or fitness room.
The lat pull-down is one of the simplest and most popular exercises in training, as the back muscles grow very quickly. That is why novice athletes perform this exercise as often as possible and with a large number of approaches. Pulls to the chest in parallel, with one grip, behind the head and others allow you to work your back in different planes and angles.
How is it different from pull-ups?
The block simulator, on which vertical rows are performed, is a direct analogue of the horizontal bar for simple pull-ups. Meanwhile, during the usual, well-known pull-ups, the main load involves the biceps, and the back works only 25-50%. The pull of a vertical block to the chest works exactly the opposite: the main load goes to the top, allowing you to pump the latissimus muscles of the dorsal region.
This exercise is also different in that the overhead row is performed while sitting. In this case, the projectile is pulled towards the body, and not the body towards the crossbar (projectile). Thanks to the block design with a seat, the exercises can be performed by people for whom pull-ups on bars are strictly contraindicated and those who do not know how to do pull-ups.
The ability to use different bars and additional weight (from 2 kg) is another significant difference from conventional pull-ups.
Why exercise for girls?
Depending on the goal and load, women can work on mass or exercise to “dry”, strengthen and pump the upper back and shoulder girdle. Using different variations (vertical row with a medium, straight, narrow or wide grip) allows girls to:
- master the correct pull-up technique;
- pump up the muscles of the arms and neck;
- strengthen the cervical vertebra;
- achieve a perfect V-shaped torso and narrow waist.
Who is contraindicated for
The lat pulldown has few contraindications. Block exercise machines can be found even in rehabilitation centers, where doctors strongly recommend performing this exercise. Caution should be exercised if the thoracic vertebra contains a hernia.
Vertical rows performed with one arm are not recommended if the shoulder girdle cannot or is not ready to make sudden amplitude movements. The exercise is strictly prohibited in case of severe elbow injuries, as well as in case of damage to the hands and shoulder muscles, since during the exercise there is a load on the shoulders.
Upper block row to the chest with a narrow reverse grip
This type of traction puts more stress on the lower lats. In addition, the biceps are activated a little more, and the muscles of the forearms are worked out. Taking into account the fact that these muscle groups are much weaker than the “wings”, fatigue will come much faster. Therefore, it is recommended to perform this row with a narrow reverse grip and lighter weights than with a wide grip. In other words, the load on these muscles will not allow you to properly work out the latissimus, so it is recommended to use straps for traction.
Correct technique
- At the beginning of the exercise, you should sit on the machine and grab the handle with a reverse grip.
- Arms should be extended upward at shoulder width or slightly narrower
- The body maintains a natural arch in the lower back
- As you exhale, lower the handle to the level of the middle part of the chest, bringing your shoulder blades together as much as possible
- Try to keep your shoulders and arms moving down and back
- Inhale and return to the starting position
- When lifting to the top point, the body should lean slightly forward
- Arms extend only at the highest point
- For more correct execution, try to stretch as much as possible at the very top
- Train for 3-4 sets, performing 15-12 repetitions
When performing any rows in a block machine, do not forget about the correct adjustment of the leg bolsters. If they are too high, the weight will lift the athlete upward, preventing proper load on the latissimus muscle.
Typical mistakes are considered
- Deflection of the body back at the bottom of the pull.
- When the hands work in front and the chest muscles are included in the work, as well as the abdominal muscles. From the outside it looks like an abdominal crunch exercise.
- Jerks and cheating during execution. A sudden jerk can lead to injury, and cheating loads additional muscles, signaling that the weight on the machine is heavy.
It is believed that in this type of deadlift, the load on the back and biceps is in the proportion of 50 to 50. If you do not adhere to the correct technique, then the biceps can be involved in the work in a larger percentage, stealing the load from the lats. However, this can be corrected by focusing on bringing the shoulder blades together, which will increase the benefits of this exercise.
Execution technique
To pump up your back muscles, you need to do lat pull-downs correctly. Each grip has its own characteristics.
However, one type or another begins with the preparation of the simulator.
To do this you need:
- select and install weights up to 15 kg (a large weight will lift the torso up, which should not happen);
- adjust the seat (your legs should fit snugly between the bolsters and the seat).
Narrow grip
Overhead rows work the biceps and to some extent the forearms.
The exercise technique includes 7 sequential actions:
- Stand up and with your hands, at a distance of 10 to 15 cm, take the handle.
- Sit down and feel the set weight by pulling the vertical block.
- Using the strength of the back muscles (without tension on the biceps), pull the elbow down until the bar is pulled to the bottom of the chin.
- Raise your head a little up so that it does not interfere with the moving weight and its trajectory.
- Pull the handle down (strictly vertically) to your neck, lowering the weight to your chest.
- Hold the weight for a few seconds.
- Return to original state.
The lat pulldown with a narrow grip is performed while sitting, without lifting the pelvic part of the body and tilting the back back.
Wide grip
Using a wide grip, pull the upper block towards the chest and behind the head. For both variations, as with the narrow grip, you must prepare the equipment.
A wide vertical (upper) row allows you to activate the work of the spinal muscles. At the same time, the biceps and muscle groups of the forearm, when performing a straight wide grip to the chest, are activated to a minimum.
Recommendations
Like most multi-joint exercises, lat pulldowns are effective if the technique is strictly followed. The main movement is performed precisely by contracting the lats, and not by using the biceps or jerking the body. You can put the right muscle group into work only by feeling it in dynamics. Training with light weights allows you to develop motor skills and learn to feel muscles.
A static body position is a fundamentally important technical point of the exercise. Only the hands are involved in the movement. The body is straight, the natural arch in the lower back is preserved. The back muscles contract poorly in the absence of such a deflection, which can lead to injury.
The range of motion is an important parameter that must be maintained for the correct execution of the exercise and stretching. Not bringing the handle to the bottom point cuts off the amplitude and, as a result, reduces the impact of the exercise. Working in an extended amplitude is considered correct in this technique: we bring the bar to the point of peak contraction and straighten the elbows at the top (relevant for all variations except parallel close-grip rows).
Recommendations for effective implementation
The technique of execution necessarily requires a clear sense of which part of the body bears the bulk of the load and is working at its maximum.
To perform “for results” you need to know:
- how to place your elbows correctly;
- how to work with your back;
- how to choose working weights;
- when to increase muscle contractions.
Working with your back
Sometimes the top block is performed incorrectly. That is, the main loaded pull is received by the biceps, and the rest of the weight is supplied by the latissimus muscles. In this case, the biceps get tired, and the pull-down does not strengthen or expand the back.
The upper row of the block is intended strictly for the comprehensive development of the spinal muscle groups! This is what the vertical row, performed with a wide grip, focuses on. Therefore, when the weight is pulled easily, it’s worth stopping for a split second and feeling how exactly the exercise is being done - biceps or “wings”.
How to place elbows
Rows performed while seated require different placement of the arms. The position of the elbows decides which parts of the back muscles work more. Elbows should not move back and forth. They need to be recorded. Shoulders should be at the same level.
During the exercise, the palms of your hands can be directed both towards you and away from you:
- biceps involvement increases significantly if the palm is facing towards you;
- The pectoral muscles actively work when using a parallel handle, when the palms are facing each other (seated chest pull).
Cheating
Most athletes doing shoulder exercises for their back risk straining or injuring ligaments by bringing down a heavy handle with their full weight. After all, rowing with a wide grip in a vertical block additionally engages the deltoid muscles. Their bundles must be warmed up before starting an intensive workout, that is, do a warm-up.
Without pre-warmed muscles, pulling to the chest from the upper block can have a detrimental effect on the health of the elbows and their joints. The “wings” are difficult to pull, but the shoulders are a mere trifle.
Selecting the working weight
The pull of a vertical block behind the head or to the chest is done while sitting, and implies the presence of additional weights. If jerky jerks occur during exercise, then you need to change the weight to a lighter one and check how accurately and comfortably the seat is installed. Then the block pull will be performed smoothly to the chest, without jolts.
Trainers recommend starting with light weight (from 2 kg). This approach will allow you to feel the back muscles and perform the exercise correctly 15-20 times.
We increase the quality of muscle contractions
A vertical row, for example, performed with one arm, uses one forearm and hand of that arm. To achieve better contraction without fatigue of the biceps and brachialis muscles, you need to use special loops (belts for hands). Similarly, you can neutralize the load on your arms and improve the quality of muscle contractions in your back by holding the handle with a reverse grip.
Newbie mistakes
Working the biceps and abs is the most common violation of the upper row technique. Monitoring movements and analyzing the condition of muscles allows you to notice an error. If the shoulder blades do not move, and the arms quickly get tired and hurt, then the adduction of the handle occurs due to the supply of force to the auxiliary muscle groups. In this case, the working lats do not experience the correct load and the effect of the exercise is reduced to zero.
Incorrect seating in the machine is another classic mistake. Taking the starting position on the bench, you must sit strictly under the handle and firmly fix your legs under the bolsters. In this position, the movement of the bar occurs in a vertical plane, and the body does not stretch upward behind the arms.
Body jerks are a technique violation that occurs when weights are abused. If an athlete is unable to pull the handle with the force of his back muscles and tries to help himself with chaotic movements, then the simulator is equipped with an unbearable weight. A similar point applies to trying to pull a weight by lifting yourself up and pressing your body onto the handle. To correct the error: adjust your body position on the bench, getting as close to the machine as possible, and reduce the weight of the blocks.
Pulling the bar toward your stomach is a fairly common mistake. The athlete pulls the handle not to the chest, but much lower, thereby changing the correct vertical trajectory of movement. The consequence is a complex violation of technique: the body leans back, the elbows move to the sides, the back is rounded.
Execution options
The work of certain muscles depends on the width and angle of the direction of the grip. Knowing the features and subtleties of each exercise technique, you can, together with the trainer, create the correct sequence of classes. This approach will not leave any area of the back unattended.
Standard rods include different options in their arsenal, which differ slightly from each other. In this case, the exercises allow you to work out one or another part of the back.
To the chest with an overhand grip
Straight-grip rows of the upper block to the chest while sitting are a classic execution, performed with a medium or wide grip.
Execution sequence:
- Grasp the bar with both hands. Turn the inside of your arms (palms) forward.
- Bend your lower back, tilt your head 15-20 cm back.
- Using the strength of your back muscles (wings), pull the weight up or down your chest.
The pull of the upper block is performed strictly vertically down in front of you, with the body tilted slightly back. Otherwise, it will be impossible to achieve the desired angular position to increase muscle mass.
Per head
The vertical wide overhead row allows you to feel literally all the latissimus muscles. That is why this traction option is suitable for beginners. After all, initially the back is trained, and then it is “pumped up”.
The exercise technique is simple:
- Place and fix the palms of your hands at the bend of the handle.
- Tilt your head down (literally 5 cm maximum).
- Without bending your body, pull the weight up to your neck, with the bar behind your head.
- Fix the weight on the upper block (literally for 1-2 seconds) and return to the starting position.
The pull should not go all the way to the chest. You should also not push your elbows back behind your back. Actions must take place with a perfectly straight torso.
Parallel grip
Parallel overhead pull-down in a block to the chest with a wide grip received a second name - neutral pull-down of a vertical block towards yourself. The only difference from other types of traction is that stronger loads are applied. For parallel traction of the upper block, the simulator must be equipped with special handles to make it easier to hold onto the handle when working with a large, serious mass of weights.
Reverse grip to chest
Pulling a block with a reverse grip to the chest pumps the lower part of the wings and implies an almost similar sequence of actions:
- Place your hands on the bar slightly wider than shoulder width.
- Sit down, leaning back so that your torso is counterweight to the cable on the exercise machine.
- Perform a press by pulling the weight down (elbows should be at a 45-degree angle).
- Pull the vertical bar of the exercise machine towards your chest.
Optimal execution mode
The lat pull-down does not load the muscles and joints, so it can be left for the final part of the workout. To begin, perform a set of targeted exercises to work your back. In the main block, it is recommended to do deadlifts with a barbell: deadlifts, bent-over barbell rows. After active strength training, a moderate load on the upper row will help complete the muscle development.
Don't neglect warming up. The rear parts of the delta are involved in the movement of the shoulder blades. They are easily injured when performing exercises with unwarmed muscles.
Common mistakes
In a block simulator, vertical rows require maximum concentration and the correct sequence of actions.
Often, beginning athletes make the following group of mistakes:
- curvature, stooping of the vertebra;
- incorrect elbow position;
- the movement occurs with the buttocks lifting off the seat;
- when pulling the bar, the forearms are fully extended;
- the load is distributed on the biceps and other parts of the muscles, and not on the main body (back muscles);
- too much weight is taken, so the exercise becomes difficult to perform;
- vertical row, performed behind the head or with one hand, without warming up or preliminary preparation.
The above mistakes can be avoided if you approach your studies correctly. After all, there are no quick results!
Description
In order to pump up and strengthen your back, you will need to perform various physical exercises, the main one of which is considered to be vertical pull-down. She imitates pull-ups. However, it alone will not bring the necessary results even with long-term training. Therefore, to achieve muscle growth, progressive loads are needed.
Benefit
Traction promotes the development of the spinal muscles, which are located closer to its central part. Also, by performing this exercise, the athlete develops his biceps, and the efficiency will be much higher than if he performed a standard grip, which should also be taken into account. This type of deadlift is not suitable for beginners who do not yet need to create muscle relief.
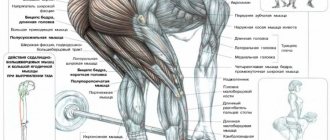
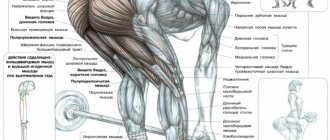
What muscles work
The main task of the deadlift is to work the wings, which are the broadest muscles. The secondary muscles working during the exercise include the biceps, shoulders and forearms.
The following muscles act as synergists:
- biceps;
- cavity;
- diamond-shaped;
- pectoralis minor;
- trapezoidal;
- brachialis.
The dynamic stabilizer during the pull-down is the long head of the triceps.
Recommendations from professionals
- the weight should be pulled with your back, not with your hands;
- it is necessary to ensure that the handle is in a strictly fixed position;
- You cannot “walk” your elbows up and move them to the sides;
- there is no need to tilt the body too much if the work is carried out with light weight;
- when working with heavy weights, use straps to make it easier to hold the bar;
- The bar bar must be pulled as close as possible and strictly to the top of the pectoral muscles;
- looking down and tilting your head is strictly prohibited;
- select the weight so that there are no jerks;
- you can’t slouch;
- at the lowest point, pause for 1-2 seconds, tense your abs and legs, without lifting them from the clamp on the simulator.
Perform any of the exercises in 2, maximum 4 approaches. In this case, it is better to have 10-12 repetitions.
Parallel Grip Row
Upper block rows using a bar for parallel placement of the hands are aimed at increasing strength and relief:
- latissimus dorsi muscles;
- biceps;
- rear deltas;
- forearms.
To increase the load from the exercises, fitness trainers recommend that girls bend slightly in the thoracic spine when the bar is in the lower position, and when moving the handle upward, slightly move the straight body forward.
The algorithm for performing vertical rows with a parallel grip is as similar as possible to the technique of the classic version of the exercise (upper row to the chest or abdomen). The only difference is the placement of the hands on the bar. In this case, the hands should be placed on the handles of a curved bar, with their back sides facing each other.
When moving the upper limbs to the lower position, the elbows should be directed straight down. Moving them to the sides will lead to a shift in the load and a decrease in the effectiveness of the training.
What is better for pumping up girls’ backs: pull-ups or lat pull-downs?
In back training, girls will be able to achieve maximum results by including classic pull-ups in their training program. This type of training not only puts a complex load on the upper body, but also maintains the tone of the muscles of the abdomen, legs and buttocks.
The main disadvantage of pull-ups is the difficulty of its technique for beginner athletes. In their case, it is advisable to start with lat pulldowns, which are considered a lightweight alternative to “professional loads” on the horizontal bar.
The lat pulldown, regardless of whether it is performed with a narrow or wide grip, to the chest or behind the head, is aimed at working the upper body. With its help, provided that the working weight is correctly selected, novice athletes will be able to master the basics of strength training, and those who play sports professionally will be able to maintain their muscles in good shape.
If the exercise is performed correctly, the risk of injury during the training process is minimal, which allows girls to exercise in the block simulator on their own, without the help of a fitness instructor.
Straight head grip
The straight-grip vertical row is considered a classic version of the exercise. It allows you to load the latissimus muscles and the central muscles of the girl’s back.
To grab the bar with an overhand grip, you should turn your palms with the outer side towards you and clench your hands into fists, while grasping the movable handle of the machine. Hands must be placed from each other at a distance equal to shoulder width.
Regularly performing vertical head pulls will help the athlete:
- increase overall strength indicators;
- improve posture;
- form a V-shaped silhouette of the upper body;
- make your back and shoulders sculpted;
- achieve a reduction in waist size.
When training in a block simulator using a straight grip, it is important for a girl to ensure that the efforts she makes to move the bar are carried out by the back muscles, and not by body movements or only with the arms. Also, fitness trainers do not recommend jerking deadlifts. With this technique, the risk of injury increases to the maximum.
Correct technique
- First you need to correctly install the seat of the exercise machine. It should be positioned in such a way that the arms can be fully extended. After this, you can grab the special handle with a parallel grip.
- The knees and hips are fixed with soft bolsters. After inhaling, you need to slightly bend your chest forward and move your back back. At this moment the handle pulls towards itself.
- When you touch the handle to your upper chest, you need to take a short pause and slowly release the load. In this movement, it is advisable not to straighten your arms completely, as this can lead to injury.
- At the top point of the amplitude, a short pause is also held, and the athlete can move on to performing a new repetition.
- The required number of repetitions is performed.
Possible mistakes
To minimize the risk of injury while performing vertical rows in a machine, it is recommended that the athlete avoid the most common mistakes.
| Possible error | Consequences of its implementation |
| Excessive body movement forward or backward. |
|
| Excessively large distance between hands with a wide grip. |
|
| Insufficient retraction of the shoulder blades when the hands are at the lowest point. |
|
| Insufficient fixation of the legs with soft rollers |
|
| Ignoring the “bear grip” (thumb on the bottom of the bar, the other 4 fingers on top). | Shifting the load on the wrist muscles. |