Fats are an important nutritional component in many foods. They have the highest energy value. And for many of us, it is also a key component of subcutaneous fatty tissue, which, with its thickness, stimulates us to exercise and a healthy lifestyle. Excess fat in food spoils our figure and provokes atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. The deficiency is no less dangerous, because of it the level of sex hormones drops, muscles atrophy, the skin becomes flabby and the nervous system suffers. How to be? Try your best to get rid of fat, declare war on it, or accept the inevitable? Let's try to figure it out.
What are fats?
Let's mentally return to our school desk (just for a second) and remember that from a chemical point of view, fats belong to the class of triglycerides. This is important for us only in order to understand how these paradoxical substances work. They are based on the well-known glycerin, which is the simplest trihydric alcohol - it has a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to each carbon atom (there are 3 of them in glycerol). For comparison, ordinary ethyl alcohol has 2 carbon atoms in its molecule and only one of them has an OH hydroxyl group attached. So, if you remove a hydrogen atom from each alcohol (hydroxyl) group of glycerol and instead add the remainder of some carboxylic acid (oleic, stearic, palmitic, etc.), then you will get a triglyceride molecule, i.e. . fat And these same carboxylic acids are also called fatty acids (precisely because they are part of fats).
Properties of fats
Actually, the properties of fats are determined by the structure of these fatty acid molecules that make up them. But here the situation is a little more complicated. Approximately 90% of all fats consist of 3-4 fatty acids (just the ones we mentioned above). If the fat contains more stearic and palmitic acids, then these are saturated fats and they are solid at normal temperatures (20 degrees Celsius). If there is more oleic and other unsaturated acids (linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic, etc.) then these are unsaturated fats; they are liquid at normal temperatures.
All fats we are familiar with are insoluble in water. Under certain conditions, they can form an emulsion (a suspension of tiny droplets in water). A typical example is milk. Fats themselves can act as a solvent - for example, water-insoluble vitamins (A, D, E) are often dissolved in natural fats. Thanks to this, they enter our body along with fats.
Hydrostatic weighing of a person (underwater)
Underwater weighing has always been considered the best method of measuring body composition compared to all others. But it is not without its drawbacks: and the first of them is that not everyone likes it when they are dipped in water.
Here is a description of how to find out the percentage of subcutaneous fat in the body using the hydrostatic method: a person is immersed sitting on a chair under water. The experience is based on the fact that fat is lighter than muscle. The fatter you are, the more buoyant you are, and the more buoyant you are, the less you will weigh underwater. For thin people it's the other way around.
There are also a few other disadvantages. There are several factors that can ruin the accuracy of the measurement. For example, blacks have denser bones than other races and may therefore be reported to have lower fat content than they actually do. In addition, men, in principle, always have denser and heavier bones than women. Bone density also decreases with age.
Even if you take into account race, gender and age, you can still make mistakes. Another factor that affects the accuracy of the measurement is your “remaining volume.” Residual volume is the amount of air that remains in the lungs after a complete exhalation. Before being immersed in the tank, you must exhale all the air from your lungs. If this is not done, the test will show a higher body fat content than it is.
This type of research is mainly used in hospitals and scientific institutes. This is a rather expensive method, although very fun.
Why do we need fats in the body?
A natural question arises: why do we need all this organic chemistry? What, you can’t live without her? Unfortunately no. Fats play an important role in our metabolism and even more than one. Their functions can be briefly summarized as follows:
- structural - fats are part of cell membranes,
- thermoregulatory - subcutaneous fat is an excellent heat insulator, it is not cold,
- protective - our internal organs are surrounded by a layer of visceral fat, which protects them from damage, displacement, shock, etc.,
- energy - the body extracts energy from fats, which is required for all processes without exception,
- storage - adipose tissue stores not only energy reserves, but also other necessary substances: vitamins, large amounts of water, minerals.
The energy content of fats is colossal - approx. 9.3 kcal/g. That is, the energy released during the processing of 1 g of fat is enough to lift a load of 2 tons to a height of 2 meters. And 100 kg of fat is enough to send a 65 kg rocket into space.
Fats are involved in the absorption of the so-called. fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E). It is the content of vitamins and some other substances that determines the value of fatty products such as fish oil.
In addition, fats are required for the secretion of a large number of hormones: including testosterone, estrogens, cortisol, etc. From this alone it is clear that fats cannot be completely excluded from the diet - without them the hormonal system will suffer. Their amount in food should not be less than 10-15%.
Animal and vegetable fats
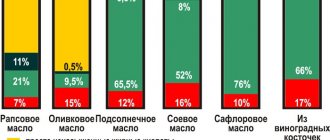
Fats obtained from plant or animal foods differ in their composition and properties. Animal fats (beef, pork, lamb, etc., as well as butter), also called “lard,” are usually solid - we have already said that this is due to the high percentage of stearic and palmitic acids in their composition. They are difficult to break down by the body and are absorbed by only 20-30%.
Vegetable fats are more diverse in composition, but they are united by the fact that the proportion of saturated fatty acids in their composition is minimal, so they not only exist in liquid form, but are also easily absorbed by the body. Vegetable fats (also called oils) are unsaturated, which means that their molecules contain double chemical bonds. They are more unstable and easily ruptured, causing unsaturated fats to enter into biochemical reactions (for example, oxidation). Because of this, our body likes vegetable fats more - it can more easily obtain energy from them, and besides, it is unsaturated fats (omega-3 groups) that are required for the construction of cell membranes.
Both animal and vegetable fats are needed by the body; in no case should they be completely excluded from the diet, as we have already said. Even when losing weight.
Healthy and harmful fats for the body
It is believed that excess animal fats in food increases harmful cholesterol in the blood and is one of the important factors of atherosclerosis. Today this point of view is disputed by many experts. The fact remains: when microdamages appear in the walls of blood vessels, cholesterol molecules begin to accumulate in these places, as if covering up the damaged areas. Cholesterol deposits are formed, under which the walls of blood vessels degrade even more, and the lumen of the vessel narrows due to cholesterol deposits, impairing blood flow and oxygen supply to tissues, which leads to coronary heart disease, strokes and other tragic events. The question of what came first - damage to the walls of blood vessels or cholesterol deposits - is still being debated, but it is quite clear that cholesterol brings not only harm, but also benefit.
Harmful fats are generally believed to be saturated animal fats. But it is important to consider that it is not the properties of these substances themselves that make them harmful, but their excessive consumption. If you eat a lot of fatty meat and lard, the fat will harm the body. If you do not overuse lard and fatty lamb, then even animal fats will bring more benefit to the body than harm. Of course, only overcooked fats are harmful. At high temperatures (190 degrees Celsius), fats quickly oxidize and some of them break down into toxic substances. Accordingly, the higher the temperature and the longer you fry something, the more harmful the fat becomes. You should absolutely not eat fat from frying or even reuse it for frying.
One way or another, vegetable fats are considered to be more healthy; it is also recommended that they make up at least half of the total share of dietary fats. The most common vegetable fats found in nature are omega-9 unsaturated fats: oleic acid, which makes up 90% of olive oil, and is also present in large quantities in sunflower and other common vegetable oils.
And the healthiest fats are unsaturated fats from the omega-3 group. There is a lot of alpha-linolenic acid in flaxseed oil. And some omega-3 (eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids) are present almost exclusively in fish oils, which is why it (although technically it refers to animal products) is extremely useful and is considered an important means of preventing cardiovascular diseases, and is indispensable for brain growth and development in children.
So, healthy fats include unsaturated fats omega-3 (fish oil, flaxseed oil), omega-6 (nut oils, safflower, flaxseed, canola), omega-9 (olive oil). But for those who can't get enough unsaturated fats from regular foods, there are special dietary supplements that contain healthy fats.
How to measure body composition anthropometrically
This is a measurement of body composition based on determining bone diameters and body circumferences at several locations. Circumferences are measured with a simple tape centimeter, bone diameters with an anthropometer. Both methods are based on the fact that there is a relationship between the size of skeletal bones, body circumference and muscle mass.
For example, the ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference is one example of a ratio. You might have seen all these patterns in fitness magazines. You simply fill in your measurements, height and weight and get a body fat estimate! The test is quite simple, but less accurate than other methods. Studies have shown greater error compared to skin fold pinching or underwater weighing. I don't recommend this method. It can only be used for preliminary testing.
Measuring body fat percentage with a caliper
When choosing a method with which to take measurements, it is best to choose a method that is practical, easy to use, and easily accessible for repeat measurements.
Try measuring skinfold thickness using a caliper. This method is based on the fact that you store most of your body fat just under your skin. This is the so-called subcutaneous fat. Its remainder is located around the internal organs and inside the muscles. Let's look at how to calculate your body fat percentage using a caliper. Typically, several areas of the body are measured (except for Accu-Measure, they only measure one area) and then a total is obtained. Using the tables that come with each tool, you get your body fat percentage. Digital calipers add up the measurements and give an answer on their own.
Most formulas for measuring body fat require you to measure the skin fold in several places. Some require 1 measurement, and some require 11. Standard measurement locations include abdomen, thigh, biceps, triceps, chest, back (subscapularis), armpit, and calf. Taking three measurements is most optimal. Research shows that more than 4 measurements no longer provide a large increase in accuracy. Although a smaller number reduces the accuracy slightly.
Video: “How to determine your muscle to fat ratio.”
Healthy fats for women
Fats can bring a lot of benefits to the fair sex. And we won’t even talk about the use of fats as cosmetic procedures, in which various oils and fats are constantly present. Let's consider only the benefits of ingestion.
- Healthy fats help you lose weight. Yes, paradoxically, unsaturated fats (especially omega-3) stimulate fat metabolism, accelerate the processing of fats in the body and thus activate weight loss.
- Fats support the secretion of hormones, incl. estrogens. As we know, the result of low estrogen levels is such unpleasant things as sagging skin, mood swings, sleep disturbances, osteoporosis (weakening bones).
- Vitamins enter the body with fats: A protects vision, D supports immunity and calcium balance in bones, E – health of the reproductive system. If there is a lack of fat, vitamin deficiency with all the accompanying troubles is likely to occur.
We have already said which fats are most beneficial (including for women), but let us remind you: these are unsaturated fats of the omega-3 group (fish oil and flaxseed oil), and to a lesser extent omega-6 and omega-9.
Fats in food are not always present in sufficient quantities and in good quality. Not every fatty fish is rich in unsaturated omega-3 fats - they break down very easily at high temperatures and in light. Therefore, if you want to supplement your diet with healthy fats, it is better to purchase appropriate supplements, and it is better to choose them in capsules rather than in bottles - capsules better preserve unsaturated fats.
Bioelectrical analysis method
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) is a method based on the different electrical conductivities of your body tissues. Muscle tissue contains more water than fat tissue, and therefore is more conductive. For the test, you need to attach electrodes to your right wrist and right leg. By passing a small current through the body, we can determine the amount of fat in the body.
Since the test is based on body water content, the result varies greatly depending on the body's hydration status. If the body is dehydrated by drinking coffee, alcohol or normal sweating, then the results cannot be considered correct. Since the amount of water changes throughout the day, it is better to take measurements at approximately the same time.
Bioelectric analysis is a fairly reliable method. However, this method tends to detect elevated fat levels in athletes such as bodybuilders. And until more precise methods appear, bodybuilders use skin tucks.