Carbohydrates or proteins?
Since childhood, we have been told that we must eat porridge for breakfast, otherwise “we won’t have the strength.” Nutritionist Alena Vozhakova explains that this is a big misconception.
When you eat fast carbohydrates in the morning (sweet cereals from white cereals, muesli, baked goods, etc.), your blood sugar level quickly rises, and you really feel energetic. But at exactly the same speed the opposite reaction occurs, a feeling of even greater fatigue and hunger comes. Such insulin surges lead to weight gain and the development of diabetes.
If breakfast consists of proteins, fats and slow carbohydrates, then the blood sugar level gradually rises within normal limits and slowly falls. You remain productive for a long time. And a repeated feeling of hunger occurs already at lunchtime, which is physiological and correct.
What's healthier: fats or carbohydrates?
When choosing foods, we are interested in their calorie content and the percentage of fat and carbohydrates. After all, these components increase the calorie content of foods and can lead to obesity. Let's try to figure out whether it is possible to give up fats or carbohydrates, giving preference to protein foods. What's healthier: fats or carbohydrates?
What are fats for?
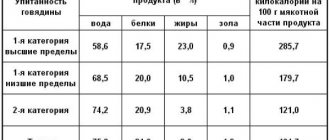
If you want to lose weight, a person most often refuses fat. Indeed, why replenish supplies of what we already have in abundance? However, fats make food more filling and it is with these elements that our body receives vitamins A, E and D. The caloric content of fats is very high and it is twice as high as that of carbohydrates. There are animal and vegetable fats. The first include butter or pork fat. Vegetable fats are found in plant oils. Fats can also be divided into saturated and unsaturated.
Animal fats, or beef for example, can lead to metabolic disorders. They increase cholesterol levels and can lead to atherosclerosis. That is why you should not eat fatty meat in large quantities. Vegetable fats do not contain cholesterol and are less dangerous for our body. By consuming exclusively vegetable fats, you can reduce cholesterol and “heal” blood vessels. Vegetable fats must be present in the human diet, but animal fats must be reduced to 30 percent.
Animal fats are part of the foods we eat every day - sausages, cheeses, butter and fatty meats. Nuts and cereals are rich in vegetable fats. It is best to consume vegetable fats fresh. Heat treatment destroys their properties and they can become harmful. With a lack of fat in the body, problems with the nervous system and immunity can occur. While excess animal fats lead to atherosclerosis, problems with the cardiac system and obesity.
What are carbohydrates for?
Carbohydrates provide energy to our body. Simple carbohydrates are glucose, lactose, sucrose, and complex carbohydrates are fiber, starch and glycogen. Almost all simple carbohydrates enter our body through confectionery products. Complex carbohydrates are found in cereals, potatoes and bread. Fiber and pectin, which are complex carbohydrates, are considered ballast substances that are necessary for digestion. They normalize metabolism, reduce cholesterol levels and remove harmful substances from the body.
To avoid obesity and metabolic problems, it is best to consume complex carbohydrates, which are found in large quantities in cereals and vegetables. A lack of carbohydrates can cause nervous disorders and exhaustion. The person becomes weak and experiences difficulty in mental and physical labor. Lack of fiber most often leads to digestive problems and increases the risk of intestinal cancer. An excess of simple carbohydrates leads to excess weight, atherosclerosis and diabetes.
In order for the body to develop and function normally, you should not give up carbohydrates and fats. It is worth replacing simple carbohydrates with complex ones, and giving preference to vegetable fats. These elements are necessary for our body and refusal of them will cause a metabolic failure.
The purpose of breakfast is to fill you up
In the early 1950s in England, a breakfast consisting of scrambled eggs, bacon and beans became very popular among the working class. It was proteins and fats that gave workers the necessary boost of energy and a long-lasting feeling of fullness. This is confirmed by modern research.
A scientific article was published in the journal Nutrients in 2021 that examined the difference between eating eggs and oatmeal for breakfast. The experiment found that participants who ate eggs every morning felt fuller longer than those who ate oatmeal. It was also found that eating protein for breakfast reduces the amount of ghrelin in the blood.
Ghrelin
is a hormone that stimulates hunger and often makes you want to eat something you don't need. When your levels remain low, you lose weight faster and find it easier to maintain weight.
And another study found that athletes who ate a low-carb, high-fat diet had improved endurance performance.
Photo: istockphoto.com
What you need to know about fats and carbohydrates
Origins
When choosing products labeled “sugar-free” or “low-fat,” you cannot be sure that they are beneficial to our body. Doctors have long established a link between eating fat and sugar and an increased risk of heart disease. Studies dating back to the 1950s showed that sugar leads to the development of coronary heart disease. Scientists began to actively study the effect of cholesterol, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals on our body. In the 60s, two hypotheses were put forward. According to the first, the main cause of the development of coronary disease is refined sugar, and according to the second, it is the abuse of fatty foods, which are rich in saturated fats and cholesterol. For some reason, in the 60s, it was saturated fats that were recognized as the source of all ills, ignoring the role of sugar.
The harm of sugar
The average girl in Russia eats approximately 120–160 g of sugar during the day. If we do the calculation, we get one kilogram of sugar per week. Back in the 90s, the World Health Organization (WHO) drew attention to a pattern: high consumption of fast carbohydrates affects the increase in mortality and the development of cardiovascular diseases. Today, research shows that sugar is more dangerous than animal fats and cholesterol, which were the first to come under the radar of scientists and nutritionists. Recently, obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis, stroke, and cardiovascular diseases have been associated with high sugar consumption.
In Western countries, food labels indicate not only the sugar content, but also its daily value. Such information helps to understand what percentage of the permissible amount of sweets remains in stock for the day. In the domestic market, it is not yet customary to display this data on product packaging. On boxes of breakfast cereals, instead of the daily sugar intake, you can only find tempting information about the content of calcium, fiber or vitamin C, which is explained by banal marketing purposes.
Expert comment:
Inga Marieva, nutritionist, candidate of medical sciences
“International statistics show that such precautions help reduce the amount of sugar consumed. When a person sees how much sugar he actually eats at breakfast, lunch, dinner or in between meals, he is much more careful about his diet. At least, he thinks about the fact that the notorious muesli, cereal cookies and juices contain a decent amount of sugar. I’m not talking about some confectionery products that can 100% replenish the daily amount of sugar in the body.” Ten teaspoons of sugar are allowed throughout the day, but it is even better to reduce this amount to three to five spoons. Of course, this is difficult to calculate, since in principle it is almost impossible to calculate the volume from the norm.
In addition, fast carbohydrates weaken the immune system. If blood sugar is too high, it affects antibodies, which contribute to immune reactions. As a result, they begin to function worse, the body weakens and picks up viruses. This is why diabetic patients tolerate infectious diseases worse, their wounds take much longer to heal, and pustules appear on the skin.
If we talk about the skin, then sugar has a detrimental effect on its condition. It is deposited in the collagen of the skin, thereby reducing its elasticity. Those with a sweet tooth develop acne, the skin becomes oilier or, conversely, dry. Sweets negatively affect the beneficial bacteria that exist in the intestines. At the same time, it stimulates the proliferation of harmful microorganisms. It is necessary to monitor the total amount of sugar that we treat ourselves to when we are tired, in a bad mood or feeling hungry. You can replace the habit of eating sweets with dried fruits in moderation, fruits and even vegetables. Joy hormones (endorphins) are present in bananas, plums, berries and apples. And the hormone of happiness (serotonin) will begin to be produced during normal physical activity.
Expert comment:
Larisa Bavykina, endocrinologist, medical geneticist
“It’s important to know the downside of carbohydrates. They are necessary in the daily diet, for example, the brain feeds only on sugars and nothing else. How can you understand what level your blood sugar and lipids are at? For this, there are laboratory tests: the level of blood sugar (glucose) must be less than 5.5 mmol/l. Such an analysis should be included in the annual medical examination for people over 40 years of age, especially if they are overweight. This is extremely important for people whose first-degree relatives (father and mother) have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. As for the metabolism of fats in the body, its condition will be shown by a lipid profile analysis. This will reveal the ratio of “bad” and “good” cholesterol. “Bad” cholesterol, or low-density cholesterol (LDL-C), should not exceed a blood level of 3 mmol/l.”
The benefits of fat
In the 60s, there was a stereotype that fat was harmful to the body. Therefore, we willingly take low-fat products that boast 0% fat content. At the same time, nutritionists claim that fat is one of the key elements for normal growth, development, tone and absorption of all necessary vitamins and minerals. For the body to function properly, we need to consume up to 20–35% fat per day of total calories. This also applies to those who are on diets.
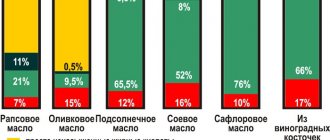
Together with food, our body enters saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats are solid animal fats that contain high amounts of fatty acids. These include butter, white fat on meat or chicken, cheese, and kidney fat. Such fats do not melt at room temperature. They are difficult to digest and poorly absorbed by the body. Saturated fatty acids are found in eggs, dairy products and even chocolate. Our body needs 15–20 g of such fats per day.
There are two types of unsaturated fats: polyunsaturated and monounsaturated. It is important for the body to receive them from food. They can be of plant origin, for example, nuts, avocado, olive and sunflower oil, or animal - red fish meat, seafood.
Amount of fat
The Little-Known Role of Insulin
Basal insulin is our “glue”, manager, dam
When we take a blood test for insulin, we measure it on an empty stomach. That is, insulin is present in our blood, even if we haven’t eaten anything for a long time. This is the so-called basal insulin (if you know type 1 diabetics, then you probably know that they use different insulin - basal, for the whole day, and also insulin after each meal).
The function of basal insulin is the long-term regulation of energy sources in the blood, be it glucose, ketones or fatty acids.
Somewhere I heard an excellent comparison of basal insulin to glue, which allows you and me to literally keep our shape and not dissolve into an “energy puddle” of fat, protein and sugar.
This function of insulin is also illustrated very clearly by people with type 1 diabetes - who do not have insulin.
Before the invention of insulin drugs, people with type 1 diabetes died from exhaustion. These are people whose reserves - in the form of fat or sugar (glycogen) - are not retained and cannot be stored, since there is no insulin, which can be called their manager.
The picture shows a boy with type 1 diabetes before and after starting insulin therapy.
Insulin can be compared to a thrifty owner: it closely monitors energy status and only releases energy sources into the blood when necessary. At other times, it stores them in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles, as well as in the form of fat reserves.
And its absence is real chaos, when all reserves rush into the bloodstream like an avalanche. As you may know, type 1 diabetics have very high levels of glucose, fatty acids, and ketones in their blood at the same time. This is a very life-threatening condition.
Why doesn't basal insulin decrease with just a low-carb diet?
It depends on how much energy reserves you have. The more reserves - in the form of adipose tissue - the more resources are needed to maintain shape.
That is, our basal insulin levels are proportional to the amount of fat we store, which in turn is proportional to the amount of energy we take in through food.
This function of insulin is perfectly illustrated by the meme (as he calls it) of Dr. Ted Neumann. Here, basal insulin is like a dam that holds back all the energy we have accumulated.
The more of this energy (stored fat), the higher your dam (basal insulin level) must be to keep it from overflowing.
Now let's imagine a very overweight person on a low-carbohydrate diet. By reducing carbohydrates, his insulin responses to meals decreased.
But until fat stores decrease (weight loss occurs), basal insulin levels will need to be maintained at a high enough level to support the avalanche of energy in the form of stored fat mass.
The positive effect of low-carbohydrate diets is explained by many experts as a decrease in hunger and its important consequence: we naturally begin to eat less.
True, not all. Since fat is sometimes perceived as an indulgence to consume as much food as you can fit.
And here we move on to other news about insulin.