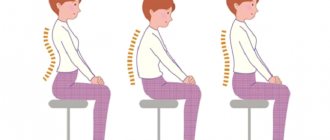
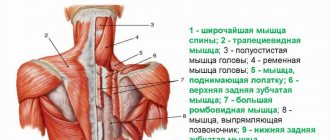
Good posture is important not only for beauty, but also for health. It helps develop strength, flexibility and balance in the body, minimizes muscle pain, helps to properly distribute loads and avoid injuries.
Poor posture can cause various health problems, such as:
- poor sense of balance;
- labored breathing;
- headache;
- urinary incontinence;
- heartburn, etc.
Researchers also see a link between poor posture and sleep disturbances, fatigue and mood swings, according to Harvard Health.
Just imagine: if a person's head is pushed forward at least 6-7 cm due to postural problems, this puts 19 kilograms of pressure on the neck and upper back muscles. To put it more clearly, there are three heavy watermelons on your shoulders, which you have to walk with 24/7 every day. Sounds so-so, right?
We have already talked about how to determine whether there are problems with posture at home in one of our previous articles. In this one we will focus on exercises that can help you get rid of the problem.
The key to correcting poor posture is to strengthen and stretch the muscles of your upper back, chest, and core.
Child's Pose
This exercise stretches and lengthens the spine, glutes, and hamstrings, and helps relieve tension in the lower back and neck.
How to perform an exercise for a straight back?
- Sit on your shins with your big toes touching and your heels out to the sides.
- Bend down and extend your arms in front of you.
- Gently move forward until your forehead touches the floor.
- Relax in this pose for up to 3 minutes and breathe deeply.
- Take the starting position and repeat the exercise several more times.
Yoga for Posture: Eight Best Exercises
1. Tadasana with arms back (Mountain pose).
Technique:
- stand in Tadasana;
- feet together and pressed tightly to the floor;
- kneecaps are pulled up, hips and buttocks are toned;
- Tuck your tailbone down;
- move your shoulders back, stretch the top of your head up;
- clasp your palms behind your back and stretch your arms back and up (if you can’t connect, then use a belt, belt or any available means);
- stay in this position for a minute or more, bring your shoulder blades closer to each other, stretch your arms back and up.
This exercise helps open the chest, loosen the shoulders, relieve tension, increases the mobility of the shoulder joints and affects the heart center, filling you with a sense of peace and trust in life.
2. Marjariasana (Cat pose).
Technique:
- lower your knees to the floor pelvis-width apart, thighs perpendicular to the floor;
- place your palms under your shoulders, fingers spread wide and pressed firmly to the floor;
- while inhaling, make a smooth deflection: stretch your stomach down, point your tailbone and chin up;
- as you exhale, round your back, point your tailbone down, press your chin to your chest, look at your navel;
- As you inhale, continue to go into a smooth arch, and as you exhale, round your back. By time - 1-2 minutes, or by feeling.
This asana works the entire spine, warms up, helps stretch the back and abdominal muscles, increases blood circulation, strengthens the shoulders and wrists, improves the functioning of the digestive system, helps relieve tension in the body and eliminates anxiety.
3. Virabhadrasana I (Warrior Pose).
Technique:
- from the Marjariasana position, take a wide step forward with your right leg so that your foot is between your palms;
- stretch your arms up, if possible, bring your palms together above your head and move them back, keeping your arms straight at the elbows;
- the right knee at an angle of at least 90 degrees is located strictly above the heel;
- the left leg is straight, the kneecap and thigh are tucked, the foot of the left leg is turned outward at approximately an angle of 45 degrees;
- press your feet firmly to the floor;
- Strive upward with your neck, crown and spine;
- Tuck your tailbone under you, slightly tone your stomach;
- move your shoulders back and down;
- look - forward or upward;
- stay in this position for 30 seconds or more;
- do the same on the other side.
Positive effects: the asana opens the shoulders and chest; strengthens feet, ankles, hips; increases concentration and endurance; fills with a sense of harmony.
4. Paschimattonasana (sitting straight leg bend).
Technique:
- from a sitting position, place your legs in front of you: feet together, toes pointing up, kneecaps pulled up;
- the body is perpendicular to the floor, the top of the head is stretched upward, the back is straight (if you feel that it is difficult to keep your back straight, perform the asana near the wall; you can also bend your knees and then try to gradually straighten them);
- with an inhalation, stretch your arms up and as you exhale, smoothly lower your arms, grabbing yourself by the feet, toes or shins (if it is difficult to bend, remain without bending, stretch the top of your head up, keep your back straight);
- lower your stomach to your hips, point your chin forward;
- stay in this position for one minute and then slowly return to the starting position.
This incredibly useful exercise is also called the longevity asana. It promotes stretching of the entire back of the body, especially the spine and legs; harmonizes the functioning of internal organs and systems, improves digestion and has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart. Relieves anxious thoughts.
5. Purvottanasana, basic version (Table Pose).
Technique:
- in a sitting position, place your feet 20–30 cm from the buttocks, hip-width apart, feet parallel to each other;
- place your palms 15–20 cm away from you behind your back, fingers pointing back;
- while inhaling, lift your pelvis up, tighten your buttocks;
- push off the floor with your feet and palms;
- hold for 20-30 seconds and return to the starting position.
Performing Purvottanasana helps to lengthen the front part of the body; loosen the thoracic region; open your shoulders and wrists; strengthen the muscles of the back, abdominals and buttocks. Relieves fatigue and increases vitality.
6. Shalabhasana, simplified version (Locust Pose)
Technique:
- take a lying position on your stomach, arms along your body, forehead on the floor;
- join your hands behind your back in a finger lock, if possible, then so that your palms are together; if you can’t connect your hands behind your back, then use a strap or belt: grab it from opposite sides and bring your palms as close as possible along the strap;
- as you inhale, lift your head and legs, and use the lock from your hands to stretch back and up; look at the floor in front of you, make sure that your neck does not overstrain;
- breathe, don’t stop breathing;
- stay in this position for a time that is comfortable for you;
- then lower your legs, place your hands in front of you: palm on palm, lower your forehead on your palms;
- Take a few deep breaths and exhalations, relax your entire body as much as possible.
The practice of this asana effectively affects the muscular corset and works the deep back muscles that run along the spine, as well as the muscles of the arms and legs; is the prevention of radiculitis, lumbar osteochondrosis, vertebral displacement; promotes the treatment of intervertebral hernias; increases the useful volume of the lungs and relieves fears; gives a feeling of lightness and fills with energy.
7. Ardha Navasana (Half Boat Pose).
Technique:
- from a sitting position, round your back and smoothly lower your lower back onto the mat and shoulders;
- leave your shoulders and thoracic back hanging, the top of your head pointing upward;
- Stretch your arms forward parallel to the floor, palms turned inward;
- legs are straight, kneecaps are tucked, hips are toned;
- as you inhale, lift your legs up about 30 degrees (if this is difficult, you can raise your legs higher or just leave them on the floor), your toes can be pointed forward or up;
- use your abdominal muscles to press your lower back to the floor;
- stay in the asana for a comfortable time and maintain even breathing;
- then lower yourself to a lying position and take a few relaxing breaths.
Thanks to this asana, you will feel how the muscles of the back, abs, and hips are strengthened; correct posture is formed; the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract improves, the functioning of the liver and pancreas is stimulated; immunity increases.
8. Urdhva Chaturanga Dandasana (Plank Pose).
Technique:
- go to Marjariasana (Cat Pose), place your toes on the mat;
- as you inhale, push your pelvis up so that from your heels to the top of your head your body lines up in one straight line;
- Place your palms clearly under your shoulders, spread your fingers wide: the middle ones are directed forward and parallel to each other;
- Twist the tailbone down so that there is no arch in the lower back;
- push your heels back, pull forward with the top of your head, gaze fixed on the floor;
- tighten your kneecaps, tighten the muscles of your thighs, buttocks and abdomen;
- breathing is even, calm, without delays;
- stay in the asana for a time that is comfortable for you;
- return to Cat Pose.
The asana is very effective for strengthening the entire body and maintaining beautiful posture. It stimulates the functioning of the abdominal organs, improves blood circulation, helps relieve fatigue, increases physical and mental endurance, and fills with confidence.
And, of course, after practice, lie down for at least 5-10 minutes in Shavasana, spreading your arms and legs to the sides in the most comfortable position. Observe your breathing and relax your entire body as much as possible with each exhalation. After such a little practice, you will feel lightness in your body and a surge of energy.
Downward facing dog
A classic exercise familiar to many from yoga. It strengthens the entire body (back, arms, shoulders, stomach and legs), stretches the spine, ankles, calves, hamstrings, and stimulates blood circulation.
Very briefly, the pose resembles an inverted letter V. If described in more detail, the exercise to improve posture is performed as follows:
- Get on your fitness mat on all fours. Begin to slowly raise your knees, pressing your toes firmly into the surface to feel support.
- Stretch and lengthen your spine, lifting your pelvis as high as possible, keeping your head down so that it forms a straight line with your back.
- Keep your body in this position and watch your breathing. Slowly lower your knees to the floor to return to the starting position.
Do at least three repetitions at 30-second intervals.
Safety precautions
It is important to perform exercises to improve posture while observing safety precautions.
- It is necessary to start a set of exercises with a warm-up. To do this, it is enough to spend 5-7 minutes on a treadmill or on an ellipsoid, and if you are at home, jump or run in place for the same amount of time.
- Stretching after strength exercises will relieve muscle tension and protect against injury, increasing the rate of tissue recovery, so this element should not be neglected either.
- Most back strengthening exercises should be done by squeezing your shoulder blades and keeping your back as straight as possible. Otherwise, you can achieve not correction of posture, but a training injury. You also need to maintain a deflection in the lower back, and do not bend it under any circumstances.
- It is important to dilute exercises for posture in the gym with tasks on other parts of the body. This will allow you to put the load on the body more evenly and form a beautiful body.
- The “wall stand” exercise is important to perform daily, as it forms the habit of keeping your back straight.
Cat-cow/cat-camel
Stretches the spine, helps relieve tension in the torso, shoulders and neck, improving blood circulation.
To do this exercise for beautiful posture, you need to:
- Get on all fours, evenly distributing your weight between all four limbs.
- Inhale, raising your head up and lowering your stomach to the floor, thereby stretching your spine.
- Exhale, stretching your back up and pressing your chin to your chest.
Alternately change positions for a total of at least a minute.
Pigeon pose
Pigeon pose is good for relaxing and stretching the spine, working the hamstrings and glutes, and helping to stretch the sciatic nerve and quadriceps muscle. Opening and stretching these muscle groups makes it easier to correct postural imbalances.
How to straighten your back with exercise?
- Bend your right knee and walk your leg forward as if about to lunge. Lower your right knee to the floor next to your right wrist. In this case, the shin can be directed back (towards the left thigh) or parallel to the mat, depending on your range of motion.
- Lower your left knee, slide your leg back so that it rests completely on the mat and your heel is pointing up.
- The situation must be stable. As you inhale, stretch your spine up, pull in your navel and try to open your chest wide. Hold this position for up to 1 minute.
- Repeat the pose, switching legs.
You can make the load more difficult by bending forward. It is important that there is no pain or discomfort.
Exercises on simulators
Exercising both at home and in the gym has one goal: strengthening muscles and creating a beautiful and healthy body. The difference lies in the speed of achieving results. Posture straightening machines allow you to get a beautiful back much faster. A competent trainer will help you create a training complex, but if you have certain knowledge, you can create a program yourself. What exercises for proper posture in the gym should you include on your list?
- Pull-ups in the Smith machine. The main advantage of this exercise is that even beginners can easily perform it. At the same time, its effectiveness is practically not inferior to conventional pull-ups. The higher you set the bar, the easier it will be for you to pull yourself up. However, ideally, the distance from the floor to the back at the lowest point should be minimal. If it is too difficult for you to perform the exercise with straight knees, you can bend them, this will make the task somewhat easier.
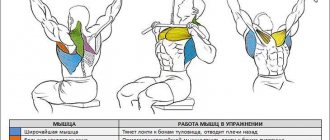
- Raising arms on the simulator. This exercise is similar to bent over dumbbell swings. If your gym does not have such equipment, then a crossover can easily replace it. Raising your arms allows you to pump up the central part of your back, which is largely responsible for straight posture.
- The vertical pull-down on a machine is another great exercise for correcting posture. There are several ways to perform it: to the chest, behind the neck, with a reverse grip, as well as narrow or wide. Depending on the technique, the load area also changes. In the classic version, the pull is carried out behind the head. At the same time, you should absolutely not hunch over, otherwise you may get injured.
- The lat pulldown on the machine is aimed at strengthening the latissimus dorsi muscle. When performing this task, it is important not to keep your back straight all the time. The technique allows for slight “stretching” following the load. But at the end of the movement, it is important to straighten your back, arching it in the lower back, and bring your shoulder blades together.
Side and regular plank
Planking strengthens your spine and core muscles, which naturally leads to better posture. In addition, coordination of movements and balance develops. Read more information about the types of planks and their benefits in a separate article.
How to correct your posture using a plank?
- Get on all fours and straighten your legs, lifting your heels and hips. Hands are shoulder-width apart; they can be either fully straightened or bent at the elbows.
- Straighten your back and engage your abdominal muscles, arms and legs to maintain an even posture. The head looks to the floor.
- Hold this position for up to 1 minute.
- To perform a side plank, you need to transfer your body weight to your forearm. In such a way that the elbow remains strictly under the shoulder.
- The hips must be raised up so that they form an even line with the body.
- The right leg rests on the floor, and the left is on it.
- The position is held for up to 1 minute, then the side is changed.
Exercises to correct posture in children. When is a doctor needed?
In case of serious postural disorders, special physical therapy (PT) is indicated. Exercises for straightening posture for children are a special complex that is prescribed only by a doctor for medical reasons after an external examination of a small patient. When selecting exercises, a specialist takes into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body, the degree and nature of the curvature of the spine and many other nuances.
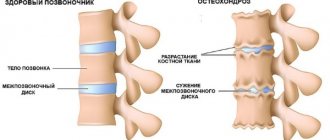
Causes of poor posture
Doctors identify the main factors that can lead to spinal curvature.
- Inactive lifestyle and physical activity. Muscles weaken due to prolonged sitting at a table, playing with a gadget, etc. Children of any age should move a lot, run, be in the fresh air for at least two hours a day and in any weather, play outdoor games. Ideally, a child should attend a sports section and exercise regularly under the guidance of a coach.
- Overload. Dosing physical activity and preventing injuries is a prerequisite for children’s health. Excessive exercise is no less dangerous for children than a sedentary lifestyle. If age standards regarding the duration of activities and their high intensity are not observed (for example, when preparing for sports competitions), the risks of injuries to the spine and muscles of the back, neck and shoulder girdle increase significantly. Wearing a heavy and non-ergonomic backpack also leads to poor posture.
- Bad habits. When reading or playing on a smartphone while lying down, drawing in an inappropriate position, etc., the spine gradually becomes deformed. It is necessary to teach your child to sit at the table correctly.
- Congenital pathologies of bone tissue. Doctors identify a special group of children with weakened back muscles and hereditary bone diseases. These children have a high risk of developing orthopedic diseases. For them, observation by an orthopedic doctor is mandatory. The specialist recommends a preventive or therapeutic set of exercises to strengthen posture for children at risk.
- Poor nutrition. An unbalanced daily menu becomes another factor that causes back curvature. Nutrition should include minerals, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the daily norms precisely indicated by doctors. In case of deficiency of useful elements necessary for the growth and development of bone and muscle tissue, the risks of scoliosis formation increase. This is especially true for preschool children.
- Poor workplace organization. Ergonomics is one of the most important points in a healthy posture program. If the workplace for games, meals and homework is poorly organized, curvature of the spine is inevitable even if all other doctor’s orders are followed. If a child walks a lot, eats right and even does posture exercises for children, but sits in the “wrong” chair, all the parents’ efforts are nullified.
| You can learn more about what doctors advise from this article. |
Bend forward with hands behind back
Thanks to this load, the pectoral muscles, as well as the back muscles, are stretched. This is a good way to get rid of sloping shoulders and a sunken chest.
The exercise for stooping is very simple:
- Stand up straight and move your arms back behind your back.
- Inhale deeply, clasp your palms together, crossing your fingers, opening your chest as much as possible
- As you exhale, tilt your body and raise your arms up, moving them forward as far as possible, relaxing your neck and head.
- Rise to the starting position and do at least 7-10 repetitions.
Exercise to lift internal organs
One of the very important exercises. Yes, it is not directly related to the position of the shoulders or back, but it is significant for the formation of posture. If we talk about visible results, then this exercise is more effective than any other in removing a protruding belly. Why is another story, which is called “prolapse of internal organs.” So, the mechanics of performing this exercise:
We perform it lying on our back. Legs are bent at the knees.
Step 1: just breathe with one belly. The chest is motionless.
Step 2: exhale all the air from yourself and strongly draw in your stomach, it should seem to stick to your back.
Step 3: Using the fingers of our palms, we pull the insides from the womb to the navel and a little higher.
We gently remove our hands, the stomach returns to its place. You can breathe!
The exercise is not easy to do at first! You may experience a feeling of discomfort; this is a completely natural situation. Continue in this manner every day before bed for six months. For clarity, I suggest watching this exercise on video.
Back extension lying on stomach
The purpose of the exercise is to strengthen the muscles that extend the back, in particular the erector spinae, as well as to work on the abdominal muscles to protect the lower back from injury.
This simple exercise for the spine is performed like this:
- Lie on your stomach, legs straight, arms bent at the elbows and lying in front of you, gaze directed forward.
- Keeping your forearms on the floor, slowly lift your upper body, arching your back.
- Hold this position for a few seconds, then smoothly lower your body to the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 8 to 10 times in one go.
Sports for scoliosis
Health-improving and preventive effects in patients with scoliosis can only be achieved through reasonable exercise. These include:
- therapeutic exercises;
- swimming;
- hydrokinesitherapy (recreational gymnastics in water);
- walking, including Nordic walking;
- skiing and skating;
- Pilates;
- fitness;
- yoga;
- exercises on the horizontal bar and exercise machines;
- running on a rubber or dirt track;
- body-building.
Swimming and gymnastics in water
The health value of therapeutic swimming lies not only in the effect of physical exercise on the musculoskeletal system, but also in the beneficial effect of water on the human body. Water normalizes metabolism, strengthens the skin, increases the vital capacity of the lungs, increases the mobility of the chest, hardens the body, improves the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Regular swimming lessons for scoliosis promote the development of the muscular system, improve the mobility of the ligamentous-articular apparatus, help maintain the spine in the correct physiological position, and inhibit further progression of the deformity. Staying in water has a beneficial effect on the spine: the load is reduced, the intervertebral discs are relaxed, the muscles are stretched, and the axial skeleton is straightened.
To eliminate deformities of the spine and chest, breaststroke swimming is the most optimal, due to the absence of additional body movements and stable body position. In order for swimming to be beneficial, you need to train 2-3 times a week for 45-60 minutes. The water should not be cold, the optimal temperature is 28 degrees. Before swimming training, be sure to warm up.
Healing Fitness
Regular exercise therapy for scoliosis solves the following problems:
- formation and strengthening of the muscle corset;
- improved coordination of movements;
- training strength endurance;
- activation of blood circulation;
- reducing the severity of pain;
- development of correct posture and prevention of its violations.
Therapeutic physical training is recommended at all stages of scoliosis development or during the rehabilitation period after spinal surgery. The physical therapy complex includes active exercises, those performed by the patient himself, and passive exercises—performed with the help of special devices or by someone else’s hands. Exercises to strengthen the shoulder girdle (push-ups, rows, presses), abdominal press, hip joint, legs, and self-extension of the spine are useful. Exercises that increase the flexibility of the spinal column and lead to its overextension are contraindicated.
To achieve a positive result, classes must be systematic, at least three times a week. The treatment program is drawn up by an orthopedist or a rehabilitation medicine doctor on an individual basis. In the early period, exercises are performed under the supervision of a specialist, which is necessary to develop the correct technique, establish breathing, and prevent injuries. In the future, independent studies are possible.
Running and walking
Running for scoliosis should be moderate; you should move along a special rubber or dirt track, which will help reduce the load on the spinal column. In order to avoid shock-absorbing injuries, prevent the formation of corns and calluses, and increase the effectiveness of exercise, experts recommend the use of orthopedic insoles. With a slight curvature of the spine, running helps strengthen the back muscles and increase the overall tone of the body.
During the period of active growth of a child, with scoliosis of 3-4 degrees, running can only aggravate the course of the disease, increase the curvature, and provoke back pain. In such cases, walking is more beneficial. Nordic walking is especially useful for scoliosis. During exercise, muscle tone, the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems improves by 85%, blood flow to the muscles increases, a strong muscle corset is formed, and the load is evenly distributed throughout the body. A positive result is possible with regular exercises 2-3 times a week for 30 minutes.
Fitness
Orthopedic doctors recommend doing fitness if the degree of curvature of the spine is low, there is no back pain, and general health is satisfactory. The physical exercise program aims to correct poor posture, restore muscle symmetry, improve muscle tone, strength and flexibility, relax the spine, and increase physical abilities.
Skiing and skating
Recreational skiing and skating have a positive effect on the back muscles: they increase their flexibility, endurance and elasticity, form a strong muscle corset, thanks to which curvature can be eliminated or further progression of the deformity can be prevented. During skating, the pectoral muscles actively work, which allows you to form good posture and prevent deformation of the chest. The exception is alpine skiing, hockey, and figure skating, as there is a high probability of injury.
Pilates
The result of regular Pilates classes for scoliosis will be the development of muscles throughout the body, improved posture and coordination, and the relief of tension and pain in the body. People of any age, with different levels of physical fitness, and different angles of spinal curvature can engage in physical exercise, since the exercises are performed at a smooth, slow pace with minimal risk of injury. It is necessary to start classes under the supervision of a trainer; after good preparation, independent training is possible.
Exercises on horizontal bars and exercise machines
Strength training for scoliosis has a multifaceted effect on the condition and functionality of the spine: it stretches and straightens the spinal column, strengthens the muscle corset, eliminates back pain, reduces the angle of curvature and prevents further progression of the deformity. The training program should be drawn up by a specialist, as well as the exercise technique controlled. To eliminate spinal curvature, special attention is paid to the superficial and deep back muscles, shoulder girdle muscles, shin flexors and gluteal muscles.
Most often the set of exercises includes:
- horizontal block rods;
- trapeze with barbell and dumbbells;
- hyperextension;
- raider traction;
- tilted dumbbell swings;
- pull-downs from the upper block to the chest and behind the head;
- French press;
- exercise bike;
- orbitrek.
Correction of spinal deformity is carried out using exercises on the horizontal bar. Typically, weights are used without weights, during which the spine is stretched, the abdominal muscles are strengthened, tension and load on the axial skeleton are reduced, and displaced vertebrae return to their physiological position. Exercises on the horizontal bar are contraindicated if the angle of curvature reaches 26 degrees (third degree) or more.
Yoga classes
Yoga can be practiced both in the early period of spinal deformity and in cases of curvature of more than 50 degrees. In a clinical study by researchers at Columbia University, it was found that just one yoga pose, the side plank, can reduce the severity of the spine by 32%. To do this, patients with scoliosis must maintain body balance at least three times a week, leaning on their palms and feet for 90 seconds. The course of treatment lasts six months.
Yoga classes help relax muscle tissue, restore healthy tone, activate blood circulation, restore the physiological distance between the vertebral bodies, strengthen the muscle corset, straighten posture, and improve the functioning of internal organs and systems. The specialist recommends a set of exercises individually, excluding compression load on the spine, anti-gravity and unnatural poses, shoulder stands, and back bends. Yoga is contraindicated for infections, inflammation, blood and heart diseases, mental disorders, and traumatic brain injuries.
Reverse bridge
The reverse bridge or reverse plank lengthens and straightens the lower back and corrects rounded shoulders.
It's very simple:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet hip-width apart.
- Place your arms along your body, palms down.
- Stand firmly and lift your hips and torso up. Make sure that the body does not bend and forms a straight line.
- Hold this position for up to 30 seconds and return to the starting position.
- Repeat the exercise 5 to 10 times.
Set of exercises[edit | edit code]
Always do a warm-up, including the exercises below, and also don't forget about the rotator cuff, as shown in the video before strength training and gymnastics.
Trapezius stretch
Stretch the upper trapezius and levator scapulae muscles
- Take a sitting or standing position. Tilt your head to the side, helping with your hand, place the opposite hand behind your back. The direction of stretching is indicated by arrows.
Stretching the pectoral muscles
Chest stretch at the counter
The peculiarity of gymnastics for stooping lies primarily in the accentuated stretching of the pectoral muscles, which tighten the shoulders in front.
- Stand next to the post or door frame, as shown in the picture. Begin to progressively rotate your torso so as to create tension in the pectoral muscle. After a few repetitions, switch hands.
- Clasp your hands behind your back. Slowly stretch forward, arching your spine as much as possible and moving your clasped hands back. Repeat the exercise 6-8 times.
- Hands at your sides. Raise your right hand up, take your left hand back, bend your elbows and try to connect them behind your back, return to the starting position. Repeat the exercise, changing the position of your hands, 6-8 times with each hand.
Sternal elevation
To strengthen the lower trapezius muscles and stretch the pectoral muscles, sternum lifts (the bone connecting the ribs in front) are performed. Sit or stand freely and begin to push your chest forward and up as much as possible, while moving your shoulders back. Maintain this position for a few seconds, then relax. Repeat 5-10 times.
Abdominal retraction
Pulling in your stomach is one of the main ways to make it fit. Simply pull your belly in as far as possible toward your spine as you exhale, then slowly relax as you inhale. Repeat this exercise several times a day for 3-5 minutes.
Chin retraction
Chin retraction
- gymnastic exercise for the neck
Shrugs
Can be performed on a chair. Pull your chin toward your neck (using the neck muscles, not the lower jaw) as shown in the first image, maintaining tension in the neck muscles for 3-5 seconds, then relax. Repeat 10-20 times. This exercise targets stretching the back muscles of the neck and strengthening the front muscles. In this way, the correct position of the head is restored, as well as the straightening of the spine in the cervical region.
Shrugs without weights
- necessary to strengthen the trapezius and rhomboid muscles, the weakness of which causes stooping
Squeeze your shoulder blades together, pushing your shoulders back and up. Maintain tension for 2-3 seconds. Repeat 10-20 times.
Raising arms and legs while lying on your stomach (“Superman”)
One of the best exercises for perfect posture is “superman”. It works well not only the back, but also the gluteal muscles.
For execution:
- Lie face down on the floor. Stretch your arms forward, legs straight behind you.
- At the same time, raise your arms and legs up, tensing the muscles of your back and buttocks. Keep your gaze ahead.
- Hold at the top point for 10-15 seconds and slowly return to the starting position.
- Repeat the exercise at least 10 times.
Another variation is to simultaneously raise your right arm and left leg, then change to the opposite.
Physiotherapy
Exercises to prevent postural disorders take much less time than correcting scoliosis. 10-15 or even 7 minutes a day, as well as the habit of keeping your back straight, will help you forget about going to the doctor or unpleasant pain for a long time. It is better to start all exercises with a short warm-up, which will warm up the muscles, and end with stretching. In this case, you can only do symmetrical exercises that equally affect both sides of the back. Therapeutic physical exercises effectively cope with the prevention of spinal curvature. What set of exercises can be done at home?
- The “fish” exercise has been familiar to everyone since kindergarten. Lying on your stomach, you need to lift the front of your body and legs and pull them in different directions, trying to hold in this position for as long as possible.
- Hyperextension can be done at home. Having taken a position lying on your stomach, you need to raise and lower your back, making sure that your pelvis remains pressed to the floor.
- Having assumed a position on all fours, you need to extend your right arm forward and raise your left leg. Alternately changing limbs, you need to linger in each position for about 10 seconds.
- Without changing the starting position, arch and arch your back. The head should follow the spine, rising and falling.
- A simple horizontal bar can seriously help correct your posture. Just hang on it, relax and spend a few minutes like this. During this time, under the influence of your weight and gravity, your spine will straighten and the distance between the discs will increase.
- Standing against a wall does not train your back muscles, but it does develop the habit of correct posture. In order for your muscles to “remember” how to behave correctly, you need to spend one minute in this position in the evening and in the morning. You need to press against the wall with four parts of your body: the back of your head, shoulders, buttocks and legs.
Each exercise must be performed 10-15 times in 2-3 approaches. If you feel that this load is no longer enough, you can increase the duration of classes or try weight training.
Bend forward from a sitting position
The last way to straighten your posture is to bend forward. For comprehensive health of the back and lumbar region, it is important to regularly do stretching and exercises for the spine. This helps improve the elasticity of muscles and ligaments, as well as maintain the health of the musculoskeletal system.
Technique:
- Sit on the floor or fitness mat with your legs straight.
- Slowly lower yourself forward, arching your spine and keeping your arms in front of you. Lower your chin to your chest.
- As you lower and raise your torso, imagine a rope tied around your waist with someone pulling from behind, bringing your belly closer to your spine.
- Repeat the exercise at least 5 times.
Exercises with dumbbells
5. Bent-over dumbbell swings
The exercise trains the rear deltoid and the muscles surrounding the shoulder blades. With each swing of your arms, you need to bring your shoulder blades together, while arching your back. Its effectiveness in terms of muscle pumping is low, but it has an effect on posture.
6. Bent-over dumbbell row
Technically, this is a rather difficult exercise. If you simply pull without arching your back or squeezing your shoulder blades, you will work mainly with your arms. And we need your back. If you do it correctly, the entire upper back will be involved.