General information
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa.
Over a long period of time, gastritis leads to disruption of various functions of the stomach, mainly by disrupting the production of hydrochloric acid and the associated digestion process. For a long time it was believed that the main cause of gastritis lies in a violation of the diet. However, today a number of authoritative studies have established that a violation of the diet is an insignificant factor in the development of gastritis. There are several real reasons for this pathology:
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori. According to statistics, up to 90% of all gastritis have a bacterial etiology. In the aggressive environment of the stomach (where there is concentrated hydrochloric acid), the vast majority of bacteria die. However, Helicobacter pylori manages to survive and reproduce in such unfavorable circumstances. During their life, H. pylori bacteria release toxic substances that cause an inflammatory reaction and encourage the stomach lining to secrete more acid. Thus, the walls of the stomach become defenseless and ulcers can form on them.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol negatively affects the condition of the epithelial tissues lining the inner wall of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to direct irritation, alcohol also increases the production of gastric juice, thereby increasing the likelihood of damage to the mucous membranes by hydrochloric acid.
- Reflux. A continuation of the stomach is the duodenum, into which the bile duct opens. If the functioning of the pylorus (the sphincter that separates the stomach from the duodenum) is impaired, reverse reflux of bile is possible. This process is called duodenogastric reflux. Bile and intestinal contents irritate the gastric mucosa, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes. It is noteworthy that attacks of duodenogastric reflux also occur in healthy people. Gastritis develops only after a number of such episodes. Often, the reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach causes chronic gastritis.
- Autoimmune processes. As you know, cells of the immune system fight foreign microorganisms that enter the body from the outside. However, with some disorders, the immune system begins to attack the body's own cells. The cells of the gastric mucosa are no exception, and their immunity can also be attacked. Autoimmune gastritis is a relatively rare phenomenon and accounts for only 5% of cases.
- Eating disorder. Some eating habits can cause inflammatory pathologies of the esophagus and stomach. For example, a passion for eating too rough food, which injures the mucous walls. It was previously believed that spicy foods and coffee contribute to the development of gastritis, but recent research does not confirm this. If a person does not have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), then spicy food will not harm him. The national cuisines of many southern countries are replete with spicy dishes, but this does not in any way affect the incidence of gastritis and other gastrointestinal pathologies. The opinion regarding long breaks and fasting is also questionable. There is no convincing evidence that short-term fasting (up to 24 hours) contributes to the appearance of gastritis.
- Medications. Some drugs (particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can cause gastritis. If you need to take these medications regularly, be sure to talk to your doctor about side effects.
- Other factors. Gastritis can also occur due to allergic reactions, parasites and radiation exposure.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Photo: k_e_n / freepik.com Gastritis goes through several stages in its development. Initially, when exposed to unfavorable factors, the gastric mucosa turns red and swells. As the disease becomes chronic, the stomach wall thickens. As the disease progresses, the affected areas of the gastric mucosa become thinner and atrophy. At this stage, the epithelial cells of the stomach are replaced by connective tissue cells (scars appear). At the last stage, erosions and ulcers appear.
Important! Since advanced stages of gastritis are fraught with the appearance of erosions and ulcers, it is important to begin treatment measures as early as possible. This will stop the pathological process and avoid complications.
Depending on the nature of the course and etiological factors, different types of gastritis are distinguished.
According to the nature of the flow:
- Acute - develops suddenly, for example, with an allergic reaction, alcohol abuse or poisoning. The acute form of the disease is characterized by severe pain, heartburn and nausea. A characteristic feature of acute gastritis is its transience. With proper treatment and timely elimination of the unfavorable factor (allergen, alcohol, toxins), the disease goes away within a few days.
- Chronic - develops slowly and has mild symptoms. A person may not be aware of chronic gastritis for years, which makes it more dangerous than acute gastritis.
Man with stomach pain.
Photo: drinkins / freepik.com According to the nature of inflammation:
- Erosive - characterized by the appearance of erosions on the gastric mucosa. This is one of the most common types of gastritis. As a rule, it develops in adults and very rarely in children.
- Atrophic is a type of chronic gastritis in which the secretory cells of the stomach atrophy. Thus, the production of gastric juice is reduced, which leads to a number of serious complications, including stomach cancer. Subatrophic gastritis is also distinguished, the clinical picture of which is similar to atrophic gastritis, but less pronounced.
- Catarrhal is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by certain aggressive agents, such as infections, too hot or cold foods, toxins and other damaging factors. Catarrhal gastritis occurs in both acute and chronic forms. The development of a chronic form can be avoided if treatment is started on time.
- Superficial - represents the initial stage of inflammatory damage to the stomach. This is the most favorable stage of gastritis, which is easier to treat than others.
By localization:
- Antral - localized in the pyloric part of the stomach, where the hormone gastrin is secreted, which stimulates the production of gastric juice. With antral gastritis, gastrin synthesis increases, which leads to increased secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Increased feeling of hunger
Diabetes
Thyrotoxicosis
48109 August 25
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. The feeling of hunger is an expression of the body's need for nutrients. The formation of feelings of hunger occurs due to the mechanisms of hormonal and neuro-reflex regulation. The food center is a complex complex, the central link of which is the nuclei of the hypothalamus, located in the diencephalon. When these nuclei are irritated, a feeling of hunger occurs, and when they are destroyed, a refusal to eat occurs.
Types of increased hunger
An increased feeling of hunger may occur for natural reasons, or may not correspond to objective indicators of satiety.
Hunger, like any feeling, is subjective.
True hunger
is caused by a lack of nutrients (glucose, amino acids, fats) and occurs with prolonged emotional stress and intense exercise.
However, modern man suffers much more often from false, psychological hunger
.
Psychological hunger has as many varieties as human habits. For example, having gotten used to eating at a certain time, a person consumes food regardless of the presence or absence of true hunger. The same applies to the habit of eating while watching TV or reading. The need for rest after hard work sometimes makes a person think about food. Boredom or, conversely, the desire to have a holiday - all this is realized through the feeling of hunger. However, there is also constant pathological hunger
caused by an imbalance of hormones or a violation of neuro-reflex regulation due to certain diseases.
Possible causes of increased hunger
The reasons for the constant feeling of hunger may be due to the lack of substances in the blood that have an inhibitory effect on the food center, for example, glucose. For diabetes
due to a lack of insulin or tissue resistance to this hormone, glucose cannot enter the cells. Lack of glucose in cells causes excitement in the food center and a feeling of hunger. However, eating a new portion of food when insulin levels are low does not lead to satiety.
At the same time, obesity develops, which increases insulin resistance and aggravates the disease.
With
thyrotoxicosis,
increased metabolic processes lead to muscle atrophy, causing weakness and increased sweating.
Trying to satisfy their increased appetite, patients with thyrotoxicosis eat a lot, but do not gain weight, but rather lose weight.
Due to the activation of peristalsis, defecation becomes more frequent. Hormonal shifts lead to the development of neurasthenia and irritability. A characteristic symptom of thyrotoxicosis is tremor of the limbs, which manifests itself at rest and during movement.
Another example of an increase in hunger due to hormonal changes is increased appetite during pregnancy.
. Pregnancy causes an increase in the concentration of estrogen in the blood, which, reaching the pituitary gland, triggers the production of prolactin.
This hormone promotes appetite growth and leads to the replacement of adipose tissue of the mammary glands with glandular tissue.
After childbirth, prolactin interferes with the secretion of progesterone, which prevents another pregnancy.
Increased secretion of prolactin occurs with the growth of prolactinoma
, a benign tumor of the pituitary gland, as well as in response to taking
antipsychotics, antiemetics, and hormonal contraceptives
.
Another hormone that causes hunger is ghrelin
, which is produced by ghrelin-producing cells in the stomach. Entering the blood, it affects the food center of the brain, inducing hunger. This hormone also has a stimulating effect on gastric motility and peristalsis. As body weight decreases, ghrelin secretion increases. Stretching of the stomach walls after eating leads to a decrease in ghrelin secretion. This hormone has an antagonist, leptin, which affects fat metabolism and suppresses appetite. With low leptin levels, morbid obesity develops in the presence of a number of genetic diseases.
Obese patients are characterized by high concentrations of leptin in the blood. But the cells become resistant to this hormone, and the feeling of hunger does not go away.
At night, leptin secretion increases, which allows a person to sleep without feeling hungry.
The feeling of hunger can be triggered by increased acidity of gastric juice. An acidic environment is necessary to denature large protein molecules, ensure the functioning of gastric juice enzymes, and neutralize pathogenic microorganisms that enter the body with food. However, when acid affects the esophagus, the fornix of the stomach and the anterior wall of the duodenum, where there should be a neutral environment, heartburn and hunger occur. Eating suppresses this condition, but after a while the unpleasant sensations resume. With prolonged exposure to hydrochloric acid on the gastric mucosa, erosions are first formed, which, if left untreated, develop into an ulcer.
With increased acidity of the stomach, the patient experiences, in addition to heartburn, aching pain in the epigastric region and sour belching.
In addition to hormonal and secretory reasons, increased feelings of hunger are caused by neuropsychiatric diseases.
For example, patients with Parkinson's disease
lack control over food intake. They often eat at night, consuming significantly more than their needs.
Bulimia, an eating disorder, is widespread among adolescents and young girls. It is caused by a pathological fear of obesity and is accompanied by constant thoughts about food.
Patients with bulimia cannot stop themselves from overeating and consume excessive amounts of food.
After an episode of overeating, they either induce vomiting or take laxatives and diuretics.
Causes of increased hunger include the effects of low-energy diets
. Lack of food is accompanied by a decrease in blood glucose levels, which causes a feeling of hunger.
With a rational and long-term refusal of high-carbohydrate foods, the body changes metabolic processes, switching to energy sources such as fats and hard-to-digest carbohydrates. With intermittent dieting, the body experiences metabolic stress. Nutrients accumulate for future use, and in the absence of a diet, the body requires more calories than necessary, which is accompanied by a constant feeling of hunger.
Which doctors should I contact?
If hunger occurs soon after eating, you need to find out its cause. You should first visit to make a diagnosis. In case of hormonal imbalances or pregnancy, the therapist will refer the patient to a gynecologist-endocrinologist. If you suspect gastrointestinal disorders, you should contact. If psychological or neurological problems are identified, consultation with a neuropsychiatrist or. Hunger, as a diet companion, is almost inevitable. However, it is advisable to regulate body weight based on the recommendations of a nutritionist.
Diagnostics and examinations
An increased and constant feeling of hunger can serve as a symptom of disease. Therefore, you should definitely take a general urine and blood test.
Nutrition rules for gastritis
Nutrition is one of the most important elements in the successful treatment of gastritis. A diet for gastritis is prepared by a doctor depending on the type of gastritis, its stage, the general health of the patient, his age and a number of other characteristics.
There are several important nutritional rules for gastritis that must be strictly followed. The main rule is to chew food thoroughly. The digestion process begins in the oral cavity, where food is crushed and partially digested by enzymes. If unchewed food enters the stomach, it can irritate the mucous membrane.
With this pathology, you need to give up dry food. You need to be careful with crackers, dried fruits and other hard and dry foods to avoid irritation of the gastric mucosa. Food should be soft and warm.
Diet
In case of inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, the diet is extremely important - the number of meals and the time of consumption. Forget about 2-3 meals a day. If you have gastritis, you can’t eat so rarely. The doctor will recommend eating at least 5 times a day. This means that, in addition to breakfast, lunch and dinner, there will be at least 2 more meals. These could be small snacks. It is important that with gastritis there is no strong feeling of hunger. There must be food in the stomach, otherwise the acid will eat away the stomach lining. When eating 5-6 meals a day, it is important to monitor the caloric content of food - it should not be excessive.
It is best to eat at the same time every day. Compliance with the diet normalizes the secretion of gastric juice. The body will know when a person usually eats and prepare accordingly. At the same time, the composition (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) of the food should be approximately the same. In other words, if a person eats eggs in the morning, then it would be best not to break this habit.
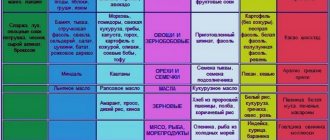
Figure 1. Reminder about gastritis - causes, causative agent and main symptoms. Source: MedPortal
Daily diet: menu for the week
All diets for gastritis have much in common. However, there is a difference between dietary nutrition for acute and chronic gastritis. Let's look at these features.
In the acute course of the disease, on the first day a person has almost no appetite due to pain and nausea. On the first day of acute gastritis, it is better to abstain from eating. Warm drinks (water, tea) are allowed.
Already from the second day, with acute gastritis, the patient is shown table No. 1A. This diet allows liquid foods, mashed potatoes and meat, soup with cereals, milk soups, soft-boiled eggs, as well as jelly, jelly and honey. All food is boiled or steamed. Such food will cause the least problems for the gastric mucosa.
In acute cases, raw vegetables and fruits, meat broths, baked goods, sweets, cheese and coffee are not recommended. You should limit your salt intake (table salt increases the secretion of gastric juice), or it is better to avoid it altogether during the treatment period. You should also not eat spices, hot or sour foods. Food should be neutral in taste.
Dietary food for gastritis. Photo: yuliyafurman / freepik.com
Sample menu for the week:
- Breakfast - thin porridge with butter. All types of porridges are allowed, except millet.
- Snack - cottage cheese.
- Lunch - cutlets with stewed vegetables, compote.
- Snack: soft-boiled egg.
- Dinner - steamed fish, tea.
- Before bed - a glass of milk.
As a rule, such a menu for gastritis needs to be maintained for several days while the acute period of the disease lasts. After the situation has stabilized, you should not cancel the diet menu. Your doctor will help you create a further diet and menu based on the dynamics of your recovery.
As for chronic gastritis, the menu is selected depending on a number of factors, such as acidity (high or low), as well as the type and stage of gastritis. Read more about nutrition for various types of gastritis below.
Prohibited and permitted foods for gastritis
The table provides general recommendations regarding permitted and prohibited foods for gastritis. Often, with gastritis, it is not the product itself that is prohibited, but the method of its preparation. For example, there is no ban on meat. The only condition is that meat and fish must be steamed or boiled. The same condition applies to eggs - soft-boiled or hard-boiled eggs are allowed, as well as steamed omelettes.
| Allowed for gastritis | Prohibited for gastritis | |
| Bakery products | Dried wheat bread, crispbread, crackers and savory cookies. Moisten the previously indicated products in a drink (for example, tea) or chew well to avoid injury to the mucous membrane. | For gastritis, it is not recommended to eat fresh bread and any pastries. |
| Porridge and pasta | For gastritis, it is best to eat oatmeal, rice, buckwheat or semolina porridge. Grind the cereal first. | Pearl barley and millet. Also, if you have gastritis, you should not eat pasta made from whole grain flour. |
| Vegetables | Only stewed and boiled vegetables. It is also allowed to bake vegetables, but you need to remove the crust before eating. Potatoes, beets, pumpkin, carrots, zucchini, cauliflower, and broccoli are allowed. | Fresh vegetables and legumes are prohibited. |
| Fruits | You can eat bananas, as well as baked apples and pears. Compotes, jelly and jellies are allowed. | All sour fruits and berries - apples, kiwi, citrus fruits, pineapple and others. |
| Meat and fish | For gastritis, it is advisable to eat dietary meat. This is lean turkey, chicken or beef. Boiled or steamed meat is allowed. The same rules apply to fish. | Fatty meats. Fried, smoked meat and fish. |
| Dairy | It is allowed to consume milk and dairy products whose fat content does not exceed 1.5%. | Milk and all dairy products whose fat content exceeds 1.5%. |
| Eggs | For gastritis, you can eat no more than 2 soft-boiled or hard-boiled eggs per day. You can also cook an omelette, but only steam it. | Fried eggs should not be consumed. It is not recommended to eat more than 2 eggs per day. |
| Sweets | Fruit marshmallows, marshmallows and honey can be allowed in small quantities. Low-fat ice cream (up to 3-4% fat content), low-fat curd soufflé and sucking sweets are also allowed (in the absence of an acute phase of gastritis). | Fatty sweets are prohibited - chocolate, fatty ice cream (more than 4% fat), cakes (especially with a lot of butter) and others. |
| Butter and vegetable oil | Butter and vegetable oils are allowed, but not more than 20 grams per day. | It is not recommended to consume more than 20 grams per day. It is important to consider the oil content in prepared dishes. |
| Mushrooms | — | All types of mushrooms are prohibited. |
| Spices and seasonings | — | Completely excluded from the diet. |
| Beverages | Boiled, still mineral water, weak tea. | Carbonated drinks, coffee, strong tea, as well as cocoa and alcohol are prohibited. |
The information given in the table is valid for most patients with gastritis. At the same time, depending on the type of gastritis and the acidity of the stomach, certain relaxations or tightening of the diet are allowed. Let's take a closer look at examples of diets for different types of gastritis.
Authorized Products
Nutrition for high stomach acidity includes:
- First courses with weak vegetable broth. Finely chopped vegetables and cereals, vermicelli or thin noodles are added to soups. You can prepare milk soups. It is allowed to add dill in small quantities. The degree of grinding of the ingredients was indicated above.
- Vegetables without coarse fiber (potatoes, pumpkin, beets, carrots, zucchini, green peas, cauliflower). They are prepared as a puree with butter, but without adding spices.
- Lean meat (lean pork, beef, lamb, chicken and turkey) in the form of steamed and baked dishes. Before stewing or baking, meat must be pre-cooked to reduce extractive stimulants. You can cook zrazy, meatballs, cutlets, quenelles, meatballs, aspic, beef stroganoff. Eating protein foods is very important because it helps normalize acidity.
- Well boiled or pureed: buckwheat, semolina, oatmeal or rice porridge without hot seasonings and spices. Porridge can be cooked with the addition of milk, you can also use boiled vermicelli or thin noodles, puddings and casseroles with cereals and cottage cheese.
- Soft-boiled eggs or steam omelet, omelet baked with a little butter.
- Lean, chunky and minced skinless fish, steamed or baked.
- Dairy products - milk, calcined cottage cheese, cream (for adding to soup), milk jelly. Mild cheese, cottage cheese dishes (cheese pancakes, puddings, lazy dumplings).
- Sweet fruits with coarse fiber (bananas, strawberries, pears, cherries, blueberries, apples). During an exacerbation, it is better to exclude fruits, then they are introduced in pureed form (mashed potatoes, jelly, jelly, compotes), and vegetables are consumed in heat-treated form;
- Stale white bread, low-fat biscuits and biscuits.
- Fruit juices, tea with milk, rosehip infusion, weak coffee with milk.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Examples of diets for gastritis
The following nutritional recommendations for different types of gastritis allow patients to quickly cope with the painful symptoms of the disease. It is important to strictly adhere to your doctor’s nutritional instructions, since even minor deviations from the diet immediately affect your well-being. When following a diet for gastritis, the patient must adhere to the principles of a balanced diet. This means that the daily diet must satisfy the body in terms of calories, nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), vitamins and minerals. All these issues are discussed with your doctor.
Nutrition during exacerbation of gastritis
For acute gastritis, as well as chronic gastritis at the acute stage, the diet should be as strict as possible. All food is either boiled or steamed. It is prohibited to consume pasta, legumes, fatty meat, and seasonings.
The main task in acute forms of gastritis is to calm the gastric mucosa as quickly as possible. Therefore, all food should be thoroughly chewed and be warm.
Features of nutrition for gastritis with low acidity
With gastritis with low acidity, many restrictions are removed, since there is no danger of increased secretion of gastric juice. For this reason, the consumption of fermented milk products (kefir and yogurt) and weak natural coffee is allowed.
Prohibitions regarding fatty foods and fried foods for gastritis with low acidity remain. Also, with low acidity, you should not eat grapes, fresh baked goods and canned food.
Diet for gastritis with high acidity
Chronic gastritis with high acidity requires extreme discipline on the part of the patient. Sour vegetables, fruits and berries are strictly prohibited. Instead of fermented milk products, it is allowed to consume warm milk and natural non-acidic yoghurts.
For gastritis with high acidity, jelly will be useful, since it protects the stomach from the action of hydrochloric acid. Occasionally, with high acidity, you can afford honey and marshmallows.
Diet for erosive gastritis
With erosive gastritis, special attention should be paid to diet. Severe hunger and long breaks between meals should not be allowed. It is also important to monitor the temperature and texture of the food. When erosions occur, the stomach walls are especially sensitive to hot, cold and sour foods. You should not create additional problems for your stomach; it is important to strictly follow all recommendations.
Diet for atrophic gastritis
For atrophic gastritis, you can eat porridge with a small amount of milk, lean poultry, boiled and stewed vegetables, low-fat chicken broth and dried bread. When choosing a nutrition plan, the doctor must take into account acidity. It is allowed to eat baked vegetables, but only without crusts.
Diet for superficial gastritis
The principles of nutrition for superficial gastritis are practically no different from the general recommendations for patients with gastritis. It is important to avoid hot, cold, sour and mechanically rough foods. Such food irritates the gastric mucosa, only increasing painful symptoms.
Diet for antral gastritis
In case of antral feeding, special attention should be paid to the principles of fractional nutrition. You need to eat in small portions, without overloading your stomach with food. Kefir and yogurt should be excluded from dairy products. You are allowed to drink warm milk (with honey).
Diet for catarrhal gastritis
With the catarrhal form of gastritis, the patient should adhere to the standard nutritional requirements for gastritis. Strictly adhering to dietary recommendations is especially important in acute forms of catarrhal gastritis. This will help prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
Fruit diet
Doctors categorically do not recommend moving away from nutritional therapy for gastritis. This is especially true for special diets for weight loss. The fruit diet is no exception, which many use to combat extra pounds.
A fruit diet is dangerous for gastritis, primarily due to the abundance of organic acids contained in fruits. This is an additional irritation of the gastric mucosa, which will only worsen the course of the disease. A fruit diet is especially dangerous for acute gastritis and exacerbations of chronic forms of the disease. Doctors strongly do not recommend this kind of diet during acute stages. During remission, some relaxations in dietary nutrition are possible, but they also require prior consultation with your doctor.
Diet for gastritis for children
Unfortunately, gastritis occurs not only in adults, but also in children of different ages. The principles of dietary nutrition for adults and children with gastritis are the same. Children should also eat small, frequent meals. Fatty and fried foods should be excluded, and all nutritional recommendations should be followed depending on the acidity of the stomach.
A serious problem in the treatment of gastritis in children is the difficulty of controlling the child’s nutrition. This is especially difficult during school time, when a child can spend his pocket money on junk food. Parents should make an effort and always explain to their child the logic of dietary restrictions.
Figure 2. Basic dietary recommendations for gastritis. Source: MedPortal
Diet for high stomach acidity
A special gentle diet is recommended to improve the digestion process and get rid of the unpleasant manifestations of high acidity of gastric juice. “The diet is aimed at reducing the excitability of the stomach and reducing the acid factor,” says our expert. — The gentle regime includes fractional meals, which promotes good digestion and rapid absorption of food. The degree of sparing and grinding of food depends on the severity of pain and dyspeptic syndromes, so different options for a therapeutic diet may be prescribed. “Everything that stimulates secretion, irritates the mucous membranes and causes increased gas formation is excluded from the menu.”
What not to eat or drink if you have high stomach acidity:
- Mushrooms, coarse vegetables and greens: onions, garlic, radishes, radishes, turnips, beans, peas, white cabbage, rutabaga, sorrel, tomatoes. Salted, pickled and pickled vegetables, canned vegetables. Sour fruits and berries.
- Fatty meat and poultry: fatty pork, lamb, goose, duck. Canned meat, smoked meats, sausages. Products with connective tissue (skin, cartilage, veins).
- First courses with meat, fish and mushroom broth. Cabbage soup, borscht, okroshka. Fatty fish. Smoked, dried fish. Canned fish.
- Cereals: barley, pearl barley, corn, millet. Thick and rough pasta.
- Ready-made sauces: tomato, mayonnaise, mustard. Horseradish, vinegar, spices.
- Fried and hard boiled eggs.
- Animal fats, margarine, cooking fats for deep-frying.
- Rye and fresh bread, butter and puff pastry products.
- Confectionery and sweets: chocolate, ice cream, sweets, cakes.
- Drinks: strong coffee and tea, carbonated drinks, kvass. Alcohol. Citrus juices.
- Fatty, fried and spicy foods.
How to eat if you have high stomach acidity and what foods can reduce stomach acidity?
Depending on the severity of symptoms, the following types of therapeutic diet are prescribed:
No. 1 is the main table, which involves a diet balanced in basic nutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, fats). At the same time, the amount of animal fats and simple carbohydrates is limited. Avoid eating foods that cause fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract. The diet must include protein foods: it helps normalize acidity. Dishes are prepared with the addition of vegetable oils and a small amount of butter. Cooking methods: steaming, stewing and baking. Anyone suffering from high stomach acidity should adhere to this diet constantly to avoid exacerbation. “Compliance with a diet for acid-dependent diseases is one of the most important factors for successful treatment,” says Olga Khafisova. — Nutrition according to this therapeutic diet is aimed at improving the general condition, accelerating the process of regeneration of the mucosa in the presence of ulcers and erosions of the stomach or duodenum, relieving inflammation in the digestive system and preventing relapse of the disease. Therapeutic nutrition according to diet No. 1 helps to normalize the functioning of the stomach and intestines - effective regulation of the motor-evacuation and secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract occurs. A properly selected menu contributes to the effectiveness of complex therapeutic measures and permanent normalization of digestion.”
No. 1A is the most gentle diet, which is prescribed for severe exacerbation. Includes only boiled, pureed and liquid dishes: slimy soups, porridges, meat puree. Vegetables and fruits are prohibited.
No. 1B - the diet is recommended during the period of improvement after an exacerbation. It is also recommended to wipe dishes, but their consistency may be thicker. The menu includes purees made from soft vegetables, as well as soufflés made from meat and fish.
Pevzner tables for gastritis
Manuil Isaakovich Pevzner is a famous Soviet therapist, one of the founders of dietetics in the USSR. Known primarily for the development of special diets for groups of diseases. The Pevzner diet includes 15 therapeutic nutritional regimens, each of which is used for a particular disease or condition.
For constipation, tables 1 and 2 according to Pevzner are recommended. The first table according to Pevzner is used for gastric ulcers, as well as for gastritis with low acidity. Table No. 2 is nutrition for chronic gastritis with low acidity and chronic colitis.
The general principles of nutritional schemes for tables 1 and 2 according to Pevzner correspond to the above nutritional requirements for gastritis.
First table according to Pevzner:
- It is allowed to eat dried and stale wheat bread. Baking from yeast-free dough is acceptable.
- You can eat vegetable and milk soups with the addition of cereals (except millet). You need to prepare soups with ground ingredients.
- Avoid consumption of fatty meats.
- Eating cabbage is not allowed.
- Sour vegetables and fruits are excluded.
- You can include low-fat varieties of poultry and fish in your diet.
- It is permissible to use jam and jam in small quantities.
- The use of vegetable oil (preferably olive) is allowed.
Important! The first table according to Pevzner excludes the consumption of canned food. This is not only canned fish or meat, but even home canned food (including vegetables).
Second table according to Pevzner:
- Dried or stale bread is allowed, except black bread. Yeast-free baking is allowed.
- You can eat vegetable soups with cereals.
- Low-fat varieties of poultry, meat and fish are allowed. Meat and fish dishes should be prepared by boiling, baking or steaming.
- Porridges made from well-cooked cereals are allowed.
- The consumption of fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt) is allowed.
- You can eat boiled vegetables, except radishes and sweet peppers.
- Drinks allowed are compotes, jelly, weak tea, and weak natural coffee.
Important! As with the first table, try to grind the food. Dishes should be warm - comfortable for the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
For some patients with gastritis, doctors also prescribe table No. 5 according to Pevzner. This diet plan is intended for diseases of the liver, gall bladder and biliary tract. If gastritis occurs against the background of diseases of the liver and gallbladder system, then this imposes some additional restrictions. For example, with gastritis against the background of liver and gallbladder diseases, there are more stringent restrictions regarding fatty foods, including eggs, butter and vegetable oils.
Forecasts for recovery from gastritis
Prognosis for gastritis largely depends on the patient himself. The lion's share of success is diet. Therefore, it all depends on how conscientiously the patient adhered to the therapeutic diet.
Whether a person can get rid of gastritis forever depends on the root cause of the disease. For example, infectious gastritis can be completely cured. This requires only competent antibacterial therapy. But gastritis of an autoimmune nature is still incurable. In this case, the patient needs to monitor his health throughout his life, control both the immune system and adhere to a special diet.
Prognosis for recovery from gastritis depends on the nature of the course and type of disease. As mentioned above, acute gastritis is much easier to treat. As for chronic forms, much depends on the type of gastritis. For example, atrophic gastritis is considered one of the most complex and dangerous, since with this type of gastritis part of the glandular tissue of the stomach atrophies.