General rules
Diseases of the digestive system occupy third place in the structure of morbidity among adults.
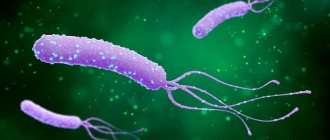
Chronic gastritis develops due to errors in diet (eating poorly chewed, coarse and very spicy food), the presence of Helicobacter pylori, bile acids in gastric contents, prolonged neuropsychic stress, occupational hazards, smoking and alcohol abuse. Currently, “chronic gastritis” is considered as a concept that includes inflammatory and dystrophic changes in the gastric mucosa. In practice, the diagnosis of chronic gastroduodenitis is made by endoscopic examination.
Its main forms include superficial (catarrhal) and atrophic. This division means the preservation or loss of glands, which has functional significance. A number of classifications include an intermediate form - subatrophic, meaning beginning atrophy of the glands.
Depending on the prevalence of altered cells and the depth of penetration of inflammation into the thickness of the mucosa, non-atrophic gastritis is divided into mild, moderate and severe gastritis. The inflammatory process can cover the mucous membrane of the entire stomach ( pangastritis ) or some part of it, then focal gastritis .
Atrophic gastritis is characterized by changes in cells of a dystrophic nature, a decrease in the number of glands and inflammation of the mucous membrane similar to that of severe superficial gastritis. Depending on the decrease in the number of glands, moderate and severe degrees of atrophy are noted. In 50% of cases, this form of gastritis is combined with restructuring of the mucosa (metaplasia of the fundic glands, intestinal metaplasia , epithelial dysplasia ). A true precancerous change is considered to be epithelial dysplasia, which comes in three degrees.
In addition to the main forms of gastritis, its special forms are also distinguished: hyperplastic (“warty”, polypous), hypertrophic , granulomatous , hypertrophic , collagen and others. Focal mucosal hyperplasia is considered to be the earliest form of polyp. When bile is thrown into the stomach under the influence of bile acids, severe inflammation, metaplasia, gland atrophy and focal hyperplasia develop.
H. pylori infection causes the most severe forms of the disease. Thus, most often the infectious factor is detected in the erosive and hypertrophic form, somewhat less often in subatrophic, atrophic and superficial gastritis. In persons with a long history of the disease (17-20 years), a reduced level of acidity is more often determined, and normal or increased acid formation is observed for a shorter period.
Symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of the disease are nonspecific and varied. Patients are concerned about the appearance of pain and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, distension and fullness of the stomach or a feeling of hunger after eating, a burning sensation in the epigastric region and premature satiety, bloating after eating, heartburn, belching, nausea , vomiting , drooling, regurgitation of food, loss of appetite.
Hemorrhagic gastritis is one of the most severe injuries, accompanied by the formation of multiple erosions and manifested by bleeding. Patients experience vomiting in the form of “coffee grounds” and tarry stools. With excessive blood loss, loss of consciousness occurs and anemia . The most common cause of this form of gastritis is long-term use of glucocorticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of gastritis is aimed at eliminating all factors that provoke exacerbation of the disease. In the first place are drugs that reduce gastric acidity - H2 blockers , but currently proton pump inhibitors are widely used, since they are 3-10 times H2 blockers
When Helicobacter pylori is detected, it is eradicated using a 3-component treatment regimen ( De-nol in combination with two antibiotics or proton pump blockers in combination with two antibiotics). If these regimens are ineffective, quadruple therapy is performed (bismuth drug, PPI and two antibiotics).
In parallel, to prevent dysbiotic changes in the intestines, complex probiotics ( Bifiform , Linex ) are prescribed, containing antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms and populating the intestines at different levels. Antacid drugs ( Phosphalugel , Almagel ) have little effect on the pH level, but are used as coating agents that increase the resistance of the mucous membrane to the effects of hydrochloric acid and pepsin . If motility is impaired and gastric contents are evacuated, prokinetics are prescribed ( Motilium , Motorix ). For reflux gastritis, it is advisable to take Magalfil 800 (four to six tablets per day), the binding capacity of which for bile acids is not inferior to cholestyramine .
For symptoms of gastritis, diet treatment is of great importance, since dry food, irregular and irrational nutrition, consumption of excessively cold or hot food and large amounts of spices cause exacerbation of gastritis. For many decades, with this disease, it has been recommended to follow a diet, as with a peptic ulcer .
Is a strict diet necessary for gastritis? Despite the fact that recently they are moving away from strict restrictions in the diet even with peptic ulcer disease, nevertheless, food, especially during an exacerbation, should not contain irritating substances. A gentle diet is recommended, and the degree of sparing depends on the severity of the exacerbation. In addition, the composition of the diet depends on the condition and acid-forming function of the stomach.
For those who have gastritis with low acidity, Diet number 2 , which provides for moderate stimulation of the secretory function of the stomach and includes juice products and dishes. Allowed:
- First courses with low-fat meat/fish/mushroom broth, rassolnik with pureed vegetables and cucumber brine.
- Porridge with water or meat broth (excludes millet and pearl barley).
- Boiled and stewed vegetables - potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower and cabbage.
- Salads from ripe tomatoes, salads from boiled vegetables (excluding fresh onions, sauerkraut and pickles), vegetable caviar, herring and mincemeat.
- Kefir, yogurt, curdled milk and other fermented milk drinks, sliced or grated cheese, omelet with cheese.
- Heat treatment in the form of frying without the formation of a rough crust and stewing, which stimulates the production of gastric juice.
- Ripe, unpureed fruits. Oranges and lemons (in tea), tangerines, watermelon, grapes.
- Sauces based on meat broths, jellied dishes using broths.
- Tea with lemon, vegetable juices, coffee and cocoa, fruit juices (all juices diluted).
For these gastritis, foods and dishes with a choleretic effect are also prescribed: vegetable oils, beets and beet juice, lemons and lemon juice, melons, watermelon, avocado, turmeric, fresh herbs, rose hips, dandelion leaves and root. Restrictions (pea, bean soup, okroshka, millet soup, fatty coarse meat, salted, smoked fish, canned food, hard-boiled eggs, corn, pearl barley porridge, raw vegetables) are necessary only during the period of exacerbation, and as it improves and during the period of remission, nutrition must be complete.
At the same time, the following are excluded: fresh bread, pastries, pastry products, legumes, okroshka, millet soup, fatty meat and poultry, smoked meats, fatty fish, salted and smoked fish, legumes, millet, corn, pearl barley, barley, raw vegetables, pickled vegetables, onions, radishes, radishes, cucumbers, rutabaga, sweet peppers, garlic, mushrooms, very spicy snacks, mustard, pepper, horseradish.
For hyperacid gastritis (high acidity), Table No. 1 and its varieties are recommended. Diet 1A is sequentially prescribed for up to 10 days, then 1B and No. 1 (up to two to three months). The diet includes neutral dishes that have a weak juice effect: milk, eggs, boiled meat and fish, milk porridge, sweet fruit juices. In addition, split meals in small portions are recommended. The absence of strong irritants in food creates the conditions for effective treatment. The main principles are:
- Exclusion of foods that increase secretion (spicy, pickled dishes, rich broths, mustard, alcoholic drinks, smoked and fried foods, coffee, tea, carbonated drinks).
- Exclusion of irritating foods (cranberries, tomatoes, garlic, onions, citrus juices, sour fruit juices, peppers, chocolate, turnips, radishes, alcohol, ginger) and foods that increase gas formation (cabbage, legumes, kvass, beer).
- Increasing protein intake and reducing fat in the diet (fatty pork, cream, butter, goose, duck, cakes and other baked goods with cream, animal fats, lamb).
- Reducing the amount of food consumed (no more than 200 g at one time).
- Frequent meals (up to 6 times a day).
- Eating food warm, excluding cold dishes and excessively hot ones that irritate the mucous membranes.
- Using boiling, stewing and baking in cooking.
- Exclusion of foods that do not combine (proteins and carbohydrates) to avoid rotting and fermentation.
- Inclusion in the diet of potato juice, bananas, oat decoction, sweet apples (first baked, later fresh).
In general, dietary nutrition should be followed for 1-3 months. Table No. 1 is complete and physiologically balanced (proteins up to 90-100 g, carbohydrates 300 g, fats 100 g). Gradually, the diet expands to what is familiar to each person, but spices, spices, spicy foods, pickles, smoked foods, canned food, and fatty foods (meat and fish) are definitely excluded. The further course of gastritis depends on the patient’s attitude towards his health, compliance with preventive recommendations and discipline regarding food intake and medications.
Eliminating bad habits and correcting lifestyle is of no small importance. Previously used seasonal therapy is now rarely used. But in the presence of provoking factors (business trips, exams, mental stress), it is advisable to change your usual diet and switch to a dietary diet.
Diet table
Among the various therapeutic diets in the Pevzner classification, there is table No. 1, which is used as food for high acidity of the stomach. It is prescribed to treat hyperacid conditions, relieve pain, eliminate heartburn, and has options indicated for varying degrees of gastric damage. Some dietary principles need clarification.
No ads 1
Excluding secretion stimulants means a categorical ban on eating foods that increase acid formation in the stomach:
- rich broths of fish, meat, mushrooms, cabbage;
- all types of alcohol (including medicinal tinctures);
- salted, smoked, pickled food;
- vegetables with coarse fiber;
- hot seasonings, ketchups, mayonnaise;
- rye bread;
- carbonated and sour drinks.
The stomach sparing regimen involves:
Menu for gastritis with high acidity
- frequency of meals at least six times a day;
- reduced portions;
- avoiding overeating;
- sufficiently crushed and pureed food;
- exclusion of hot and cold foods, maintaining a feeding temperature of about 38 degrees;
- Among the methods of culinary processing, only boiling, steaming, and baking without crusts are allowed.
In addition, the incoming food should consist of easily digestible components and should not allow a long delay in the stomach for digestion, therefore, if you have high acidity, you should not eat fried and fatty meat dishes.
The diagram shows the acid-base reaction of food products; in a hyperacid state, it is necessary to select only alkalizing properties
Authorized Products
The therapeutic diet includes:
- Low-fat soups made from oatmeal, semolina, buckwheat, and rice in vegetable broth or water. First, soups are pureed, and when the condition improves, soups with finely chopped vegetables and well-cooked and mashed cereals are allowed. It is possible to prepare puree soups with the addition of boiled chicken or beef. To improve the taste, you can add cream, egg-milk mixture or butter, meat puree, a small amount of dill or parsley to soups.
- Wheat bread, thinly sliced crackers made from premium flour, not very browned.
- Savory buns, baked pies (with cottage cheese, apples, boiled meat, jam).
- Lean meat and poultry (beef, young lamb, lean pork, chicken, turkey are recommended). They prepare steamed and boiled dishes from minced meat (souffles, cutlets, meatballs, zrazy, quenelles). As the process subsides, lump meat baked in the oven is allowed.
- For second courses, you can prepare mild homemade sauces based on milk or cream.
- Fish in the form of cutlets, meatballs and quenelles, which are prepared from pike, hake, cod, pollock, ice fish and blue whiting. Fish or meat dishes are present in the diet twice a day.
- Potato, carrot, zucchini, pumpkin puree with cream and butter, vegetable soufflé from the same vegetables, green peas. Dill and parsley are added to dishes.
- Buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina, rice. Prepare pureed or well-cooked porridge with milk and butter.
- Milk, fresh cottage cheese (with added milk), cottage cheese soufflé, baked cheesecakes, lazy dumplings, milk jelly. Cream is added to soups, mashed potatoes and tea. Milk is allowed to drink up to 600-800 ml.
- Eggs (2-3 pieces per day) soft-boiled or steamed omelet, they are added to soups and other dishes.
- Processed berries (jelly, jelly, mousse). They cannot be consumed fresh. Apples baked with honey and sugar.
- Butter 20 g per day and vegetable oil are used as additives in ready-made dishes.
- You need to follow a drinking regime and consume 1.5 liters of liquid. This can be a decoction of wheat bran, weak tea with milk, diluted berry juices, carrot juice, filtered water, rose hip infusion.
- Caramel, meringues, meringues, jam, milk jelly, honey, sugar, marshmallows, marshmallows.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The gastrodiet provides an exception:
- Any broths, fried and spicy foods, animal fats, fatty fish and meat, smoked meats, any snacks, pickled and pickled vegetables, bird skin, fish, cartilage.
- Raw berries.
- Millet, barley, pearl barley, corn cereals.
- Fermented milk drinks, sour cream.
- Mushrooms (as a difficult-to-digest product), onions, garlic, radishes, radishes, legumes, white cabbage.
- Strong tea, coffee, carbonated drinks, kvass, undiluted fruit juices from sour fruits.
- Sauces, vinegar, ketchup, mayonnaise, pepper and spices.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet menu for gastritis of the stomach (Diet)
The dietary menu of Table No. 1 has been expanded in terms of products, as well as cooking methods (baking is added). The food is quite varied and complete. Some vegetables are included and the list of cereals is expanded, so you can create a menu that takes into account the daily alternation of protein and cereal dishes.
Preference is given to dairy products, since meat and fish protein is difficult to digest compared to milk and chicken egg protein. The choice of meat and fish dishes is wide - cutlets, quenelles, souffles, zrazy, lump meat and beef stroganoff; a multicooker can help in preparing them. Eggs and cottage cheese are introduced into the diet every day.
Proper nutrition for gastritis (weekly menu) may look like this:
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Menu (Power Mode)
Sample diet menu for acute gastritis for 10 days:
First day
| Complete fasting |
|
Second day (Diet 1A)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Third day (Diet 1A)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Fourth day (Diet 1A)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Fifth day (Diet 1B)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Before bedtime |
|
Sixth day (Diet 1B)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Seventh - tenth day (Diet No. 1, not pureed)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
A diet for acute gastritis is prescribed for 21 days, but its duration can vary depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, complaints, and objective examination data. At the same time, the length of time spent on one type of diet or another is determined individually.
Example of a diet menu for acute gastritis with low acidity, starting from 7-10 days (Table No. 2)
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
The diet menu for hypoacid gastritis includes first courses (soup, borscht, pickle), which are prepared in low-fat, weak meat/fish, mushroom, vegetable broth with the inclusion of potatoes, cereals, and vegetables.
Second courses include boiled, fried, baked lump meat, fish, cutlets, baked pancakes with meat.
Boiled and baked pieces in the form of casseroles and mashed vegetables (potatoes, carrots, white cabbage, zucchini, beets, pumpkin, cauliflower, green peas). The diet includes fermented milk products, cottage cheese, cream, fruit and vegetable juices (diluted with water), bran decoctions, ripe pureed fruits and berries.
Recipes for gastritis
Recipes for dietary dishes for gastritis differ during different periods of the disease. Mucous dietary soups are consumed during periods of severe exacerbation and pain. They are simple decoctions of long-cooked cereals (usually rice, oatmeal or buckwheat). The broth is filtered, and the cereal is removed without rubbing. The strained broth is slightly salted, and to add nutritional value and taste, it is seasoned with an egg-milk mixture and boiled. You can add cream and butter.
Milk soups are widely used in Tables 1A and 1B . Usually these are cereal soups cooked in water and milk (1:1). The cereals are cooked until tender, pureed, and then milk is added and brought to a boil. Milk soups have a sweetish and at the same time slightly salty taste, since they are lightly salted.
Puree soup is the basis of a diet for gastritis
The basis of the first table is pureed soups. They are boiled with cereals, adding potatoes and carrots, the well-cooked ingredients are pureed and oil is added. For second courses, cooking (steamed or in a water bath) is preferable. When cooking with steam, the product being cooked is on the grill and does not come into contact with the boiling liquid, so the loss of all substances is minimal. Cooking in a water bath is carried out in a container that is lowered into another container with hot water. Cooking takes place at a temperature of 40-700. This way you can prepare omelettes, puddings, sauces, and egg porridge.
The meat is boiled in small pieces (this removes as much extractive substances as possible from it), then the broth is drained, and the meat is cooked in new water. Ready meat is used for stewed and minced dishes. Below are recipes with photos.
First meal
Slimy rice soup with cream and minced chicken
Beat the boiled chicken fillet in a blender; if necessary, wipe it additionally. The resulting puree is mixed with slimy rice water, salted and boiled. After cooling the soup to 70°C, pour in the egg-cream mixture and beat well.
Creamy squash soup with dill
Boil zucchini and potatoes and blend in a blender. Bring to the desired consistency with vegetable broth, add salt, add cream and finely chopped dill.
Second courses
Turkey cutlets
Made from raw turkey meat. Add salt, butter, and wheat bread soaked in milk to the prepared minced meat. Knead thoroughly, form cutlets and steam.
Egg porridge
Beat eggs with cream, add salt. Pour the whipped mass into the mold and place it in a container with water. Cook while stirring until done.
Dessert
Curd soufflé
Beat cottage cheese, semolina, milk, cream and yolks. Add the whipped whites and mix gently. The resulting air mass is placed in a mold and steamed.
Rice pudding with apples
Cook rice porridge, add grated apples, yolk and sugar. Beat the mixture and add the pre-whipped whites. Place in molds and steam for at least 30 minutes. Pour fruit jelly over the finished pudding.
WEDNESDAY
Breakfast: milk buckwheat porridge in a slow cooker
Lunch: hake soup (do not fry vegetables); risotto with pumpkin and baked veal (excluding frying and garlic)
Afternoon snack: zucchini stewed in sour cream
Dinner: casserole of zucchini and carrots (bake in foil so that it turns out without a thick crust) + chicken cutlets (steamed)
Nutritionist's comment:Try to bake so that a dense crust does not form; it can irritate the walls of the stomach and cause discomfort. |
Comments from nutritionists
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is important for patients to switch to a diet that excludes strong secretion stimulants and irritants. Therefore, it is important to know the following.
Mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane is caused by:
- large meals;
- a large amount of coarse fiber - they contain radishes, beans, turnips, radishes, bran bread, gooseberries, grapes, currants, dates, raisins;
- stringy meat, animal cartilage, poultry and fish skin.
Chemical irritation is caused by:
- sour foods (kefir, whey, yogurt), sour unripe fruits;
- broths, infusions of vegetables and mushrooms, spices, canned food, fried foods, smoked meat and fish products, pickled, salted and pickled vegetables, tomato sauce, stewed meat and fish, hard-boiled eggs, rye bread, butter dough, heat-treated edible fats ;
- strong tea, carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol, raw vegetables (especially onions, garlic, radishes, radishes) and fruits.
Thermal effects are caused by very cold or hot food.
A gentle regimen, in addition to eliminating irritants, also provides for regular and small meals, which facilitates the digestion and absorption of food. Preference is given to foods that are quickly evacuated from the stomach - these are mushy and liquid dishes.
Taking into account all of the above, the patient’s diet during an exacerbation should include warm, non-rough, pureed dishes that have a weak juice effect. These are milk, eggs, milk porridge, boiled fish, minced meat, steamed.
Is it possible to fast with this disease? There is no clear answer. The positive effect of this treatment method is noted, but not always. Most foods significantly increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid; even just the entry of food into the oral cavity causes a reflex to release gastric juice. When fasting, these two factors influencing acidity are eliminated at once. Therefore, you can count on its reduction. The digestive system reduces the production of not only gastric juice, but also saliva, bile, and pancreatic enzymes. Peristaltic movements of the intestines are also reduced.
One of the signals about the need for food fasting is lack of appetite. The greatest effect of treatment is observed during the period of exacerbation, if fasting for 3-5 days is combined with the subsequent consumption of light foods. To achieve the effect, fasting is combined with water procedures and daily cleansing enemas. At the same time, decay products and toxins leave the body faster. On the other hand, therapeutic fasting reduces the body's vital resources. It should not be used for anorexia and severe weight loss, against the background of antibacterial, Helicobacter eradication and in pregnant women .
Hunger should not begin with a complete lack of food; first you need to switch to light foods, for example, kefir (during the day, in 5 meals, you can eat 900 ml of kefir, 200 g of cottage cheese, one apple). Such kefir fasting days are carried out for 2-3 days in a row, and then switch to fasting.
It can be performed in two versions - dry fasting (even drinking water is prohibited). The second option is to drink boiled or mineral degassed water. On the second day, you can drink weak tea. This goes on for 4-5 days. Resumption of nutrition begins with the consumption of rice water and crackers made from wheat flour. Then they switch to liquid, well-cooked oatmeal, rice and semolina porridge, which is boiled in water or with the addition of milk. You can consume cereal decoctions with soups and mucous soups throughout the day. It is prohibited to take fresh vegetables, fruits, and juices.
Today, among scientists there are those who are “for” and “against” separate nutrition for gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases. The debate about its benefits and harms continues. The bottom line is that food is divided into three groups: proteins, fats and carbohydrates, which are consumed separately. The main prohibition is combining starches (cereals, pasta, legumes, starchy vegetables) and animal proteins in one meal. Meat can only be combined with non-starchy and green vegetables. Green vegetables, in turn, are combined with many foods: fats, cereals and proteins. Sugar and confectionery products should be consumed separately from all other foods, otherwise they cause fermentation, causing heartburn and belching . These are the basic principles of separate nutrition.
Proponents of this technique believe that the combined products are absorbed easily and quickly, do not cause rotting or fermentation, and toxic substances do not appear in the blood and intestines. At the same time, digestion and metabolic processes are normalized, overeating is eliminated and weight is normalized.
However, there are no scientifically proven facts about the benefits of this diet. Scientists still believe that mixed nutrition is more natural and beneficial for humans. The principles of separate nutrition contradict the habits and traditions of our national nutrition. Strict adherence to it in everyday life is difficult. In addition, organizing a new diet is accompanied by a feeling of hunger, and mental discomfort can result in uncontrolled gluttony. The choice is yours; if it is possible to organize it and as a result you get good health results, then it is quite possible to adhere to such a diet constantly.
Diet No. 1 can be used for weight loss. Of course, you cannot count on significant weight loss, but limiting fats, carbohydrates, baked goods, as well as steaming or boiling foods will affect your weight. Thus, this is a smart way to lose weight and not cause aggravation of gastritis.
Diet for weight loss with gastritis
Gastritis of any form requires mandatory adherence to a diet. But it does not solve the problem of excess weight in patients with this disease. More often, this problem occurs in women with chronic gastritis, when it is combined with problems of the liver and pancreas.
A diet for weight loss for gastritis has its own characteristics:
- Firstly, patients need to lose weight very carefully, avoiding sudden weight loss. This can have a negative impact on your overall health.
- Secondly, during an exacerbation, it is strictly forbidden to use a diet for weight loss.
In order for the body not to suffer from a lack of nutrients when losing weight, and also to avoid exacerbating gastritis, it is necessary to consume the “right” foods:
- Meat of rabbits, chickens, veal, boiled sea fish, low-fat cottage cheese. These products make up for protein deficiency while reducing the total calorie content of food and its volume;
- Olive oil is a source of vitamin E, necessary in the body's metabolic processes at the cellular level. Since the product is high in calories, it should be consumed in limited quantities;
- Cereals are the main source of B vitamins. They are prepared in the form of boiled porridges, or a slimy consistency. Buckwheat and oatmeal are especially useful, as they not only saturate the body with low-calorie foods, but also restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Fruits and berries of non-acidic varieties are sources of vitamins, organic acids, sugars and antioxidants. They should be consumed after heat treatment, or pureed, without peel.
There are certain recommendations for losing weight with gastritis that must be followed in order to avoid complications of the underlying disease. When choosing a diet for weight loss, you must first calculate the number of foods per day and their total calorie content.
For gastritis with low acidity, the daily calorie requirement for an adult is on average at least 2100 kcal, and for hyperacid gastritis - at least 2700 kcal.
Reviews and results
For people suffering from gastritis, therapeutic nutrition is of great importance. If the history of the disease is long, then patients are well versed in medications and know what diet for gastritis they need at the moment.
Table No. 1 can be prescribed for a long period, since it contains the norm of protein and fat. Compared to varieties, it is expanded in terms of products and methods of processing them. If you are not lazy, you can learn new cooking recipes. Reviews from patients indicate the effectiveness of therapeutic nutrition, its ease of implementation and the possibility of long-term use.
- “... In the hospital, during an exacerbation of gastritis (I was there for the first time), they immediately prescribed Table No. 1 and told me to stick to it for another month. Proper nutrition certainly helps with treatment, and milk, dairy products and cereals with milk also worked for me - they did not cause any pain, bloating, or diarrhea. How could I not love them before? The doctor said to choose milk with low fat content: the lower it is, the lower the risk of “rejection” by the body. At home I cooked everything in a double boiler or baked it. In general, I was on it for 2 months because I wanted to lose more weight. And it was successful, although only by 4 kg, but that’s good. Now I have found a diet option for myself both for weight loss and for the stomach, and generally for health”;
- “... I, like many gastritis sufferers, manage without a hospital. Having a long history of illness, I switch to medications (the doctor recommended them 2 years ago) and dietary nutrition. I have a normal attitude towards steamed cutlets, boiled meat without spices, I eat almost all porridges, and in the morning and evening - milk ones, to which I add honey or a little dried fruit. Sometimes you want fried and smoked meats, but you can live without it for 1.5 months. I can say that the main thing for stomach diseases is proper nutrition. I take cutlets or boiled meat with me to work, sometimes soup or porridge. I gave up instant cereals, although it’s convenient at work”;
- “... Signs of an exacerbation, which happens once a year, force us to eat right. Since the exacerbation is not severe, I follow Diet No. 1. I really like milk porridges, and everything dairy in general. I not only eat cottage cheese, but also make casseroles, soufflés and cheesecakes in a slow cooker. I stick to the diet well and it’s not labor-intensive, since my husband has a peptic ulcer and he also sticks to this diet with me for company. So it’s a double benefit, but it’s a little difficult to organize it at work.”