Bariatric surgery, whose world history has crossed the eighth decade, continues to develop rapidly. According to the best bariatric surgeons on the planet, the expression “there is no limit to perfection” could not be more suitable for obesity surgery.
Leading specialists of the Clinical Center for Surgery of Weight and Metabolic Disorders in Moscow, Professor V.V. Fedenko and Dr. V.V. Evdoshenko are bright representatives of the elite of world bariatric surgery. Having started working in this direction back in the 90s of the last century, they improved almost all classical restrictive and malabsorptive interventions, increasing their effectiveness and safety. What remains unchanged is their commitment to minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, in which they are true virtuosos and have performed more than 5 thousand bariatric interventions.
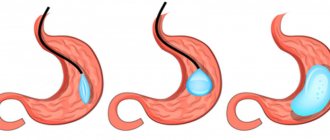
Sleeve gastroplasty in 2021
Sleeve gastroplasty is a restrictive operation. Its essence lies in a sharp reduction in the volume of the stomach by removing its bottom and most of the body. According to its slight curvature, a narrow tube is formed that can accommodate a minimum amount of food. Slowly moving along this “sleeve”, it irritates the receptors that perceive pressure. They send signals to the brain about satiety, as a result a person loses up to 80% of excess weight without suffering from hunger.
Professor V.V. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko has been performing sleeve gastroplasty for about 15 years. However, the disadvantages of its classic version (the risk of suture failure, “sleeve” obstruction, and hiatal hernia formation) prompted them to significantly modify the surgical technique. Today, sleeve gastroplasty performed by them is:
- Absolutely smooth, without contractions or expansions of the gastric “sleeve”;
- preservation of the abdominal (abdominal) part of the esophagus;
- fixation of the “sleeve” to the ligaments inside the abdominal cavity;
- reinforcement of the staple seam by surface coagulation;
- preventive sutures that prevent the formation of a hiatal hernia.
Gastrobypass surgery in 2021
Gastric bypass, or gastric bypass, is one of the most powerful and popular operations in modern weight surgery. It allows you not only to reliably eliminate up to 90% of extra pounds, but also to cure type 2 diabetes.
Gastrobypass surgery combines:
- restrictive (limiting) mechanism, since the gastric reservoir is reduced to the size of a small pouch cut from the upper part of the lesser curvature of the stomach;
- malabsorptive mechanism, since a decrease in food absorption is ensured by disconnecting up to a third of the length of the small intestine from the process of its digestion.
In the classical version, gastric bypass was an operation with two anastomoses - gastrointestinal and small-intestinal. More than 15 years ago, it was modified into a better version involving the creation of a single anastomosis - the OAGB procedure.
Our surgeons V.V. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko developed several fundamentally new, key techniques that significantly improved the long-term results of gastric bypass surgery. This:
- the formation of a retrocolic anastomosis between the stomach and the small intestine instead of the anterior colon one used before, which threatens complications due to the tension of the small intestinal loop;
- transition from gastrointestinal anastomosis using the “side to side” method to the “end to side” method, which eliminates the reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach;
- the use of smaller templates to form the intestinal tube, which increased the restrictive effect of the operation.
Gastrobypass surgery
This weight loss method is suitable for patients with severe obesity. During the operation, by cutting off the stomach in the upper part, the surgeon creates a “small stomach” with a volume of 20-50 ml. Then a loop of the small intestine is sutured to the “small stomach”. The operation is performed laparoscopically through small punctures in the abdominal wall. As a result, the amount of food consumed is reduced several times, and the entry of food into the small intestine already causes a feeling of fullness. The laparoscopic method of surgery reduces the rehabilitation period and allows you to quickly return to your previous lifestyle.
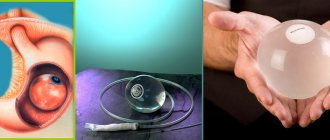
Gastric banding in 2021
Gastric banding is a restrictive bariatric procedure. It differs from all others in that limiting the intake of food is achieved not by restructuring the gastrointestinal tract, but by installing a special device in its upper sections - a bandage. One of its main components is a hollow, closed cuff that can be filled with fluid through an adjustable subcutaneous port, thereby determining the degree of narrowing of the opening for food to enter the stomach. The narrower it is, the greater the pressure on the esophageal receptors, which notify the brain of satiety.
Despite all the advantages, gastric banding in its original form also has serious disadvantages. In particular, the bandage can migrate, and the connecting tube connecting it to the adjustment port can create conditions for intestinal strangulation with the development of intestinal obstruction.
Professor V.V. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko improved the classical technique, and now gastric banding is as safe as possible. In their modification:
- the bandage is applied high, at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach, so the latter is not overtightened and is not injured;
- the bandage is not sewn to the stomach, but is fixed solely due to its location using a new technique - between the wall of the stomach and the peritoneum;
- the connecting tube does not move freely in the abdominal cavity, threatening to strangulate the intestine, but is firmly fixed in the tissues under the peritoneum.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
What is this?
Sleeve gastrectomy (SLG) is a procedure that reduces the size of the stomach and gives the organ the appearance of a narrow “tube.” Due to the shrinkage of the stomach, the patient requires small portions of food to feel full; accordingly, the number of calories consumed is reduced, and weight loss gradually occurs.
The procedure is performed in patients with morbid obesity, which can significantly reduce body weight and improve overall health and comorbidities associated with obesity such as diabetes, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis and hypertension. Longitudinal resection is gradually gaining widespread acceptance as an independent surgical procedure for the treatment of obesity.
What you need to know:
Laparoscopic gastrectomy (sleeve) is a restrictive procedure that reduces the size of the stomach but does not change the function of the gastrointestinal tract.
The available data from a ten-year observation of patients after this operation showed its high effectiveness with an extremely low number of intra and postoperative complications, good tolerance of the operation by patients and a small number of post-gastroresection syndromes.
Sometimes, in the pursuit of weight loss, the main goal that a doctor should strive for when helping a patient is lost - quality of life.
This operation is the only one among bariatric operations that allows preserving many anatomical and functional structures of the body with a high weight-loss component.
This operation currently ranks first in the world in the treatment of obesity in terms of the number of operations performed.
Positive aspects of the operation:
Sleeve gastrectomy has a number of undeniable advantages: After sleeve gastrectomy, saturation occurs with less food. Due to the reduction in the size of the stomach, the number of biochemical elements and hormones involved in the process of satiation decreases, which leads to a decrease in the feeling of hunger. In addition, now filling the stomach “to the top” (and this is necessary for many people to feel full) is done with less food than before, which leads to excess weight loss. Weight loss, in turn, helps normalize blood pressure and reduce the manifestations of diabetes and other diseases. With sleeve gastrectomy, the possibility of dumping syndrome is excluded, since the pylorus, the valve that separates the stomach from the duodenum, is not affected. With dumping syndrome, food in the stomach is not completely digested, which leads to a variety of gastrointestinal disorders and painful symptoms.
Sleeve resection preserves the physiological passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
Sleeve resection is carried out without the introduction of foreign bodies (unlike, for example, bandaging), so there is no fear of complications or any pathological changes caused by the presence of a foreign object in the body. Sleeve resection can be performed laparoscopically even in patients with excessively high body weight.
It is important to note that if this procedure does not achieve the desired degree of weight loss, it may be followed by another bariatric surgery.
Negative aspects of the operation:
Sleeve gastrectomy also carries some risks: Sleeve gastrectomy is an irreversible operation. Once most of the organ is removed and it takes on a new shape, the organ becomes more sensitive to the quality of food. Thus, poorly chewed food can cause vomiting and discomfort. After surgery, the stomach may stretch again.
Other postoperative complications are possible, such as the development of pneumonia, the appearance of blood clots, infection entering the body, etc. Failure of the staple suture with the leakage of gastric juice and the formation of a gastric fistula is extremely dangerous. The risk of complications is minimal, but it increases for patients with excessively high body weight.
Indications for surgery:
If you have excess body weight, surgery is prescribed under the following conditions:
*body mass index above 40 kg/m2;
*body mass index is slightly higher than 35 kg/m2, but at the same time the development of comorbid conditions is observed - diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension and arthralgia;
*body mass index is more than 35 kg/m2, but other treatment methods in the form of diet, medications, and physical therapy are powerless.
Preparation for surgery*:
The patient is prescribed the following series of examinations:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity, veins of the extremities, pelvis (prostate).
- Electrocardiography (ECG), if necessary, ECHO heart.
- X-rays of light.
- Gastroscopy (EGD)
- Consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Laboratory research:
6.1. detailed blood test (especially erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and urine;
6.2. a set of biochemical tests, for example, total protein, bilirubin, total cholesterol, urea, glucose, creatinine (a product of muscle metabolism) and others;
6.3. tests for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis markers, blood type and Rh factor;
6.4.coagulogram (carried out to study the patient’s blood clotting);
Analysis of urine
6.5.therapeutic conclusion.
Before surgery, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination and pass all the necessary tests. A consultation with a therapist, psychiatrist, cardiologist and other specialists is carried out. The patient is allowed to undergo surgery if his test results are within normal limits. If there are any deviations, then a course of necessary treatment is carried out, which allows the condition to normalize. It is also necessary to stop taking medications that affect blood clotting 3 days before surgery. At the preparation stage, it is very important to adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and strictly follow them.
Progress of the operation:
The operation is performed under general endotracheal anesthesia.
The main purpose of resection is the so-called restriction principle - narrowing of the stomach in the longitudinal direction. This allows you to limit the amount of food entering your stomach. Laparoscopic gastrectomy takes up to 1 hour. Under general anesthesia, 5 incisions from 0.5 to 1.0 cm are made. Using special instruments and stitching machines, most of the stomach is removed - about 75-85%. Special endosurgical equipment is used.
The patient is left in the intensive care unit for 2-4 hours after surgery, then in the surgical department for 3 days. The general rehabilitation course in a hospital takes about 4-5 days, then the patient is discharged, having previously been prescribed a two-month diet. Resection is much easier to carry out than bypass surgery, which contributes to the absence of complications.
Contraindications for surgery:
Absolute contraindications are:
- Pregnancy,
- Oncological diseases.
- Organic pathology of the esophagus,
- Cirrhosis of the liver,
5.Drug addiction and psychiatric diseases.
Postoperative rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation after gastrectomy averages from 1 to 2 months. Patients usually return to their normal lifestyle within 4 weeks. To make recovery faster, you should follow some recommendations.
You can get out of bed 5–7 hours after surgery.
To relieve pain, the doctor recommends taking analgesics, painkillers or antispasmodics.
If there are no postoperative complications, the patient may be discharged within 3-5 days.
An excellent option is walking for 1-2 hours.
You can start playing sports only after 2-3 months. In the first months, it is not recommended to visit public reservoirs, swimming pools, saunas and baths. Sunbathing in the solarium or on the beach is prohibited.
Nutrition after surgery:
It is very important for the first time after surgery to follow the correct diet and drinking regimen. You cannot drink on the first day after surgery; the lack of fluid is compensated by drip infusions. On the second day, you can drink 10 ml (1 tablespoon) in small sips every 15 to 20 minutes. The first week is only a drinking regime (water, broths, tea, compotes, low-fat milk). In the future, patients are advised to adhere to the following principles:
Eating only liquid foods for the first two weeks after surgery to avoid stress on the sutures.
Starting from the second week, liquid, well-mashed food.
Complete exclusion of flour during this period of time.
Frequent meals in small portions - 5-6 times a day.
A single meal should not exceed 120-150 ml (3 weeks after surgery).
2 weeks after surgery, the predominant consumption of pureed foods is recommended.
Starting from the third week, thicker pureed food with the gradual introduction of usual food products into the diet to balance proteins, carbohydrates, fats;
Good nutrition: natural vitamins, healthy foods (fiber, live cultures of fermented milk products), animal proteins are required.
Cost of surgery at the Weight Correction Center:
Consultation with a surgeon:
– preoperative – free of charge,
– advisory – 1,800 rubles.
Laparoscopic sleeve longitudinal gastrectomy (SLIV) from RUB 200,000**
*Preoperative examination can be completed both in our clinic and in any other medical institution. In this case, you must bring the test results with you. An examination and conclusion from a therapist must only be done by our specialists!
**The final cost of the operation is determined by the surgeon during consultation and depends on the category of complexity and concomitant pathology.
Bypass drain in 2021
Bypass drainage, or short-loop gastric bypass, is a technique developed by bariatric surgeons V.V. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko based on the technique of sleeve gastroplasty, gastric bypass with one anastomosis and their own previous development - the formation of a retrocolic gastrointestinal anastomosis. The technology for creating this anastomosis makes it possible to form not only a long loop of the small intestine, as with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, but a very short one, only 20 cm, which does not affect the absorption of food.
Thus, a fundamentally new operation was created - bypass in its technology, since an anastomosis (shunt) is created between the stomach and the small intestine, but absolutely restrictive in essence, like a sleeve gastroplasty.
This intervention made it possible to eliminate as much as possible all the disadvantages of sleeve gastroplasty, practically without interfering with the physiological processes of food digestion.
Biliopancreatic bypass in 2021
Dr. Evdoshenko V.V.
Biliopancreatic bypass in 2021 is performed in the modern version of SADI. It differs from the original version in a longer section of the small intestine involved in the absorption of food - 2.5 m versus 0.7-1 m in the outdated version. This made it possible to reduce the negative consequences of too strong a malabsorptive component.
And so that the operation does not lose its effectiveness, now at its first stage a full-fledged sleeve gastroplasty is performed with the formation of a very narrow “ventricle-sleeve”, while in the classical version the stomach remained wider and the restrictive component was not so noticeable.
Professors V.V. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko are the only Russian surgeons who perform the most complex SADI biliopancreatic bypass surgery using the laparoscopic method. The benefits of this for a superobese patient, where surgical risks are obviously high, cannot be overestimated.
Repeated bariatric surgeries in 2021
Repeated bariatric surgery may be required if the first one no longer serves its purpose and the patient begins to gain weight again. Sometimes this happens due to a violation of the recommended dietary regimen, sometimes because the bariatric surgery itself has become less effective. The last reason is not at all uncommon, since any surgical reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, by definition, cannot be not only better, but even at the level originally created by nature. Therefore, repeated bariatric interventions have been developed to eliminate disorders that appeared some time after the first operation.
At the Clinical Center, surgery for weight and metabolic disorders is performed after:
- gastric banding – Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, mini-gastrobypass, SADI biliopancreatic bypass;
- Sleeve gastroplasty – strengthening of the stomach wall “sleeve” with “Permacol”, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, biliopancreatic bypass SADI;
- gastric bypass - installation of a non-adjustable band, strengthening the wall of the “small ventricle” with Permacol, distal gastric bypass (lengthening the Roux branch);
- biliopancreatic bypass - strengthening the wall of the gastric tube with Permacol, transferring the anastomosis, eliminating a hiatal hernia.
Of course, during repeated bariatric surgeries, all the improvements in classical techniques developed by Professors V.V. are used. Fedenko and V.V. Evdoshenko, increasing their effectiveness and safety, including the widespread use of the absorbable biocollagen mesh "Permacol".
The desire of bariatric surgeons to make interventions even more effective, safe and functional motivates them to develop new approaches and techniques in weight surgery. Therefore, the face of bariatric surgery is rapidly changing and becoming more attractive every year.
Indications and contraindications for bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery is today the most effective method of combating excess weight. Obesity is a global epidemic of the 21st century. Approximately 1.7 billion people in the world are overweight. As more people seek treatment for obesity, bariatric surgery has grown in popularity, with the number of surgeries increasing by approximately 70% in recent decades.
Boris Tsvetkov, Honored Doctor of Russia, Candidate of Medical Sciences, chief physician of the clinic, answers questions about indications and contraindications for bariatric surgery.
Please tell us about the indications for bariatric surgery and who should do it?
Indications: excess weight, as follows from the name of the operations. Moreover, we start not only from the weight that the patient currently has, but from the maximum weight that he had during his life. If, for example, a patient now weighs 80 kilograms, and it seems that he is still small for bariatric surgery, and six months ago he weighed 120. Having lost weight to 80 with great difficulty, he knows that at any moment he will gain all his kilograms back again, so We start from a weight of 120 kilograms.
Excess weight is the reason why patients come to us. On the one hand, if we examine such patients, which is what we do, we will find many concomitant diseases, such as incipient diabetes, hypertension, menstrual irregularities, infertility or joint diseases. The list of diseases that accompany obesity is large and they are growing like a snowball, complicating each other. On the other hand, patients come with a primary reason, for example, destruction of the joints, and they are not taken for a transplant, because the joints are designed for a person weighing 90 kilograms. He is trying to lose weight, but he is not succeeding. There are also quite a lot of such patients. Or consider diabetes - sugar affects many functions in the body, from the eyes to the tips of the legs. Vessels and nerves are affected first of all - polyneuropathy, blindness, venous diseases, which can lead to gangrene of the legs, loss of limb. But diabetes is a 100% indication for treatment.
Could it be that low body mass index and, for example, diabetes are indications for surgery?
Not every diabetes can be cured with our surgery. There is a certain selection of patients. We look at the tests to see if the function of the pancreas is preserved, whether it contains beta cells that produce insulin. If they are not there, then it is useless to stimulate such a patient and, unfortunately, we will not be able to help him in any way. If they are, then we take patients even with a normal body mass index, without excess weight, and they have an excellent effect in treating diabetes.
Do you recommend having surgery right away or trying other weight loss methods first? And which ones do you recommend?
As a rule, patients do not come to us immediately for surgery. Patients always choose any operation: for excess weight or something else, as the very last option. Therefore, before us, they independently make attempts to lose weight. This includes coding and diets – many different ones. And only after exhausting this option do they choose surgery. It is very rare for patients to start with surgery.
But we don't force them to go on diets. Usually it is clear from a person that it is useless to waste time and, most importantly, money. Diets aren't cheap either. Some patients tell why they went on diets, they lost money three to four times more than the cost of the operation.
For what purposes do people usually perform operations? In terms of aesthetics or more for health?
If we take young age, then the aesthetic side is more. They don’t yet think about the fact that soon, for example, joints will begin to deteriorate, and there are still untapped hidden capabilities in the body. But I no longer like the way my work colleagues look at me, it’s difficult to find a husband and other social problems. Who wants to be fat?
But for older people, indications are more in the direction of health. They already have a family, children, grandchildren, they may no longer care about appearance so much, but it’s hard to continue living with such weight.
At what age are people most often referred for bariatric surgery?
The average age is from 34 to 45 years. And more women than men.
What are the contraindications to bariatric surgery?
Peptic ulcer, acute conditions, mental illness, pregnancy.
Stomach ulcer
Pregnancy
Heart failure is an acute condition of the body
Are there people whom you strongly do not recommend having surgery and why?
In my practice there were practically no such people. There were patients who could not be operated on immediately because they could not bear it. These are huge, obese patients who need to be prepared: some for a month, some for three months, others for six months. But in the end they all underwent surgery. Patients came with stomach ulcers: but it’s not forever, it’s treated and you can have surgery. There were patients with severe cardiovascular diseases, but if they were not operated on, they would die. And so there is a good chance.
Have you ever had a time in your life when you met a person or acquaintance who clearly needs surgery and who had never even thought about the existence of such operations, but after your communication he began to think about it?
No, the patient must reach this point himself. If he comes up to me and says: “You seem to be dealing with this issue. Maybe you will take on me? Of course, no problem, I will advise him and work with him.
Or if a patient comes, for example, with another pathology. I recently had a patient with gallstone disease. But that’s how she came in – just big sizes! I look at her and think: “Not only that, but the first thing you should think about is your weight.” Moreover, everything is fine with her: her husband is loving, her finances are in order. I offered it to her, of course, gently and unobtrusively. We talked to her, and it turned out that she didn’t even think about being overweight.
I thought that only men, when they look in the mirror, see themselves as Apollos, and women, when they look in the mirror, see themselves as anyone. Even thin people see themselves as fat. But she thought and thought and decided that: “Yes, I probably need it.” I operated on both of them at the same time - both for the gallbladder and for excess weight.
Based on the survey, clinical recommendations were obtained for the surgical treatment of obesity, namely for whom bariatric surgery is indicated and contraindicated. If after reading the interview you still have questions, you can sign up for a free consultation with Boris Yuryevich or call the phone number listed on the website.