Most methods of combating excess weight are based on restricting diet and increasing physical activity. But in severe cases of obesity, gastric resection may be prescribed. This is a radical measure that is carried out in exceptional cases and has a number of nuances.
The information presented here is of interest from a purely educational point of view. It cannot be used to decide whether a particular case requires resection or not. Only a doctor can determine this.
What is gastric resection, the essence of the operation
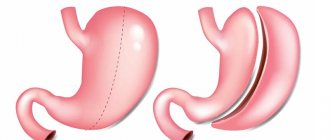
Gastric resection was initially used only to treat certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It involves partial cutting off or complete removal of the stomach. This can be longitudinal removal or using the Balfour method. After such an operation, the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract is restored. Not so long ago, this kind of intervention was used only when all other methods of treatment had been exhausted and the person was in danger of dying. But recently, resection has been prescribed for the treatment of terminal obesity.
As a result of the operation, half, a third or a quarter of the stomach may be removed. Sometimes subtotal resection is used, in which 80% of the organ is removed. The size of the removed part depends on the level of obesity. After rehabilitation, a person adapts to living with a reduced stomach. It takes less food to fill it, so the portions become noticeably smaller. As a result, the number of calories consumed is reduced, and the patient begins to lose weight.
But that is not all. It is very important to eat right after surgery. You need a balanced, well-thought-out diet. If you improve your diet, your weight will gradually become satisfactory.
Can the stomach stretch?
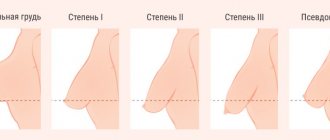
The stomach is a muscular organ. The average length of a developed stomach is 25 cm in length and 13 cm in height. In moments of acute starvation, it shrinks to 19 and 7 cm, respectively. The shape of the stomach is also subject to changes. It depends on the characteristics of a person’s physique: for overweight people it looks like a horn, for slender people it looks like an elongated stocking, for people with average parameters it has a hook-shaped shape.
Eating large amounts of food causes stretching of the stomach walls.
In parallel with the growth and maturation of a person, his stomach also grows: in a newborn baby, its volume is only 30 ml. By the first month of life, this figure increases to 100 ml. In six months - up to 250 ml. And finally, the average volume of this organ in an adult is 500 ml in the “hungry” mode.
The size of the stomach is variable. And not only the above factors influence it. Depending on the amount of food taken, its capacity can vary from 1-4 liters. In the absence of a person’s sense of proportion and control over the process of eating, over time the stomach muscles lose their tone, stretch, and gradually, in order to be satiated, the person has to increase the amount of food served.
Benefits of the procedure
Distal gastrectomy allows you to achieve truly impressive results. In just six months or a year after it, people lose from 50 to 90% of excess weight. The rehabilitation course is very short, patients quickly return to normal life, since minimal incisions are made during the operation, and the scars are very small.
During the resection process, only the stomach is affected. The remaining organs of the gastrointestinal tract continue to work. The operation is performed once. Repeated interventions or corrective procedures are usually not required. The remaining part of the stomach will forever retain its new size, so satiety will occur with less food consumption.
Flaws
This operation has its negative consequences. For example, after excision the stomach has reduced peristalsis; a person with a reduced organ may face the problem of intestinal obstruction. When a staple seam is performed incorrectly, inflammatory and infectious processes sometimes occur. Therefore, it is very important to be observed by a doctor during the postoperative period.
Gastric truncation is an irreversible procedure. Having made a resection once, it is no longer possible to return the organ to its original state. Sometimes a hernia forms at the sites of micro-incisions and sutures.
The first six months after surgery undergoes a process of adaptation of the body. During this time, such phenomena as constipation, diarrhea, and flatulence are common. There are side effects that do not go away even after the end of the adaptation period - heartburn, spleen diseases, stomach bleeding, inflammation of the abdominal cavity. If you look at the reviews, you can see that all sorts of complications of this kind are not uncommon.
Among other things, the passage of solid food with an excised stomach will be difficult. The first time after the procedure, abdominal pain appears when eating solid food. Over time, the pain goes away, but mild discomfort may remain.
Stomach reduction: disadvantages, advantages and effectiveness
The disadvantage of this method is that not all patients adapt easily to new dietary rules. Eating after the procedure may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Some people complain of heartburn after eating. But unpleasant symptoms can be corrected with medication. The doctor prescribes medications that reduce discomfort and simplify the adaptation period.
The advantages of the method are much greater:
- The physiology of digestion is not affected.
- Food moves through the digestive system naturally. There is no shunt (anastomosis) that radically changes the path of the bolus.
- Medicines, amino acids, omega-3 essential fats, vitamins, minerals and other nutrients are absorbed in full. There is no malabsorption syndrome after gastric reduction.
- There are no foreign bodies in the abdominal cavity. What kind of foreign bodies we are talking about will become clear from the next section of the article.
The high efficiency of the method deserves special mention. After surgical treatment, obese patients get rid of 65-70% of excess body weight, and the formation of correct eating behavior leads to normalization of metabolism.
After surgery, fat and carbohydrate metabolism levels improve. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood are reduced. The level of LDL, which contributes to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels, decreases, and the concentration of beneficial HDL increases. Blood sugar is normalized, cell sensitivity to insulin increases.
Improving metabolic processes allows patients with chronic pathologies of the cardiovascular and/or endocrine systems to achieve remission. In the absence of such diseases, the risk of their development is significantly reduced. The risk of heart attack, stroke and premature death from these diseases is reduced. Life expectancy increases and its quality improves.
Comparison of the method with other methods of stomach reduction
There are several other surgical methods to reduce the absorptive surface of the stomach. Each of them has its own characteristics and is prescribed for certain indications.
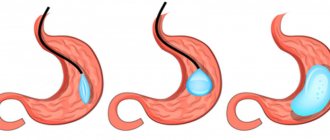
Ballooning
With this technique, a silicone bladder is inserted into the stomach, which is then filled with saline solution. Being inside the stomach, the bubble creates a feeling of fullness, as a result of which a person eats much less. After it is performed, the patient can immediately go home, and after resection, he must spend at least 3 days in the hospital. But ballooning ensures a loss of only 40% of excess weight, and resection – from 50 to 90.
Ballooning is a fairly simple medical procedure that does not involve surgery. During the first days after the procedure, nausea and vomiting are possible. But these complications are not nearly as serious as the possible consequences after organ truncation surgery.
After 6 months, the balloon should be removed. During this time, a person, theoretically, should get used to small portions. But if he resumes his previous eating habits, the weight will increase again. Another nuance is that sometimes the balloons burst right inside the stomach. This can happen without a person noticing. Therefore, the saline solution with which it is filled is colored blue. If the balloon suddenly bursts, the saline solution will turn the urine blue, and the patient will see this the first time he urinates. Blue urine for people with ballooning is a signal to urgently go to the doctor and remove the balloon.
Bandaging
This procedure involves placing a bandage – a silicone ring – on the stomach. The ring compresses the stomach, dividing it into two parts. At the site of compression, a gap as thick as the esophagus is left. The upper part of the stomach turns out to be very small. Food goes into it first. It fills quickly and signals that saturation has occurred. Then gradually the food moves to the lower part of the stomach, and then to the small intestine.
After the bandage, the person spends one day in the hospital. The procedure allows you to lose up to 50% of excess weight. Banding is performed using a minimally invasive method, which is much easier for the patient than a full-fledged surgical intervention such as resection. Complications with banding are the same as in other cases when a foreign body is placed inside.
Gastroplication
This is a method in which the stomach is folded in its expanded part and sutured in a special way, after which it takes the shape of a tube. It is performed laparoscopically, without organ incisions. Provides loss from 35 to 50% of excess weight. After the procedure, you may have problems eating. Long-term results have not yet been studied, as the technique has only recently become widely used.
Bypass surgery
During bypass surgery, a small part of the stomach is separated from the main one and connected to the small intestine in a bypass. After the procedure, the capacity of the working part of the stomach is reduced, and the degree of absorption of nutrients decreases. Bypass surgery is an even more complex surgical operation than resection. After it, patients remain under the supervision of doctors even longer.
The result of bypass surgery is a loss of 70 to 80% of excess weight. But quite serious complications can arise in the form of insufficient absorption of microelements and vitamins. Vomiting and nausea often occur.
In this case, the weight comes off within a year or two. After this, the person’s condition stabilizes, and if one does not return to harmful eating habits, the slim figure is maintained. If necessary, you can restore the original shape of the stomach.
How to reduce a distended stomach?
Fortunately, most patients can restore their stomach to normal size by making lifestyle changes. But if even long-term fasting does not help restore the normal size of the organ, an extended consultation with a gastroenterologist will be required. It is likely that a serious medical problem is developing.
As for drug treatment of the disorder, without a doctor’s prescription you can try taking enzymes and nutritional supplements that activate the process of digesting food. Stretching of the walls of the stomach can also occur under the pressure of excess food inside. Enzyme agents ( Mezim , Pancreatin ) allow you to quickly break down carbohydrates, which, in turn, accelerates the movement of food into the intestines. And the less time food puts pressure on the walls of the stomach, the faster it will restore its former shape. As a nice bonus, enzymes help reduce flatulence and eliminate belching.
If your stomach is distended due to excess gases, you can take probiotics. Natural bacterial cultures will not only normalize digestion, but will reduce the production of intestinal gas. Some patients are advised to take antidepressants or over-the-counter anti-anxiety medications. Indeed, during stressful periods, the feeling of hunger can appear uncontrollably, even in a completely well-fed person. Anti-anxiety medications help change the perception of hunger and also relieve anxiety.
Indications for resection
Gastric resection is indicated for complex obesity, which is accompanied by severe pathologies:
- metabolic syndrome;
- apnea (short-term cessation of breathing during sleep);
- pulmonary or heart failure;
- joint diseases;
- phlebeurysm;
- hypertension;
- infertility;
- diabetes.
The appointment is made taking into account the fact that excess weight has already led to concomitant diseases, and can further aggravate the person’s condition, as well as the fact that the person himself is no longer able to get rid of obesity in more natural ways. It is also clarified that the procedure allows you to remove no more than 50 kilograms.
Is it possible and necessary to reduce the size of the stomach?
You can quickly get rid of a distended stomach through surgery, suturing it to the desired size. Other methods are not so radical, but require more time and effort. These include diet adjustments, exercise, and medications.
Usually the stomach is reduced to lose weight. Such patients constantly feel hungry and feel unwell. Their organ is very stretched, and therefore they do not eat enough in standard portions, worsening their condition for satiety.
Contraindications to gastric resection
It is immediately worth noting that obese people, as a rule, have a whole bunch of diseases, and some of them are a contraindication to resection. Therefore, patients who are ready to go under the surgeon’s knife and pay a lot of money for it are often denied the operation.
Contraindications:
- autoimmune connective tissue diseases;
- taking hormonal steroid drugs on a regular basis;
- age under 18 years;
- alcoholism;
- kidney diseases;
- psychical deviations;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- ascites.
The procedure cannot be performed if there are inflammatory processes in any organs. Among other things, the anesthesiologist must give permission for the operation, since it is performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, one should also take into account contraindications to anesthesia, and this is a whole range of cardiovascular, pulmonary and other diseases that often affect obese people.