How do chondroprotectors work?
Chondroitin is part of our bones, cartilage and joints; its task is to retain moisture in the cartilage and stimulate the production of synovial fluid. Lack of chondroitin affects the health of cartilage tissue: it begins to deform, become thinner, and loses strength and elasticity. A decrease in the amount of synovial fluid affects the mobility of the joints: first there is a creaking, clicking of the joint when moving, later pain appears and the mobility of the joints worsens. Chondroitin is used for fractures, arthritis, and osteoporosis.
Glucosamine is a building material for healthy joints and cartilage, which makes them stronger and more elastic; it is also part of chondroitin. In addition, a sufficient amount of glucosamine helps prevent inflammation and pain in the joints. Glucosamine is often used for osteoarthritis, periarthritis, osteochondrosis and spondylosis.
Both glucosamine and chondroitin allow for better absorption of calcium in the body, and also participate in the process of synthesis of sulfur, which is a structural component of joints.
Specialists
(Training manual)
Information about authors:
Bodrova Rezeda Akhmetovna
– Head of the Department of Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine, Kazan State Medical Academy, Ministry of Health of Russia, Associate Professor, Candidate of Medical Sciences;
chief freelance specialist in medical rehabilitation of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan, scientific director of the rehabilitation center of the State Autonomous Institution "Hospital for War Veterans" in Kazan, Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan. Dolgopolov Alexander Sergeevich
– postgraduate student of the Department of Rehabilitation and Sports Medicine of the Kazan State Medical Academy of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, traumatologist-orthopedist of the State Institution Hospital for War Veterans, Kazan.
Reviewers:
Pozdnyak Alexander Olegovich – Head of the Department of Therapy and Family Medicine, Kazan State Medical Academy of the Russian Ministry of Health, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Dean of the Faculty of Internal Medicine, Kazan State Medical Academy of the Russian Ministry of Health.
Yakupova Svetlana Petrovna – Associate Professor of the Department of Hospital Therapy of the Kazan State Medical Academy of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, chief freelance specialist – rheumatologist of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tatarstan, Ph.D.
This educational manual proposes a method of ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joints without signs of reactive synovitis. The advantages, therapeutic effects, and basic rules for conducting ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in this category of patients are described.
The educational manual is intended for physiotherapists, orthopedic traumatologists, neurologists, and medical rehabilitation specialists.
The educational and methodological manual was approved and recommended for publication by the Methodological Council of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Further Professional Education of the KSMA of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation on November 26, 2014. (Protocol No. 04-2/5-08).
"The use of ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate for the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joints." Educational and methodological manual / Bodrova R.A., Dolgopolov A.S. – Kazan, KSMA, 2014, 15 p.
Introduction
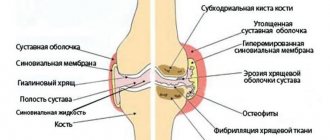
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease, affecting at least 20% of the population (7). The pathogenesis of OA is based on a metabolic disorder in cartilage tissue, expressed in the predominance of catabolic processes over anabolic ones. With age, joint diseases quite often occur, which is associated with natural involutional aging processes as a result of thinning of cartilage tissue, thickening and sclerosis of synovial membranes, and a decrease in the formation of synovial fluid , circulatory disorders in the joints, decreased general metabolic processes. Obesity and physical inactivity aggravate these age-related pathological changes, mainly by increasing the load on the joints and reducing blood and lymph flow. Cartilage tissue is deformed from excess weight and non-physiological load on the joint. Cartilaginous tissue is also replaced by bone growths or spines, especially in places of injury and inflammatory processes. This gradually leads to irreversible processes in the joints. The most common age-related joint diseases are arthritis and arthrosis of the hands, knees, ankles and hip joints.
Often, older and older people experience pain in one or more joints for no particular reason, which periodically increases or decreases. This can continue for many months and even years. But sooner or later, especially without timely diagnosis and treatment, pain becomes constant, changes develop in the joint, which ultimately lead to limitation of its mobility. The pain is accompanied by the appearance of stiffness, limited mobility, crunching and swelling of the tissues around the joint itself. These signs indicate progressive osteoarthritis.
Joint diseases are also common among people who play sports professionally. It was found that osteoarthritis and arthritis develop during traumatic (weight lifting) and jump-impact loads (running, jumping). This kind of physical activity can cause a deficiency of glucosamine and chondroitin, which helps reduce the amount of synovial fluid that softens joint friction. Regular physical activity on the joints, together with chronic injuries and minor tears in muscle tissue, lead to inflammatory and degenerative changes. This also manifests itself in the form of pain, limited mobility and joint deformation. There are also specific lesions characteristic of different sports: tendinitis of the long head of the biceps (in bodybuilders), external epicondylitis (“tennis elbow”), internal epicondylitis (“golfer’s elbow”), olecranon bursitis (in car drivers resting their elbow on the door ) etc.
Principles of treatment of joint diseases
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing the severity of inflammatory processes in the joints, relieving pain and improving local blood flow. At the same time, you need to know that today not a single drug is able to completely stop or reverse the course of the disease. In order to relieve symptoms and increase the range of motion in the joint, symptomatic therapy is used in the form of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which have many limitations and side effects, especially in old age. Chondroprotectors are also used to improve the structure of cartilage and slow down the progression of arthrosis. Their use is long-term - a course of 2 months to six months. In severe cases, hormonal therapy is used, which is also accompanied by adverse reactions, sometimes quite serious.
Physiotherapy, as a method with the least side effects and good tolerability, is almost always prescribed in the complex treatment of arthrosis and arthritis. Against the background of properly selected physical therapy, massage, heat therapy, peloid therapy, electromagnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy techniques are most often used. In the treatment of joint diseases, the main therapeutic effects of ultrasound are used: the ability to increase the permeability of the skin for local application of drugs, the effect of micromassage, improvement of microhemocirculation, blood and lymph flow processes, anti-inflammatory, desensitizing, defibrosing effects, the ability to loosen connective tissue structures, stimulate regenerative processes and activate collagen formation. These effects are based on the complex mechanism of action of ultrasound - mechanical, thermal and physicochemical, as well as local, segmental and physiological and therapeutic effects at the body level.
For joint lesions, various methods of ultrasound treatment are used, the effects are carried out directly on the area of the affected joints and on the paravertebral zones of the spine (for the upper extremities - at the level of segments CV - Thx, for the lower extremities - Thx - LI). If a drug is chosen as the contact medium, the procedure is called ultraphonophoresis. Using ultraphonophoresis, it is possible to create a high concentration of a drug in a pathological focus without causing side effects on the gastrointestinal tract or damaging the integrity of the skin. There are many methods of combined exposure to ultrasound and drugs, for which ointment or gel preparations are used, recommended for topical use in the complex therapy of osteoarthritis and osteoarthritis. In combination with ultrasound exposure, their penetration through the skin increases, which leads to the formation of a “skin depot” of the drug, an increase in phoretic mobility and, accordingly, a potentiated effect of physiotherapy with a proven clinical effect.
Considering that the cream for external use "Chondroxid® Maximum" replenishes the endogenous deficiency of glucosamine, stimulates the synthesis of proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid, restores enzymatic processes in the cells of the synovial membrane and articular cartilage, promotes the restoration of the cartilaginous surfaces of peripheral joints and joints of the spine, has chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, reduces pain and the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, inhibits the formation of superoxide radicals and enzymes that damage cartilage tissue (collagenase and fopholipase), the use of this drug in combination with ultrasound is justified for osteoarthritis of peripheral joints and spinal joints.
To improve the supply of glucosamine to joint tissue, a transdermal glucosamine complex is used - a complex of glucosamine and triglycerides.
Indications for ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate using Chondroxide® Maximum cream
1. Osteoarthritis of the knee joints stages I, II, III, without symptoms of reactive synovitis.
Contraindications to ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate using Chondroxide® Maximum cream
1. Osteoarthritis with clinical manifestations of reactive synovitis.
2. Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug, allergic reactions.
3. Osteoporosis.
4. General contraindications to physiotherapy.
Logistics of the method
Equipment: Ultrasound therapy device “UZT-I.0I F” with a frequency of generated ultrasonic vibrations of 0.88 MHz (880+0.88 kHz), No. in the State Medical Register 78/1261-33, with an emitter “IUT 0.88” -4.04 F, with a radiating surface area of 4 sq. cm. Medicinal product: cream for external use 8% “Chondroxid® Maximum” produced by Licht Far East (S) Pte Ltd. Country of origin: Singapore.
Description of the method
The proposed method consists in applying a thin layer of glucosamine sulfate in the form of 8% “Chondroxid® Maximum” cream (1-2 mm) to the surface of the damaged joint, and then applying ultrasound in a contact, labile, continuous pulse mode. Radiation intensity from 0.6 to 0.8 W/sq.cm. The exposure time is 5 minutes per joint, the total duration of the procedure is 10 minutes. Procedures are carried out daily, 10-12 procedures per course of treatment. The method differs in that, using ultrasound, glucosamine sulfate is injected into the joint tissue, which achieves a more pronounced therapeutic effect.
Efficiency of the method
The study involved 61 patients with osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee joints with radiographic stages from I to III, without clinical signs of inflammation (reactive synovitis) aged from 44 to 58 years. Patients were randomized into 2 groups - study and control. The main group included 31 patients, the control group - 30.
Patients of the main group were prescribed ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of Chondroxide® Maximum cream on the area of the affected knee joints, continuous ultrasound mode, density from 0.6 to 0.8 W/sq. cm, in fields, 5 minutes per field (one joint), total procedure duration 10 minutes, daily, No. 10-12 per course of treatment.
Patients in the control group received only ultrasound treatment on the area of the affected knee joints using the same exposure parameters as in the main group.
All patients before and after treatment were examined by us using international tests (Appendix):
1. WOMAC questionnaire.
The scale characterizes the severity of the pain syndrome and the patient’s ability to perform normal, everyday activities.
The overall effectiveness of OA therapy using ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of Chondroxide® Maximum cream in the main group was 93.3%, which was characterized by an improvement in general condition, a decrease in pain, an increase in mobility and independence in everyday life.
After treatment with ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of Chondroxide® Maximum cream, all patients of the main group showed significant positive dynamics of their condition: the sum of points on the Oxford knee joint scale decreased by an average of 7.7 points (the average value in the group was 23. 07±1.36 points, p<0.001), and the sum of points on the second knee joint assessment scale increased by 10 points (the average for the group was 78.40±2.27 points, p<0.001). Moreover, after the end of therapy, 12 out of 14 patients who complained of limited motor activity showed an increase in the range of motion in the knee joint. 5 out of 14 patients ceased to experience any restrictions of movement, in 7 patients the range of motion in the knee joints significantly increased. On average for this group, the increase in the amplitude of movements was 8.7 degrees – from 123.19±2.88 degrees to 131.79±2.87 degrees (p<0.05).
Complete disappearance of pain in the affected joints after 12 procedures of ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of Chondroxide® Maximum cream was noted by 6 patients (20.0%) and a decrease in the severity of pain - by 22 (73.3%) patients.
In patients of the main group, in addition to the reduction or disappearance of pain in the affected joints, other objective positive dynamics of motor activity were noted: an increase in walking distance in 24 patients (80.0%), an increase in muscle strength in 12 patients (40.0 %) and an increase in range of motion in 12 patients (40.0%).
The overall effectiveness of treatment in the control group was 64.7%.
After the end of therapy, all patients in the control group also showed positive dynamics, however, when assessing the patients’ condition using the international tests described above, the changes in the scores were significantly less than in the main group. Thus, the sum of points on the Oxford scale for assessing the knee joint decreased by 1.8 points (the average value in the group at the end of therapy was 27.93 ± 1.64), and on the second scale for assessing the knee joint increased by 3.8 points and averaged 72.50±2.41.
After treatment, out of 12 patients in the control group, who had limited range of motion in the knee joints before treatment, in 1 patient the range of motion in the knee joints was completely restored. In 3 patients, the range of motion in the knee joints increased. On average, the increase in range of motion in the control group was 5.6 degrees (from 123.00±2.71 to 128.60±3.25 degrees, p>0.05).
All patients in the control group with clinical improvement, in addition to the reduction or disappearance of pain in the knee joints, had objective positive dynamics of motor activity: an increase in walking distance in 19 patients (63.3%), an increase in muscle strength in 3 patients ( 10.0%). Complete disappearance of pain in the knee joints was recorded in 2 patients (6.7%), a decrease in pain in 21 patients (70.0%).
Thus, the use of ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of 8% cream “Chondroxid® Maximum” in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joints allowed for a 28.6% increase in the effectiveness of treatment compared with the effect of ultrasound therapy on the area of the affected knee joint in the control group of patients.
The study allows us to conclude that there is a significant advantage in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint using ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate over standard therapy.
The developed therapeutic method of using ultraphonophoresis of glucosamine sulfate in the form of 8% cream “Chondroxid® Maximum” is an effective method of treating patients with osteoarthritis and can be widely used in physiotherapy departments and rooms, medical rehabilitation of treatment-and-prophylactic and sanatorium-resort institutions. The expected effect from the implementation of the proposed technique is a reduction in the number of days of temporary disability in patients with OA by an average of 10-15%.
Bibliography
1. Alekseeva L.I. Modern ideas about the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis // Russian Medical Journal. - 2000.-T.2.-No.6.-P.1-20.
2. Alekseeva L.I., Benevolenskaya L.I., Nasonov E.L. and others. Structum (chondroitin sulfate) - a new drug for the treatment of osteoarthritis // Therapeutic archive.-1999.-t.71.-No.5.-P.64-65.
3. Bazhanov N.N., Petukhov N.V. On diagnosis and treatment tactics for osteoarthritis // Clinical Medicine. - 1993. - No. 4. - pp. 58-61.
4. Bodrova R.A., Lapshina S.A., Salikhova A.I. Local therapy of articular syndrome. Pathogenetic approach to the prescription of application therapy and physical factors. Educational and methodological manual. Kazan, 2005, 34 p.
5. Golubenko T.A. Low-frequency ultrasound in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis // Issues of balneology, physiotherapy and physical therapy. culture.- 1991.-No. 2.-P.36-39.
6. Grigorieva V.D., Fedorova N.V., Kiselev V.I. Complex application of cryotherapy and ultrasound in patients with arthrosis of the leg joints // Issues of balneology, physiotherapy and physical therapy. culture.- 1996.-№1.-S.- 18-22.
7. Kamenskaya N.S., Fedorova N.E. Therapeutic use of iodine-bromine chloride sodium baths in combination with hydrocortisone phonophoresis in patients with osteoarthritis and gout // Issues of balneology, physiotherapy and physical therapy. culture.- 1990.-№6.- P.47-50.
8. Rational pharmacotherapy of rheumatic diseases (Guide for practitioners), under the general editorship of V.A. Nasonova, E.L. Nasonova.- M.: “Littera”, 2003.- 506 p.
Separately or together?
Although glucosamine and chondroitin are chondroprotectors, they are used under different circumstances. Which raises the question: should I buy chondroprotectors together or separately? Answer: it is better to give preference to a complex supplement in which the components will complement each other.
What are the advantages of the complex:
- acts in several directions at once, providing comprehensive support;
- has higher dosages, which makes it possible to cover the daily requirement with a one-time dose;
- will cost less based on price/number of capsules/dosage.
How to take glucosamine and chondroitin
Preparations based on chondroitin and glucosamine are called chondroprotectors. Today they are available in different forms - tablets, gelatin capsules, powder for oral administration. Taking chondroprotectors for prophylactic purposes usually lasts 30 days, repeating every six months.
It is recommended to take chondroprotectors during or after meals. The supplement can only be taken on an empty stomach if prescribed by a doctor. Preparations with glucosamine and chondroitin will bring maximum benefit if you perform gentle physical exercise half an hour after taking the supplement. Activity should involve problem joints, as this will improve the absorption of glucosamine.
- The standard recommended dosage for glucosamine supplements is 1,500 mg (usually taken 500 mg three times daily). The maximum daily dose of the substance is 2000 mg; it is not recommended to exceed it.
- Chondroitin supplements are recommended to be taken at 400 mg three times a day or 600 mg twice a day. You should not take more than 1200 mg of the drug.
The recommended duration of taking supplements for therapeutic purposes is from 3 to 6 months, but sometimes it can last up to a year. Chondroprotectors cannot be called fast-acting drugs, since metabolic processes in the joints occur slowly. The effect of their use occurs approximately 4 weeks after the start of treatment and increases as therapy continues. Pain may gradually decrease after a few days of supplementation, but full tissue restoration requires at least 3 months.
Conclusion
Mobility and flexibility of joints is the main condition for easy, painless movements. Chondroitin and glucosamine, natural components in cartilage tissue, help maintain the health of the musculoskeletal system. A proper diet will help you get enough of these elements from your food. They are rich in food of animal origin, poultry, beef, hard cheese, as well as special additives - chondroprotectors. Proper nutrition will help increase the density of cartilage tissue and prevent joint wear.
Who should take it?
In situations of high physical activity, the use of these substances as supplements is especially important. Wear on joints from training occurs much faster, which can lead to a number of problems with the musculoskeletal system.
In addition, we must not forget about the injuries that often accompany weightlifting, powerlifting or bodybuilding. By taking additional complexes, which include glucosamine and chondroitin, you can significantly speed up the recovery process.
Additional intake of chondroprotectors is also necessary for elderly people, as well as those who suffer from diseases of the musculoskeletal system (arthrosis, arthritis, etc.).
What are chondroitin and glucosamine
Glucosamine is a natural monosaccharide necessary for the production of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cells. It is a building material for cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. Chondroitin is a connective tissue polysaccharide that normalizes the structure of joint tissues. Both elements are produced by the human body and are found in food.
Best Chondroitin and Glucosamine Supplements
| Photos of additives | Additive name | Short description | |
| NOW FOODS GLUCOSAMINE CHONDROITIN MSM – 90 caps | Glucosamine Chondroitin MSM is one of the best supplements for the prevention and treatment of minor musculoskeletal injuries | Buy product | |
| SPORTER GLUCOSAMINE & CHONDROITIN + MSM + D 3 – 120 TAB | Glucosamine & chondroitin + MSM + D 3 - dietary supplement to the diet - a source of glucosamine, chondroitin and methylsulfonylmethane. | Buy product | |
| SPORTER JOINT SUPPORT – 500 ML | Dietary supplement to the diet - a source of collagen, glucosamine, chondroitin and MSM to improve joint and musculoskeletal health. | Buy product | |
| QUAMTRAX GLUCOSAMINE CHONDROITIN & MSM – 90 TAB | One of the best supplements for joint recovery. Quamtrax Glucosamine Chondroitin MSM - a supplement prescribed for the prevention and treatment of minor injuries to the musculoskeletal system | Buy product | |
| NATROL GLUCOSAMINE, CHONDROITIN & MSM 90 TAB | Glucosamine Chondroitin with Natrol Glucosamine, Chondroitin & MSM chondroprotector, which contains the necessary components to maintain healthy joints and bones. | Buy product |