General rules
Allergic reactions in children to a particular substance of organic/inorganic origin ( allergen ) are widespread and are a serious problem. Among a wide range of allergens, there are food, household, medicinal, insect, pollen, epidermal, infectious (viral, fungal, parasitic, bacterial). However, in children the leading one is food allergy, in which the immune system develops a reaction to a specific food product/several products that act as an allergen.
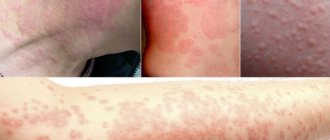
As a rule, allergic reactions develop after consuming a product to which the child’s body already has increased sensitivity (sensitization). At the same time, children's allergies can manifest themselves either immediately after consuming a food allergen or after several hours (delayed reaction). Food allergies in children have many manifestations: skin lesions - dryness and weeping, various rashes, itching, redness of the skin. Such clinical symptoms are usually called “diathesis,” in which there is a high risk of its degeneration into atopic dermatitis , urticaria , and Quincke’s edema . These may be disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: regurgitation/vomiting, increased gas formation, intestinal colic, bloating and abdominal pain, constipation /loose stools. Less commonly, in children with food allergies, the respiratory system is affected or combined manifestations of allergies occur.
Allergic reactions occur in children of all ages, starting from the first days of a child’s life. The appearance of food allergies is caused by a number of factors, the main of which are: imperfection of the child’s digestive tract (reduced enzyme ); disturbance of intestinal microflora; increased permeability of the intestinal mucosa; intestinal infections. Also, reactions are often caused by the consumption of highly allergenic foods by the mother during pregnancy , poor nutrition of the mother, early introduction of complementary foods/transfer to artificial feeding with unadapted formulas, and frequent overfeeding of the child. Diet for allergies in children is the most important condition for treatment.
Nutrition for allergies in children from 0 to 3 years old
Infants who are breastfed and allergic to cow's milk proteins require correction of the mother's diet in order to reduce the general state of hyperreactivity of her body. a hypoallergenic diet for the entire period of breastfeeding : it is not recommended to consume foods that have a high allergenic potential - whole milk products, chicken eggs, smoked meats, fish, citrus fruits, seafood, cheese, celery, chocolate, coffee, mushrooms, mustard, nuts , red caviar, spices, sauces, cocoa, canned/pickled foods, carbonated drinks, honey. Very carefully and in small quantities, it is allowed to include red-orange-yellow fruits/vegetables in the diet (tomatoes, beets, red apples, pineapples, strawberries, wild strawberries, carrots, bell peppers, pomegranates, raspberries).
All genetically modified products and those containing food additives (dyes, flavorings, preservatives) are subject to exclusion. The basis of nutrition should be first courses and cereals, dietary poultry (only domestic, since antibiotics and salicylates, food additives are used to raise chickens on poultry farms), fermented milk products, and permitted vegetables. If your baby has an allergic reaction to any product, it must be excluded from the diet.
If a child with manifestations of food allergies is mixed/artificially fed, breast milk is partially replaced with various goat milk-based formulas, adapted milk/fermented milk and soy (hydrolysates) formulas.
Complementary foods for children with allergies are allowed to be given approximately 1 month later than for healthy children (from 7 months), with individual tolerance taken into account. For the first feeding, it is better to use vegetable puree from white cabbage/Brussels sprouts, zucchini, light-colored pumpkin, and other green-colored vegetables. Vegetable purees for baby food are prepared from fresh/frozen vegetables, or you can use special canned baby vegetables. As part of the puree, vegetables must be introduced one by one, 3-5 after the previous ones, gradually bringing them to full volume. You need to start with a monocomponent puree, gradually expanding the range.
Second complementary foods can be introduced from 8-9 months in the form of rice, buckwheat, and corn dairy-free porridges. Porridge is cooked in water. If you prepare the porridge yourself, add a small amount (up to 10 g) of vegetable oil. If industrially produced porridges are used, preference should be given to gluten-free, dairy-free porridges enriched with a complex of vitamins and minerals.
The next complementary food - meat puree (turkey, rabbit, lamb) is allowed to be introduced at 9-10 months. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the child’s body’s reaction to new varieties of meat. Fruit dishes can be introduced into a child’s diet from 11-12 months, taking into account individual tolerance.
Preference should be given to green apples, and then, controlling stool consistency and skin reaction, pears, bananas, yellow currants, and plums are introduced. In children with an allergy to cow's milk proteins, the duration of dairy-free nutrition can vary from 4 months to one year. The expansion of the diet of such children is carried out by introducing fermented milk products into the diet, which are less allergenic compared to milk. First, kefir is introduced, then milk porridge/cottage cheese under careful monitoring of the child’s condition. Chicken eggs and fish are completely excluded from the children's diet during the first year of life. In the future, it is recommended to replace chicken eggs with quail eggs.
Diet for children with allergies over 3 years old
For children in this age group, when food allergies develop, more stringent restrictions are provided, since their diet is much wider than that of younger children. The daily amount of food/diet must correspond to the indicators of the child’s physical development and age standards. At the same time, foods that cause an allergic reaction (if known) are excluded from the diet - an elimination diet. If the allergen is unknown, to identify it, parents should keep a “food” diary, which carefully reflects the entire diet for the day. Each new product is noted (its quantity, time of administration) and the nature of the reactions to it - redness of the skin, itching, rash, upset stool. The new product is given to the child in the morning, 1-2 teaspoons. If there is no reaction, it is allowed to gradually increase its amount after a day, bringing its volume to the age norm within 3-5 days. If there is a reaction, it is excluded from the child’s diet for a period of time, determined individually by the pediatrician.
For older children, when allergies appear, step-by-step diet therapy is prescribed. The first stage (acute period) - a nonspecific hypoallergenic diet is prescribed for 7-10 days with the exclusion of all potential allergens, while simultaneously conducting an allergological examination of the child to identify the allergen, using the method of identifying allergens in the blood/staging allergy tests. Products containing food additives, as well as dishes that irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa (spicy, fried, pickled, salted, smoked dishes, broths, spices) are excluded.
The consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates, which often increase the manifestations of food allergies, dairy products, flour products, and some cereals is limited. The amount of animal fats decreases while vegetable fats increase, since polyunsaturated fatty acids enhance immunity and help restore damaged skin areas.
At the second stage, the doctor, together with the parents, draws up an individual diet for the child, taking into account the identified allergens, which are excluded from the diet for 3-6 months. At the third stage, as the clinical manifestations of the allergy subside, the diet is gradually expanded, introducing “forbidden” foods/dishes in small quantities (up to 10 grams per day). At the same time, obvious allergenic products are still completely excluded.
Products are introduced one at a time, monitoring the condition of the skin, the child’s well-being, stool and temperature reaction. If the product in increasing doses is not accompanied by allergic reactions, then the next previously prohibited product is introduced. By doing this, you can completely get rid of allergies or achieve a relatively long-term remission, since tolerance to the allergen product gradually increases in most children, and by school age in some of them it may even completely disappear.
In case of food allergies in children, it is important for parents to take into account the peculiarities of culinary processing of products to reduce their allergenicity:
- All products must undergo culinary processing (boiled, steamed, stewed, baked).
- When cooking meat, to completely remove harmful components, it is necessary to boil the meat and drain the broth at least once (preferably twice) before further processing.
- After cutting, it is recommended to soak potatoes in cold water (changing it periodically) for at least 10-12 hours to remove starch and nitrates.
- To remove possible toxic chemicals, cereals are soaked in cold water for 1-2 hours.
- Boiling and baking them reduces the allergenicity of fruits/vegetables.
Authorized Products
The diet for children with allergies includes dietary meats from domestic chicken (without skin), rabbit or turkey in boiled/stewed form.
The first courses are prepared without frying in a weak vegetable broth with the addition of garden herbs (dill, parsley, cilantro).
As a side dish, you can use wheat, buckwheat and oatmeal porridge or boiled potatoes in pieces.
The diet is allowed to include low-fat fresh cottage cheese, yogurt without fruit additives, low-fat fermented milk products, biscuits, whole grain bread, and pasta.
Vegetables you can take include cucumber, lettuce, cabbage, onion, zucchini, and zucchini.
Among fats, preference is given to vegetable oils (sunflower/olive).
As drinks, children are recommended to drink compote/jelly made from permitted berries/fruits, rosehip decoction, and still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Dairy | ||||
| dairy products | 3,2 | 6,5 | 4,1 | 117 |
| kefir 0% | 3,0 | 0,1 | 3,8 | 30 |
| kefir 1% | 2,8 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| beef stew | 16,8 | 18,3 | 0,0 | 232 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| steamed chicken breast | 23,6 | 1,9 | 0,0 | 113 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Hypoallergenic diet menu
A child's body fights allergies much better than an adult. In this regard, a hypoallergenic diet for children is prescribed for a short period of time - up to 10 days. A sample menu for young children with allergies should look like this:
| Meal time | Dish | Serving volume, grams |
| Breakfast | Viscous buckwheat porridge | 150 |
| Brynza | 20 | |
| Apples | 50 | |
| Tea or peach juice | 150 | |
| Galette cookies | 20 | |
| Dinner | Vegetarian soup with potatoes and chicken meatballs | 150 |
| Steam cutlet | 70 | |
| Boiled rice | 100 | |
| Rose hip decoction | 150 | |
| Afternoon snack | Biokefir | 150 |
| Oat cookies | 70 | |
| Fruits | 100 | |
| Dinner | Cabbage salad | 100 |
| Vegetable stew with cauliflower and meat | 120/60 | |
| Tea or kefir | 150 | |
| *The amount of unhealthy bread per day should not exceed 150 grams | ||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for children with allergies involves the exclusion of products such as meat/fish/mushroom broths and dishes based on them. It is not allowed to consume waterfowl meat, fatty red meats, smoked meats, milk, sausages, chicken eggs, “red” fish and caviar of all types, citrus fruits, chocolate, sweets and flour products, seafood (shrimp, mussels, squid), sour cream, all salted and pickled foods, canned food, cream, sweet curds, cooking/animal fats, salty and fatty cheeses.
Excluded from the diet: sugar, jam, honey, confectionery, ice cream, sweets, jams. White rice, pasta, and semolina are subject to restrictions.
All seasonings (vinegar, ketchup, mayonnaise, mustard, horseradish), mushrooms, pineapple, eggplant, melon, butter dough and fruits/vegetables of red and orange color (red apples, tangerines, beets, tomatoes, oranges, strawberries, strawberries) are excluded from the diet , radish, carrots, radishes), nuts (hazelnuts).
The diet menu should not include foods that contain dyes and preservatives, fruit tea, fruit/vegetable juices from red/yellow berries, coffee, or sweet carbonated drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Dairy | ||||
| condensed milk | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56,0 | 320 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| sour cream 40% (fat) | 2,4 | 40,0 | 2,6 | 381 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| dor blue cheese | 21,0 | 30,0 | 0,0 | 354 |
| blue cheese | 17,6 | 31,0 | 1,8 | 363 |
| amber processed cheese | 7,0 | 27,3 | 4,0 | 289 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| mutton | 15,6 | 16,3 | 0,0 | 209 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fried fish | 19,5 | 11,7 | 6,2 | 206 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| semi-finished fish products | 12,5 | 6,7 | 14,7 | 209 |
| sardine | 20,6 | 9,6 | — | 169 |
| mackerel | 18,0 | 13,2 | 0,0 | 191 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| coconut oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| palm oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| rendered beef fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| rendered pork fat | 0,0 | 99,6 | 0,0 | 896 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| black coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| tonic | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,3 | 34 |
| energy drink | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,3 | 45 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| cranberry jelly | 0,0 | 0,0 | 13,0 | 53 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Reviews and results
A diet for allergies in children, according to reviews from parents, can significantly minimize the severity of clinical manifestations in the acute period of the disease and prolong remission in the chronic course.
- “... The child has a burdened allergic history since birth. Since then, we have been frequent guests of the allergist. The child cannot tolerate chicken protein at all. The reaction is immediate—the skin breaks out in a rash, turns red, and itches. That's why we go on a diet all the time. The tricky part is eliminating all products that use eggs because the manufacturer doesn't always list all the ingredients completely on the label. Therefore, we try to prepare everything for him ourselves. We undergo examination every year. The doctor consoles us that in many children, allergies go away or decrease with age. We really hope so”;
- “... After the introduction of new complementary foods, the child developed severe diathesis. They called a doctor who stopped complementary feeding and prescribed a hypoallergenic diet for me during breastfeeding and advised me on how to properly start new complementary foods and which formulas are best to use.”
What is a hypoallergenic diet for children
By the term allergy, doctors mean a special condition (hypersensitivity) of the body to various substances, upon contact with which various negative reactions occur: redness of the eyelids, skin rash, sneezing, tearing, swelling.
A hypoallergenic diet is one of the treatment options for this disease, which involves excluding highly allergenic products from the menu. It helps to identify the cause of negative reactions, relieve stress from the body and improve the immune system. A hypoallergenic diet plan is necessarily included in the treatment at the initial stages of an allergy examination . It is prescribed to all children for whom the cause of the allergy could not be determined, children with weakened immune systems, with atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and a history of Quincke's edema. Sometimes hypoallergenic nutrition is recommended for nursing women to prevent allergies in newborns and to improve the quality of breast milk.