Back to Product Composition
In all living systems, proteins, also known as proteins, are of primary importance. All chemical and biochemical processes that support the life of cells and organisms are performed exclusively by enzymes, molecules of protein nature. Proteins also perform a construction function, both at the cellular level and at the level of the organism as a whole. The functional diversity of proteins is determined by their spatial structure, location, but above all, their chemical composition.
From a chemical point of view, proteins are polymers made of amino acids . This name reflects the structure of these substances, containing at least one amino group -NH2 and one carboxyl group -COOH. They differ only in the structure of their radical, which, in fact, determines their individual physicochemical properties.
Natural proteinogenic amino acids
The total number of amino acids in nature is about 300, in the human body - more than 60. However, the number of amino acids from which protein synthesis occurs is only about 20 (sometimes there are 21-22), and they are called proteinogenic amino acids, or natural. From them, in the process of protein synthesis and the formation of its structure, other amino acids are formed. These natural 20 amino acids are programmed in the genetic code of any organism, from a virus to a person, and it is their sequence in the protein molecule chain that determines the uniqueness of all forms of life on Earth.
In human organs and tissues, the main role of these compounds is participation in protein synthesis, which takes up the vast majority of all received or formed amino acids. But there are also individual amino acids that have independent functions. Thus, tyrosine is responsible for the coloring of hair, skin, eyes, and gives a dark color to food products, for example, rye bread, since with its participation dark-colored pigments - melanins are synthesized. A number of representatives of this class play the role of mediators - substances responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses from one nerve cell to another (acetylcholine, glutamic and aspartic acid, glycine, GABA, histamine, serotonin, norepinephrine). The amino acid glutamine ensures the transport of nitrogen metabolism products in human blood.
In addition to proteins, amino acids are made up of shorter molecules that play an important role in the body: oligopeptides. Among them there are not very short chains of amino acid residues, for example, the hormone insulin, and very short ones, up to dipeptides (or bipeptides), which consist of only two amino acid residues (for comparison: proteins have hundreds of amino acid residues). The most important dipeptides are carnitine and carnosine, the strongest natural antioxidant.
Replaceable and essential amino acids
The source of amino acids in food products is proteins. All food proteins differ in their amino acid composition. This is of great importance in the selection of complete diets due to the fact that a number of amino acids are irreplaceable (essential) - they can only be obtained from food products. Essential proteinogenic amino acids include valine, isoleucine, leucine, threonine, methionine, lysine, phenylalanine, tryptophan. In contrast, nonessential amino acids can be synthesized in the human body from precursors. These are glycine, alanine, proline, serine, cysteine, aspartate, asparagine, glutamate, glutamine, tyrosine. Partially replaceable ones include arginine and histidine, since they are synthesized rather slowly in the body.
A deficiency or complete absence of even one essential amino acid in the diet leads to a negative nitrogen balance, which in turn over time causes severe clinical consequences such as vitamin deficiency: disruption of the central nervous system, growth arrest, etc.
It is extremely important to note that if any one essential amino acid is deficient, this leads to incomplete absorption of others. This pattern is subject to Liebig’s law, according to which the development of living organisms is determined by the essential substance that is present in the smallest quantity.
What foods contain essential amino acids? These are all food ingredients rich in protein.
Classification
The table of amino acids reflects their classification by type: essential and essential. All of them are necessary for the human body.
All amino acids are divided into two groups:
- irreplaceable or essential. These are the amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own. They come to us with food with a rational diet;
- replaceable. The body synthesizes them independently from those substances that come with food. But you should not underestimate them, so it is advisable that they also enter the body with food.
For ease of use, a table of amino acids has been compiled, from which it is easy to determine how many essential ones will enter the body. For simplicity, there are indicators in % and in grams.
We also recommend studying this topic:
How should you take Pureprotein Arginine Complex correctly?
5228 0 1
Nonessential amino acids
This type includes:
- alanine It is a source of energy into the body's cells and allows you to accelerate the removal of toxins from the liver;
- arginine Allows you to normalize liver function, quickly restore muscles, strengthen the immune system;
- asparagine The action is similar to aspartic acid;
- aspartic acid. Allows you to normalize metabolic processes, activate energy synthesis, and also provides support for the nervous system.
- cysteine. It is involved in normalizing the condition of hair, as well as nails and skin. Helps relieve symptoms of cancer and bronchitis.
- glutamic acid. The action is similar to glutatin.
- glutamine Effectively removes toxins from the liver and takes part in muscle growth. Adds strength, endurance, and energy to the athlete.
- glycine. It restores the normal functioning of the nervous system.
- proline This amino acid improves the condition of human skin;
- serine Fills the body's cells with energy.
- tyrosine Increases brain activity, participates in the formation of muscle protein.
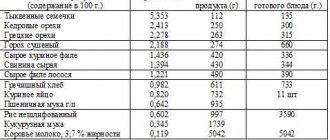
Table of amino acid content in each product in shares. Athlete's handbook.
A table of amino acids, including a list of all essential and essential ones, is like a reference book for athletes.
Important! A lack of these amino acids can lead to the body starting to replenish them at the expense of muscle mass, which is unacceptable for a bodybuilder and other athletes.
Essential amino acids
These include:
- histidine It is present in the human body and performs the functions of participating in the creation of blood cells. It is truly considered the basis of the immune system.
Important! This amino acid is consumed very quickly, so it requires constant replenishment.
- isoleucine. Its priority function is to increase endurance, as well as restore energy;
- leucine The main amino acid for the human body, which is involved in the regeneration of muscle fibers. It allows you to stop catabolism. Leucine helps regulate sugar levels, burn fat deposits;
- lysine. Ensure the body fights viral diseases;
- methionine Helps fight fat. Improves endurance as well as strength;
- phenylalanine. The priority direction of the amino acid is to normalize the functioning of the nervous system;
- threonine This amino acid normalizes protein metabolism and stimulates muscle development;
- tryptophan. Functions: normalize blood pressure, improve sleep;
- valine Provides tissue regeneration and saturates the body with energy.
Table of amino acid content in milligrams in different foods. A balanced diet will help saturate the body with the required amount of amino acids, and you can supplement it with supplements from the sports nutrition series
Replaceable and essential amino acids, the table of which is presented in the article, will serve as a reference book not only for an athlete, but also for people who care about their health.
We also recommend studying this topic:
Purpose of glutamine, its properties and dosage regimen
11122 0 0
Readers found these materials useful:
- The effect of taurine on the body in bodybuilding
- How should you take Pureprotein Arginine Complex correctly?
Food as sources of essential amino acids
Amino acids are extremely rarely presented in free form. The latter is found in special food products, for example, sports nutrition, where they are directly added in a free state for faster and more complete absorption. Basically, they enter the body as part of proteins and are then released during the hydrolysis of the latter. Amino acids or small peptides released as a result of hydrolysis can already be absorbed in the intestine.
The most important sources of essential amino acids in the required ratio are the following food products, which contain easily digestible proteins: milk, dairy products, eggs, meat and meat products, fish, seafood, soybeans, legumes (peas, lentils, beans, soybeans), cereals, bread, potatoes, etc.
Along with the amino acid composition, the biological value of proteins is determined by the degree of their absorption after digestion.
The degree of digestion, in turn, depends, on the one hand, on the state of the body (enzyme activity, depth of hydrolysis in the gastrointestinal tract), and on the other hand, on the type of pre-treatment of proteins in food preparation processes (thermal, hydrothermal, microwave and etc.). Heat treatment, boiling, mashing and grinding speed up the digestion of protein, especially vegetable protein, while heating to very high temperatures above 100°C makes it difficult. Back to Product Composition
What are amino acids?
I talked about this in my article about squirrels.
There I also briefly gave an idea of what essential amino acids are. In this article I will go into more detail on this issue. Because this knowledge is necessary for a person who has chosen a lifestyle with proper nutrition. Amino acids are chemical particles that make up protein; they also form the structure of the tissues of the human body.
So, essential amino acids are amino acids necessary for the body that are not synthesized (not produced) by the body itself, and in this regard must be supplied daily in sufficient quantities from the outside, and therefore with food.
Knowing the list of these amino acids and having a list of products that contain them, we will help our body receive the necessary nutrition at the cellular level. For restoration, construction and development.
So, let's list the 8 main essential amino acids needed by the adult human body, and plus 2 additionally for children under 6 years of age:
- Arginine (children's body)-Arg
- Valin-Val
- Histidine (children's body)-His
- Isoleucine-Ile
- Leucine-Leu
- Lysine-Lys
- Methionine-Met
- Threonine-Thr
- Tryptophan-Trp
- Phenylalanine-Phe