Arginine (diaminomonocarboxylic acid) is a non-essential amino acid that is important in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
It has anti-ischemic, antithrombotic, antiplatelet properties. Also, as a dietary supplement, it has found its use as a substance that stimulates erectile function in men. It enters the body with food or is synthesized from other amino acids.
general characteristics
Arginine was first isolated in the 1880s from animal horn. Now this substance is known for its numerous positive properties.
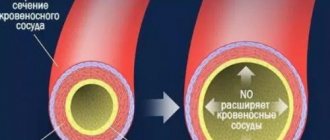
Perhaps the most important characteristic of arginine is that it is a substrate in the synthesis of nitric oxide, which regulates vascular tone, provides them with flexibility and has a strengthening effect on the entire cardiovascular system. Due to its ability to increase nitric oxide levels, arginine is considered beneficial in cardiovascular diseases, sickle cell anemia. Nitric oxide is synthesized in various cells of the human body and is involved in many physiological processes.
Content:
- general characteristics
- Arginine for treatment and prevention
- Benefits for the body
- Daily norm
- Contraindications for use
- Side effects of arginine
- Risks of shortage and excess
- Food sources
- Interaction with other substances
Arginine strengthens the immune system, regulates hormonal levels, as well as blood sugar. Enhances male fertility. Research shows that this amino acid can improve blood circulation, which is why it is so important for the treatment of heart disease and impotence.
By neutralizing ammonia and other toxins, it promotes liver detoxification. Laboratory experiments have shown that arginine can reduce fat reserves, speed up metabolism and promote intense weight loss.
High concentrations of arginine are found in the skin, connective tissue and muscles. And thanks to its ability to restore damaged tissue, it is useful for athletes and people suffering from arthritis. It also promotes rapid regeneration, including of nerve, muscle cells and epithelium.
Arginine is an important substance for adequate functioning of the brain, in particular the pituitary gland. Namely, together with ornithine and phenylalanine, it promotes the production of growth hormone.
content of the amino acid arginine in food products
Continuation.
Start here: https://zaryad-zhizni.ru/svoystva-arginina/ Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid. In the human body, it is synthesized in quantities that are insufficient to ensure normal life activity and must be supplied with food. For children, arginine is an essential amino acid, because ensures the growth and development of organs and tissues.
Arginine is a carrier of nitrogen molecules in the body. It is included in the active center of many enzymes and is necessary for the conversion of inactive proteins into active ones. It is a source for the synthesis of nitric oxide, a substance that promotes vasodilation. From arginine, the body obtains creatine, a substance that provides energy to muscles. Arginine stimulates the production of growth hormone and testosterone, which promotes muscle growth. It lowers blood cholesterol and promotes fat burning. Improves liver function, utilizes ammonia formed during the work process. Protects nerve cells from fatigue, reduces the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attacks and strokes.
Biological requirement for arginine:
for adults – 6 g/day, for children – 4 g/day.
Arginine content in food
During the cooking process, the amount of arginine in the finished dish changes:
- In boiled meat and fish, the amount of arginine is 20-25% greater than in raw meat
- Arginine is not completely absorbed from plant products, and therefore a coefficient of 0.8 has been introduced
- Legumes and grains are not consumed raw, but in the form of porridges, the ratio of grain to water is taken for legumes 1:2, for cereals 1:3, plus a digestibility coefficient of 0.8 is added
A good source of arginine are pumpkin seeds, as well as nuts; the daily dose of the amino acid can be obtained from a glass of these products. Another good source of arginine is expectedly meat and fish, although it is difficult to eat about 400 g of salmon. Other products can not be considered as complete sources of arginine, because it is simply unrealistic to consume such an amount of the product, like eating 11 eggs, drinking 5 liters of milk, or eating porridge or bread. Vegetarians can balance their diet with arginine if they consume enough seeds and nuts, but these are very high-calorie foods, and there is a problem here.
Arginine deficiency
Lack of amino acids in food can provoke the following conditions:
- Increased blood sugar
- Increased blood cholesterol
- Obesity
- Increased blood pressure
- Coronary heart disease, angina pectoris
- Brain disorders, insomnia.
- Premature aging
A severe form of arginine deficiency in children and adolescents is accompanied by growth retardation, delayed puberty, and hormonal disorders.
Arginine deficiency can develop both due to its insufficient supply from food, and due to an increase in the body's need for this amino acid.
Increased need for arginine
The need for arginine increases under the following conditions:
- Injuries: burns, frostbite, broken limbs, wounds, etc.
- Operations
- Severe infections, incl. AIDS, sepsis, cancer
- Stress, incl. psychological and emotional
- Depression, chronic fatigue syndrome
- Diabetes
- erectile disfunction
- Heavy physical labor, sports, bodybuilding
- Liver diseases, cholelithiasis, kidney diseases
- Age: children, teenagers, elderly
If there is a lack of arginine intake from regular foods, as well as to compensate for its increased consumption in medicine and sports, it is possible to use commercial L-arginine preparations.
Continued here: https://zaryad-zhizni.ru/kak-prinimat-arginin/
Arginine for treatment and prevention
Arginine is classified as a nonessential amino acid, but under some circumstances it becomes an essential substance for the body. The need for arginine is extremely high during periods of intensive growth and pregnancy. It is also important to monitor the consumption of foods rich in amino acids for people with liver disease, cancer, sepsis, and poor wound healing. The results of some studies have shown that arginine consumption reduces the risk of developing necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants, has a positive effect on intestinal motility, and protects it from inflammation. In addition, there is an assumption that the use of arginine by pregnant women helps to increase the weight of the fetus.
Intravenous administration of the amino acid (calculated from 50 to 250 mg per 1 kg of weight), according to some scientists, can increase the chances of survival in people after a heart attack or stroke. For diabetics, arginine is useful due to its property of stimulating insulin secretion and increasing the liver’s sensitivity to the hormone.
Consumption of this amino acid has a beneficial effect on the condition of people with tuberculosis or HIV: it helps increase weight and reduces cough. There is also an assumption that this substance prevents infectious complications in people after surgery.
The role of arginine
Arginine is a conditionally essential amino acid. This means that it is produced in the body, but in limited quantities. The body cannot satisfy the greater need for arginine - it has to be supplied with food and supplements. The main role of arginine is related to blood vessels - it is a donor of nitric oxide (NO), which is synthesized in the endothelium (inner surface) of all blood vessels. Nitric oxide increases the elasticity of the walls and expands the lumen of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood flow and blood supply to all organs increases. First of all, this is noticeable on the working muscles of the skeletal muscles, on the heart, and brain cells. Visible effects of nitric oxide:
- During strength exercises, muscles become thicker, engorged with blood, and grow literally before our eyes - which is the pumping effect.
- High blood pressure returns to normal, the heart beats powerfully and rhythmically.
- The brain works clearly and reacts quickly to changing situations.
- Due to blood flow to the genitals, erection increases.
- Fast healing of wounds.
But what does arginine have to do with it? This amino acid is a necessary element for the synthesis of nitric oxide. And since the length of blood vessels in the human body is enormous (100 thousand km!), the need for arginine for the pumping effect is considerable. It is synthesized in the liver and, partially, in the kidneys, enters the bloodstream, where it participates in the reactions of NO synthesis.
The second, no less important role of arginine in metabolism is the removal of protein waste, or more precisely, nitrogen from the body. The process of urea formation begins in the liver under the influence of the enzyme arginase and ends in the kidneys, from where protein waste is excreted in the urine.
In addition, arginine stimulates the release of growth hormone somatotropin into the blood, which regulates anabolic processes, in particular muscle growth. Here it should be noted the pronounced wound-healing effect of the amino acid, which regulates collagen synthesis.
Benefits for the body
Arginine participates in the cycle of conversion of ammonia to urea, thereby reducing the risk of toxins entering the blood and brain, protecting against cirrhosis and various types of hepatitis.
Also, high levels of ammonia in the body lead to insomnia. Therefore, it is important for people with sleep disorders to take care of adequate levels of arginine in the body.
By stimulating the production of the hormones glucagon and insulin, arginine helps build muscle mass and, conversely, prevents fat accumulation. And by increasing cortisol levels, it relieves emotional stress and minimizes the effects of stress.
Thus, the therapeutic benefits of arginine include the following:
- strengthen the cardiovascular system;
- promote the treatment of erectile dysfunction;
- participate in the treatment of anemia;
- act as a growth stimulator in children and adolescents;
- improve the results of bodybuilders;
- promote muscle growth and development;
- reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks;
- reduce blood pressure;
- strengthen immunity;
- participate in maintaining normal cholesterol levels;
- promote proper blood flow, in particular in the smallest vessels;
- prevent excessive blood clotting in some disease states;
- help strengthen memory and increase learning ability;
- increase insulin sensitivity;
- prevent and treat atherosclerosis and vascular calcification.
Impact on the body
Arginine's effects on the body are largely due to its ability to produce nitric oxide, which affects many processes (including blood flow regulation, mitochondrial function, and cellular communication). This has certain positive effects on health and improves athletic performance.
Nitric oxide causes blood vessels to dilate to improve blood flow. L-arginine stimulates the body's release of growth hormone, insulin and other substances.
L-arginine is considered partially or conditionally essential because it is synthesized independently in the normal state. However, under certain circumstances and conditions, its use is necessary (including pregnancy, early childhood, serious illness and injury).
In addition, it acts as a precursor to other amino acids, including glutamate, proline and creatine, and is essential for the health and function of the immune system. Arginine is also necessary for the development of T-lymphocytes - white blood cells that play a central role in the immune response.
Arginine is involved in various processes in the body, including:
- promotes wound healing;
- helps the kidneys remove waste products;
- supports immune and hormonal functions;
- ensures elasticity of arteries.
One of the important functions of arginine is the removal of ammonia, which is extremely toxic to the central nervous system. Because this compound dilates blood vessels, many people take supplements based on it to treat cardiovascular diseases and erectile dysfunction.
However, the effectiveness of arginine in these cases has not been proven. One study even found that taking this amino acid may even be potentially harmful for people who have had a heart attack.
Excessive amounts of arginine can also block the production of lysine, an amino acid used to treat herpes. People suffering from this disease should reduce their intake of this substance by avoiding foods high in it.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
L-arginine is used in pregnancy for certain conditions, including preeclampsia. Supplementation of this amino acid in such cases is usually prescribed and supervised by a physician.
There is some evidence that L-arginine supplements can improve pregnancy and also support the health of the baby and mother. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the body's need for the amino acid increases due to the development of the fetus and the growth of the placenta.
As a result, it cannot be satisfied through diet, especially in women living in low-resource settings and without access to protein-rich foods. However, taking supplements during pregnancy should always be approved and monitored by a physician.
The effects of L-arginine supplementation in breastfeeding women have not been studied. For this reason, taking the substance should only be started with the approval of a doctor.
For certain groups of people
The safety of L-arginine has been demonstrated for everyone, including pregnant women and the elderly. However, some people, including those with diseases affecting the liver or kidneys, should avoid taking this compound.
Arginine supplements are sometimes used in children in clinical settings and are considered safe when given in certain doses. However, their use by children should always be supervised by a doctor. It is not recommended to give L-arginine to your child unless medically necessary.
Daily norm
It is believed that the body of a healthy person should have from 50 to 150 micromoles of arginine. This serving is easily obtained from animal protein products. Approximately 5.5 g of amino acid per day is consumed by people whose diet includes a sufficient amount of fish and meat. Vegetarians should take care of additional sources of amino acids.
Through experiments, the approximate daily dose of arginine was established. However, the dosage depends on many subjective factors and ranges from 6-30 g of the substance per day. Usually, there is a recommendation to take about 6 g of the substance for adults, for children - about 4 g.
Arginine is sometimes called a semi-essential amino acid, because although the body produces the substance, there are cases when additional sources may be required (foods rich in arginine, dietary supplements). Increased doses of amino acids are primarily needed by people with serious illnesses and injuries, and children. In addition, during the first months, the body of newborns is also not able to produce its own reserves of arginine, so this amino acid is also essential for babies. After 35 years, the production of amino acids in the body also slows down.
Recent studies have shown that arginine is extremely useful for people with diseases that suppress the immune system (oncology, AIDS and others). But in these cases, as well as during periods of intensive growth, it can be difficult to “cover” the daily requirement of amino acids exclusively from food and by the body’s efforts. At this time, you can resort to the use of dietary supplements.
Animal products
If you are not a vegan, your diet should include meat, fish and dairy products. They contain not only a large amount of amino acids, but also other useful components necessary for the health of the body.
Meat and meat products
Most meats are rich in arginine. In terms of concentration per 100 g, they are inferior to nuts, but a person can safely eat a large portion of a dietary meat dish without fear of stomach discomfort. Arginine in foods of animal origin is concentrated in large quantities, which means that a lot of amino acids and protein enter the body.
Table 2 - Arginine content in meat products
| Product | Concentration, mg per 100 g |
| Chicken | 1230 |
| Turkey | 1170 |
| Chickens | |
| Beef | 1040 |
| Mutton | 990 |
| Pork | 880 |
Choose lean meats. Chicken and turkey are especially rich in arginine. This is a great option for athletes and bodybuilders who need a lot of protein and amino acids to build muscle mass. And dietary chicken dishes will help you lose weight faster without harm to the body.
Fish and seafood
If you don't like meat, go for fish. It also contains a lot of amino acids, as well as polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and minerals.
Table 3 - Arginine content in fish and seafood
| Product | Concentration, mg per 100 g |
| Red caviar | 1700 |
| Squid | 1560 |
| Chum salmon | 1400 |
| Herring | 1200 |
| Pink salmon | 1070 |
| Zander | 1030 |
| Pike | |
| Sea bass | 1100 |
| Pollock | |
| Mackerel | 1000 |
| Horse mackerel | |
| Cod |
Foods rich in arginine are red caviar, squid and chum salmon. Many varieties of fish and seafood are characterized by a high content of essential and conditionally essential amino acids, so fish dishes should be on the table at least once a week. You can choose both river and sea fish.
Milk and dairy products
A large amount of arginine is also found in dairy products, not only in milk itself, but also in many dishes based on it. An excellent option for replenishing amino acid deficiency.
Table 4 - Arginine content in milk and dairy products
| Product | Concentration, mg per 100 g |
| Parmesan | 1300 |
| Brynza | 1220 |
| Swiss cheese | 840 |
| Cottage cheese | 810 |
| Poshekhonsky cheese | 790 |
| Roquefort | |
| Cheddar | 720 |
| Powdered milk | 670 |
| Feta | 470 |
| Yogurt | 174 |
| Low fat cream | 109 |
| Kefir | 105 |
| Milk | 104 |
| Ice cream | 87 |
The ideal source of arginine is hard cheese. A large concentration of the amino acid is found in almost any variety, but there is especially a lot of arginine in Parmesan, feta cheese and Swiss cheese. Cottage cheese is not far behind, so athletes and those who have a special need for a conditionally essential amino acid should definitely include it in their diet.
Eggs and egg products
Such foods can also be used as a source of arginine. Any eggs will do: chicken, quail, ostrich and others.
Table 5 - Arginine content in eggs and egg products
| Product | Concentration, mg per 100 g |
| Egg powder | 2460 |
| Yolk | 1160 |
| Egg | 790 |
| Quail egg | 660 |
| Protein | 620 |
Oddly enough, the highest concentration of the amino acid is found not in fresh eggs, but in egg powder. When dried and specially processed, a highly concentrated product is obtained that contains several times more useful substances than eggs. But you shouldn't use the powder all the time. There's nothing better than a fried egg or a couple of boiled eggs for breakfast!
Side effects of arginine
Arginine can rarely cause side effects. However, although in isolated cases, diarrhea and nausea were recorded while taking the dietary supplement. Taking the drug in high doses may cause a bitter taste in the mouth. And given that the amino acid has vasodilating properties, it may lower blood pressure. Arginine in the form of intravenous injections contains a high concentration of chlorides, which is fraught with the development of metabolic acidosis. In patients with renal or liver failure while taking amino acids (taken in extremely high doses), hyperkalemia and increased urea levels are possible.
Patients with malignant tumors, those with amino acid intolerance, or those with systemic lupus erythematosus should not get too carried away with the substance.
Signs of Excessive Substance
Reducing amino acid intake is worthwhile for lupus erythematosus and other systemic diseases, for malignant and benign tumors. Adults aged 16 to 35 do not require additional arginine intake.
Symptoms of excess substance are:
- Unreasonable irritability;
- Tremor of the limbs.
The amount of amino acid in the body is influenced by the state of a person’s health and the person’s intake of arginine-containing foods.
Risks of shortage and excess
The minimum daily requirement for arginine is from 2 to 5 g.
Stress, atherosclerosis, hypertension and other factors can increase the body's requirements for amino acids. Signals of acute arginine deficiency can include heart failure, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, growth retardation, and liver problems. Other symptoms: high blood pressure, impaired hormonal metabolism and obesity, early aging, poor brain function.
An excess of the substance can cause allergic rashes, hives, tremors in the arms and legs, and at the psycho-emotional level - nervousness and aggressiveness.
Beneficial properties of arginine and its effect on the body
The amino acid is present in many products and is produced in its pure form as a dietary supplement; it is included in sports nutrition. Its systematic use makes training more effective and speeds up recovery after exercise. Taking the supplement provides endurance. But this connection is important not only for athletes. Arginine has the following beneficial properties:
- improves mood, increases vigor and performance;
- has a positive effect on attention and memory;
- participates in the release of insulin, the production of other hormones, various enzymes;
- improves blood circulation, dilates blood vessels;
- stabilizes arterial and intraocular pressure;
- strengthens the immune system;
- normalizes metabolic processes;
- lowers cholesterol levels.
For men, the amino acid is important because it activates blood flow in the genitals, and therefore relieves erectile dysfunction. For women, the compound is no less useful, because it promotes fat burning.
Signs of a lack of arginine production in the body
Although the substance is not included in the list of essential substances for adults, its systematic deficiency causes various pathologies. The main signs of amino acid deficiency:
- slow growth of the body;
- obesity, metabolic disorders;
- hypertension;
- disorders of the hormonal system;
- decreased libido, deterioration of sperm counts;
- problems with attention.
All these symptoms are not specific to arginine. To confirm its deficiency and treat this condition, you need to take a blood test.
Signs of excess amino acid
Too much of this substance can only be obtained from an overdose of tablets that contain it. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- lowering blood pressure;
- hand trembling;
- skin rashes, urticaria;
- aggressiveness, irritability, mood swings;
- sleep disturbance;
- headache, dizziness.
If taken in sufficiently high quantities, nausea and diarrhea may occur. Therefore, before using the drugs, you must carefully read the accompanying instructions and do not exceed the recommended dosage.
Daily consumption rate
The average requirement for arginine is 5.4 g per day. When entering the body in an amount of 3 to 6 g, no malfunctions in the operation of the systems are observed. It is believed that in a dosage of up to 20 g no unpleasant symptoms occur, but this amount can only be consumed by athletes after consulting a doctor.
In this case, it should be taken according to the following scheme:
- From 3 to 8 g depending on weight 30 minutes before training.
- No more than 3 g after exercise or before bed to recover from exercise.
The intake of the substance can be combined with food, protein shakes, including those containing other important amino acids, for example, lysine. It is permissible to simply drink the capsules or powder with a sufficient amount of water. There are no restrictions here. On the contrary, at the beginning of the course, it is better to combine the use of dietary supplements with meals so as not to provoke diarrhea.
Under normal conditions, without heavy physical activity, the daily dose of arginine in tablet form should be limited to 10 g, because the compound will also enter the body with food.
In the instructions for dietary supplements, the recommended dosage is even lower: 1-3 capsules per day, which in terms of no more than 2-3 g.
Interaction with other elements
For the amino acid to have a beneficial effect, it should not be taken at the same time as alcohol. As for medications, for some, arginine enhances their effect (aminophylline, antiplatelet agents). The effect of isoniazid and vinblastine is weakened by the substance.
Food sources
The best sources of arginine are protein-containing foods: meat, milk, soy, nuts (peanuts, walnuts, pine, almonds), pumpkin seeds, eggs, snails, peas.
Foods rich in arginine
| Product (100 g) | Arginine (g) |
| Pine nuts | 2,4 |
| Walnuts | 2,2 |
| Pork meat | 1,4 |
| Chicken breast | 1,4 |
| Salmon | 1,2 |
| Chicken eggs | 0,8 |
| Milk | 0,1 |
Meanwhile, it is important to know that heat treatment of foods significantly reduces the level of arginine in food. Therefore, whenever possible, you should focus on raw foods. These could be walnuts or cashews, which contain a very high concentration of the substance.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Arginine affects the secretion of insulin, glucagon, and growth hormone. Helps in rehabilitation after injuries, collagen formation and stimulation of the immune system. Increases the number of sperm and T-lymphocytes. Accelerates wound healing and prevents the formation of tumors.
Arginine value, daily requirement, sources of agrinine
Arginine is an amino acid. In an adult and healthy person, arginine is produced by the body in sufficient quantities. In children and adolescents, in elderly and sick people, the level of arginine synthesis is insufficient, so they need to get arginine from food.
The older the body, the more difficult it is for it to produce Arginine, and after 50 years, the production of arginine practically stops.
The child's body is not yet capable of producing Arginine, so it should be ingested only through food - cottage cheese, seafood, chicken, walnuts, liver, chocolate.
Daily requirement for arginine
The daily requirement for Arginine consumption ranges from 4.0 g in children to 6.0 g in an adult.
To replenish the body's daily need for arginine, you need to consume 40 g of pumpkin seeds, eat 100 g of meat or drink 1 glass of milk.
What foods contain a lot of arginine?
Argenine is found in the following foods - primarily nuts and seeds (per 100 g of product):
- pumpkin seeds - 5353 mg - champion in arginine content.
- sesame seed - 3326 mg;
- peanuts - 3506 mg;
- pine nuts – 2413 mg;
- walnuts – 2278 mg;
- almonds - 2492 mg.
Other sources of arginine are the following foods:
- pork - 1394 mg;
- liver - 1256 mg;
- beef - 1194 mg;
- chicken fillet - 1436 mg;
- domestic duck - 770 mg;
- chicken breast - 1033 mg;
- chicken, dark meat - 1211 mg;
- chicken, light meat - 1397 mg;
- chicken egg – 820 mg;
- cow's milk – 119 mg;
- cottage cheese 2% - 623 mg;
- low-fat cottage cheese - 786 mg.
Fish and seafood are also sources of argenine:
- anchovies - 1730 mg;
- white fish - 1142 mg;
- raw salmon fillet – 1221 mg;
- tuna - 1769 mg;
- cod - 1065 mg;
- flounder - 1128 mg;
- carp - 1067 mg;
- herring - 1075 mg;
- eel - 1103 mg;
- snails - 2470 mg;
- shrimp - 1776 mg;
- crabs - 1600 mg.
Flour, cereals and legumes:
- wheat flour – 642 mg;
- corn flour – 345 mg;
- unpolished rice – 602 mg;
- dried peas – 2188 mg.
Those with a sweet tooth will be pleased to know that arginine is found in desserts and gelatin-based products, as well as chocolate and raisins.
Also, this amino acid is now available in the form of special food supplements and is often included in vitamin and mineral complexes.
The importance of arginine for the human body
Arginine is a chemical that is fermented into nitric oxide. This chemical compound is responsible for a number of processes.
- Increased resistance to stress: the presence of nitric oxide in the body limits the release of stress hormones, improves mood, gives energy and strength.
- Arginine promotes vasodilation, i.e. prevents the development of hypertension.
- Strengthens the immune system (accelerates recovery processes, promotes healing of wounds and burns).
- Regulation of the process of programmed cell death, or apoptosis, one of the mechanisms of fighting cancer: if a deficiency of arginine (and, as a consequence, nitric oxide) increases the likelihood of a malignant tumor, then its presence in normal quantities reduces it.
- Stimulation of growth hormone production.
- Burning fat cells and converting them into energy, thereby protecting the liver.
- Improving memory (especially long-term memory, responsible for long-term storage of information and its reproduction).
- Accelerating muscle growth and improving metabolism.
- Improving sexual activity in men and the functioning of the genital organs in people of both sexes.
How to take L-arginine?
Arginine can also be purchased as a sports supplement. Since in this case the free form of the molecule is used (as indicated by the prefix L), the maximum absorption rate is achieved. In bodybuilding, L-arginine is used primarily as a supplement to increase muscle size.
Due to the ability of arginine to increase blood flow, taking the supplement along with pumping training (performing 12-15 repetitions of an exercise with an average weight) can lead to a visual increase in muscle mass. In addition, increased blood flow can speed up recovery time.
The recommended dosage is 3-6 g of L-arigin immediately before training.
Contraindications
A key contraindication to the use of L-arginine (or consumption of foods rich in it) is the presence of the herpes virus. In fact, herpes uses the amino acid to form new cells—significantly speeding up the rate at which the virus grows.
***
New Fitseven materials, 5 times a week - in telegram:
- fit7seven
Arginine is an amino acid needed by the body to produce nitric oxide. This substance, in turn, plays an important role in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, as well as sexual function in men. Taking L-arginine is recommended for athletes to increase pumping.
Scientific sources:
- Influence of dietary arginine on the anabolic effects of androgens, source
Harm of arginine
Despite the enormous benefits, harm still exists. It can only appear with excessive doses (taking more than 15 g/day) and without taking into account contraindications to its use. This drug will satisfy all your expectations when giving up alcohol and central nervous system stimulants; with proper sleep and rest. At this time, all research on the drug continues due to the most unexpected results.
A variety of and conflicting information about the drug has been received. For example, cases have been identified where the overwhelming number of patients taking arginine after heart attacks died.
In heart patients, the risk of death is accelerated when taking this drug. It can even cause atherosclerosis; worsen asthma symptoms. Arginine can worsen the condition of the pancreas and cause pancreatitis. Excessive consumption causes Alzheimer's disease.
The benefits and harms of taking arginine
Its role for blood vessels
Introducing arginine into the diet, which helps improve nitrogen balance, improves protein synthesis, which is necessary for increasing physical and mental abilities.
If there is an amino acid deficiency in the human body, then physical weakness, slow reaction and activation of processes that contribute to the loss of muscle mass are observed.
Other beneficial properties of the amino acid:
- increased blood flow to all organs, including the brain;
- increasing the elasticity of blood vessels and capillaries;
- liver protection;
- preventing blood clots;
- cleansing the body of ammonia;
- increased collagen production.
Additionally, the element helps reduce blood cholesterol and lower intraocular pressure. With periodic intake of the amino acid, the restorative function of the body also significantly increases - wounds and injuries disappear faster than without taking arginine.
Although there are benefits, harm also exists. In addition to individual intolerance, there are other conditions that are not compatible with taking arginine.
- colds on the lips (herpes);
- kidney and pancreas diseases;
- asthma;
- schizophrenia;
- hypotension.
In case of an overdose, the recipient may feel a sharp drop in blood pressure (although the property is useful for hypertensive patients), detect an increase in heart rate and feel pre-fainting.
! The safe limit dosage of arginine is 6.8 g per day.
Why does the body need it?
The need to search for arginine in foods and introduce them into the diet is due to the functions of the amino acid:
- Stimulation and regulation of the circulatory system.
- Prevention of cancer. The amino acid is believed to identify defective cells in the body and destroy them.
- Prevention of viral diseases and improvement of the immune system. Just like cancer cells, the amino acid detects viruses and bacteria and actively fights them.
- Prevention of depression and destruction of stress hormones. This is due to the fact that the hormone promotes the synthesis of endorphin - the hormone of happiness.
- It converts fat cells into the energy the body needs, resulting in active weight loss.
- In the female body, the amino acid has a positive effect on the function of the reproductive system, and this amino acid can also overcome infertility in both women and men.
- The amino acid significantly slows down the aging of the body.
- Heals wounds.
- Improves the condition of nails and hair.
If your body is deficient in arginine, the following health problems may occur:
- hypertension;
- heart ailments;
- disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- growth slowdown;
- decrease in muscle mass;
- increased incidence of viral or bacterial diseases;
- deterioration of brain activity;
- infertility.
Is arginine an important amino acid for the body?
Arginine in foods and the substance produced by the body are the same. The component is used during the fermentation process to convert it into nitric oxide. A new substance will be needed for:
Protecting the body from stress and its negative effects.
It is stress that often interferes with the formation of hormones, which leads to an imbalance, and often to the inability to have children.
- Providing protective functions - arginine, after conversion to nitric oxide, improves immunity.
- Normalization of blood pressure. With a proper diet and ensuring the intake of arginine from food, the risk of developing hypertension is significantly reduced.
- Normalization of metabolic processes in the body, which promotes weight loss.
- Obstacles to the development of pathogenic processes, including cancer.
- Preventing diffuse intestinal spasm.
- Wound healing after injuries of various types.
- Increasing potency in men.
- Ensuring normal brain function and muscle mass gain.
An important component for the body is produced in small quantities by the body itself. However, disruption of production leads to a deficiency that can be filled with the right food.
It is important to understand which foods contain arginine so you can supplement your diet with them.
Arginine has a beneficial effect on the pituitary gland, triggering and normalizing its function. This is what allows a person not to get lost in stressful situations, to remain active, energetic, cheerful, and cheerful.