The role of arginine
Arginine is a conditionally essential amino acid. This means that it is produced in the body, but in limited quantities. The body cannot satisfy the greater need for arginine - it has to be supplied with food and supplements. The main role of arginine is related to blood vessels - it is a donor of nitric oxide (NO), which is synthesized in the endothelium (inner surface) of all blood vessels. Nitric oxide increases the elasticity of the walls and expands the lumen of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood flow and blood supply to all organs increases. First of all, this is noticeable on the working muscles of the skeletal muscles, on the heart, and brain cells. Visible effects of nitric oxide:
- During strength exercises, muscles become thicker, engorged with blood, and grow literally before our eyes - which is the pumping effect.
- High blood pressure returns to normal, the heart beats powerfully and rhythmically.
- The brain works clearly and reacts quickly to changing situations.
- Due to blood flow to the genitals, erection increases.
- Fast healing of wounds.
But what does arginine have to do with it? This amino acid is a necessary element for the synthesis of nitric oxide. And since the length of blood vessels in the human body is enormous (100 thousand km!), the need for arginine for the pumping effect is considerable. It is synthesized in the liver and, partially, in the kidneys, enters the bloodstream, where it participates in the reactions of NO synthesis.
The second, no less important role of arginine in metabolism is the removal of protein waste, or more precisely, nitrogen from the body. The process of urea formation begins in the liver under the influence of the enzyme arginase and ends in the kidneys, from where protein waste is excreted in the urine.
In addition, arginine stimulates the release of growth hormone somatotropin into the blood, which regulates anabolic processes, in particular muscle growth. Here it should be noted the pronounced wound-healing effect of the amino acid, which regulates collagen synthesis.
Beneficial properties of L-arginine
The drug is used by cardiologists, neurologists, urologists and gynecologists for the complex treatment of patients. It is also indispensable in sports nutrition. People who lead an active life or experience heavy loads also need to replenish their amino acid supply.
Amino acid for heart and vascular health
L-arginine keeps the heart and blood vessels in good functional condition. Amino acid benefits:
- by participating in collagen synthesis, it helps to increase strength, maintain the integrity and elasticity of vascular walls;
- as a precursor of nitric oxide, it relaxes and dilates coronary vessels, improving nutrition of the heart muscle;
- prevents the formation of blood clots;
- maintains blood pressure targets;
- improves blood circulation in small peripheral vessels;
- prevents cholesterol from settling on the walls of blood vessels.
An important property of L-arginine is its ability to slow down oxidative processes and protect cells from the damaging effects of free radicals.
The supplement is prescribed to patients with cardiac ischemia, since tests show a lack of amino acids in such patients.
Preparations with L-arginine are recommended for the prevention of heart attacks, strokes and other diseases associated with circulatory disorders.
Arginine and men's health
Erectile dysfunction is a big problem for modern men. It is caused in part by a lack of nitric oxide in the body. Men need arginine to restore potency and improve fertility. How does amino acid help:
WE RECOMMEND THE ARTICLE!
Bee bread improves immunity, tones, restores strength and rejuvenates the body. Read more >>
- increases sperm production and improves its quality;
- normalizes prostate function;
- increases testosterone production;
- promotes blood flow to the genitals and blood supply to the cavernous bodies;
- relieves anxiety and anxiety and increases libido.
L-arginine is often used in the treatment of male infertility.
Women's health and beauty
For women, supplements with L-arginine are necessary to maintain external beauty and the normal functioning of the reproductive system. This is a means to maintain performance, combat depression and excess weight. The amino acid stimulates the production of collagen, which allows you to maintain healthy skin and hair for a long time. And arginine is also called a cure for aging.
Gynecologists include arginine as part of the complex treatment of female infertility.
The amino acid participates in the processes of natural cleansing of toxins and cellular decay products, which stimulates the rejuvenation of the body.
Thanks to increased blood flow in the genitals, their condition improves, libido and the quality of sex increase.
L-arginine promotes the burning of fat deposits. Weight loss occurs due to the fact that the amino acid converts them into energy during anaerobic and cardio exercise.
The amino acid promotes tissue healing, renews and rejuvenates the skin. It has found its application in cosmetics in the form of active additives in sprays, creams and shampoos. The combination of nettle and arginine has proven itself to nourish, restore hair structure and give it strength and elasticity.
Strengthening the immune system
Nitric oxide, which is easily released by the amino acid L-arginine, is a carrier of information that “notifies” brain cells about the appearance of a foreign infectious agent in the body or about cell degeneration. The brain, in turn, gives the command to immune cells to destroy the “enemy.” Thus, the faster the brain cells receive this information, the more effectively the body will cope with the disease.
Lack of amino acid reduces the capabilities of the immune system. L-arginine is prescribed to patients with immunodeficiencies, in particular, HIV-positive and AIDS patients.
Arginine in endocrinology and gerontology
Arginine is involved in the synthesis of ornithine - diaminovaleric acid. Ornithine protects the liver from obesity (fatty hepatosis), reduces the concentration of ammonia in the blood and relieves intoxication. One of the properties of ornithine is to stimulate the work of pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Arginine promotes the release of lactogenic hormone and somatotropin (growth hormone).
By replenishing the content of nitric oxide with the help of arginine, you can maintain efficiency and energy into old age, and reduce the risk of developing neoplasms. Nitric oxide stimulates apoptosis (the natural death of old and damaged cells) and their replacement with new ones.
Sports nutrition
In sports nutrition, L-arginine takes pride of place as a source of nitric oxide. In bodybuilding it is used for the following purposes:
- to increase the effectiveness of training;
- to enhance the cleansing of the body from protein breakdown products and activate the growth of new muscle cells;
- for gaining muscle mass;
- to improve blood supply to muscles and achieve maximum pumping.
The effect of L-arginine is enhanced by other substances that help transport nitrogen, improve cellular respiration, and quickly restore and build muscle mass.
Combination of amino acids
Most often found in combination with arginine:
- citrulline, which increases the concentration of nitric oxide;
- alpha-ketoglutarate, which enhances the effects of arginine to increase muscle mass, increase endurance and prevent muscle tissue breakdown;
- beta-alanine, which reduces muscle fatigue;
- glutamine, which increases energy balance, accelerates protein synthesis and recovery after exercise;
- leucine, which improves protein and carbohydrate metabolism and reduces serotonin levels, thereby increasing endurance.
A long-term result in building muscle mass is achieved by taking a special complex, including arginine, ornithine, vitamin B6 and tryptophan.
The body's need for arginine
Every day the adult body needs 5-6 g of arginine. A bodybuilder who is concerned with pumping up muscles needs an additional 3-9 g per day in supplement form. In older people, arginine synthesis is reduced, so symptoms of its deficiency appear:
- the formation of blood clots as a result of blood stagnation;
- atherosclerosis;
- high blood pressure;
- weakening of mental activity;
- pre-infarction condition;
- obesity.
Taking the supplement at a dose of 2-3 g per day serves as a prophylactic measure to prevent these changes. People with mental disorders and viral infections should not take additional arginine (it provokes relapses of herpes).
An excess of arginine causes nausea, hypotension, irritability and allergic rashes. The additive has an unpleasant taste and is difficult to take in large quantities in powder form.
After 35 years, there is a decrease in internal arginine synthesis, so you should pay attention to foods rich in this amino acid.
Contraindications for arginine use
Taking L-arginine supplements is contraindicated for herpes infections. The virus uses the amino acid for its own reproduction, so an exacerbation of the disease is possible. You can't take an amino acid:
- people with mental disorders;
- pregnant and nursing mothers;
- for those who have individual intolerance to dietary supplement components;
- children in the active growth stage;
- patients diagnosed with malignant neoplasms.
Patients with diabetes and those with electrolyte imbalance should be careful when using supplements.
Getting arginine from food
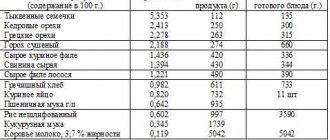
60-70% of the need for arginine is satisfied during its circulation in the body, 20-25% comes from food. The first place in the content of the amino acid arginine is occupied by pumpkin seeds: 5 g per 100 g of product. substances, to meet the daily requirement for an adult, it is enough to chew a handful of 40 g of seeds. The second most arginine content is the product beloved by men – meat. Different types of meat contain up to 2 grams of arginine. A required glass of milk per day for children gives them 1g of extra amino acid. To create a diet rich in arginine, use the data in the table.
Can there be a deficiency of arginine in the body?
Lack of arginine occurs in conditions of an unbalanced diet, as well as during significant physical activity and illness. With a lack of arginine, brain function deteriorates, the risk of developing diabetes increases, and weakness appears. A lack of this amino acid can lead to hypertension and heart attacks, causing premature aging of the body. Arginine deficiency can be eliminated with the help of special nutritional supplements and a balanced menu.
Arginine for athletes, what is its benefit?
When exercising regularly, it is recommended to take additional arginine in the form of dietary supplements. The amino acid helps increase the body's endurance and speeds up recovery after grueling physical activity.
Arginine stimulates blood circulation, which promotes accelerated blood flow to muscle tissue. As a result, the muscles are better enriched with oxygen and nutrients. Arginine also stimulates the secretion of growth hormone, so when consuming this amino acid, an increase in muscle mass is observed
Taking arginine simultaneously with regular physical activity triggers the process of active burning of fat cells. The amino acid increases the production of nitric oxide in the body, which stimulates metabolism and ensures an accelerated supply of glucose to the muscles.
Amount of arginine in food
| Name | Amount of arginine g/100 g |
| pumpkin seed | 5,5 |
| Peanut | 2,9 |
| Walnut | 2,3 |
| sunflower seed | 1,8 |
| Lentils | 2 |
| Peas | 1,6 |
| Beans | 1,1 |
| Cheese | 1,3 |
| Chicken | 1,2 |
| Beef | 1 |
| Pork | 0,8 |
| Red caviar | 1,7 |
| Sea fish | 1,2-1,0 |
| Egg white | 0,8 |
| Wheat flour | 0, 64 |
| Buckwheat | 1.1 |
| Rice | 0,6 |
| Milk | 0,3 |
Natural Sources of Arginine
A person can get arginine from food. To do this, you need to include pumpkin seeds, nuts, legumes and various types of meat - beef, turkey, chicken - in your daily diet. Arginine is also present in some types of fish and dairy products.
Products with the maximum arginine content are listed in the table.
| The product's name | Amount of arginine (mg/100 g) |
| Pumpkin seeds | 5353 |
| Sesame | 3326 |
| Peanut | 2975 |
| Egg white | 2460 |
| Chum salmon | 1400 |
| Chicken fillet | 1230 |
| Brynza | 1220 |
| Turkey meat | 1170 |
| Beans | 1120 |
| Tuna | 1794 |
Additional sources
Natural sources of arginine are food, but people rarely manage to perfectly balance their diet. When playing sports and certain diseases, the need for this amino acid increases. In this case, it is necessary to consume a large amount of foods high in arginine every day, and this is not always possible.
An additional source of arginine are special food supplements, which are available in the form of tablets, capsules, liquid solutions or powder. They can contain arginine in pure form or in combination with other important amino acids. Dietary supplements with arginine are indicated for athletes, people with diabetes, as well as patients with injuries and dangerous diseases.
Why the supplement doesn't work
It has been experimentally established that it is useless to take more than 6 g of arginine per day - in large quantities it will not leak into the blood and will not provide a pumping effect. The fact is that arginine binds to the enzyme arginase in the intestine and goes to the liver to perform its second metabolic function there. It is involved in the utilization of protein waste (ammonia), converts it into urea and carries it through the kidneys to the outside.
The supplement works for pumping in those athletes who have little arginase in their bodies - then arginine is absorbed into the blood and becomes a donor of NO, with all the ensuing effects. Such athletes praise the supplement and consider it to work. To ensure pumping, it must be taken in quantities from 3 to 7 grams. It is advisable to drink arginine on an empty stomach: before meals or 1-1.5 hours after it (so that the insidious arginase does not take the supplement to the liver). When calculating the dosage, take into account the arginine content in the supplements you drink before exercise - it is included in most pre-workout complexes.
Everyone else can be advised to take its analogue, citrulline malate, instead of arginine. The peculiarity of this supplement is that, bypassing the liver and without contacting arginase, it enters the bloodstream, where it is converted into arginine and participates in the synthesis of nitric oxide.
Instructions for use
An adult needs no more than 3 g of amino acid per day. Her reception should be divided into three times. You need to take arginine in capsules and tablets 2-3 times a day, depending on the dosage. The powder is diluted in water and taken 5 ml three times a day. Arginine solution is administered dropwise. You need to drink dietary supplements in any form during meals. The duration of the course is from two weeks to one month.
The dose and duration of the course are prescribed depending on the purpose of administration, general condition, disease and age of the patient.
For medicinal purposes to help the cardiovascular system or in the treatment of erectile dysfunction, the dose per day can range from 3 to 9 g.
Athletes require an increased dose of amino acids - 5-9 g, but not more than 10 g per day. It is optimal to use the supplement half an hour before and during training. To stimulate the release of growth hormone, complex preparations with arginine are taken before bedtime.
The break between courses should be at least 2.5 - 3 months
Having studied the effect of L-arginine on the body of athletes, scientists came to the conclusion that long-term use of the supplement does not have a negative effect and does not produce side effects.
[media=
https://youtu.be/ySfwVJ_uEAI
]
Application in sports
For athletes, L-Arginine is considered one of the most important amino acids. This is due to the pronounced effect, which is felt within 30 minutes after administration. The amino acid is of greatest value as a donor of nitric oxide. The substance dilates blood vessels and increases blood flow to the muscles. This gives:
- Improved pumping effect;
- Accelerating muscle recovery after training;
- Improved muscle growth due to increased blood flow to the muscles;
- Increases muscle growth.
There is an opinion that Arginine is able to increase the production of growth hormone, but in this area the scientific evidence base is considered insufficient. Also, the substance should not be considered as a potential fat burner. Most studies that have found a fat-burning effect have been conducted on older people or subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. For people who train, this effect may be much weaker.
Among the proven effects of the amino acid, improvement in the transport of creatine into muscles should be highlighted. Therefore, supplements are often taken together to increase efficiency and synergistic action.
Delivery throughout Russia You can order sports nutrition in the KULTURIST#1 online store anywhere in Russia. More detailed information about delivery can be found on the “Delivery and Payment” page.
Retail store addresses
#1 St. Petersburg Strike Avenue 96k3, st. m. Avtovo
#2 Novorossiysk st. Yuzhnaya, 21
#3 Sochi st. 20th Mountain Rifle Division, 18a
Biochemical profile
Arginine is a semi-independent amino acid – meaning it is not required in the diet. However, although our bodies produce it, supplementation is sometimes beneficial for athletes and bodybuilders. Arginine is obtained from foods (whole wheat, nuts, seeds, dairy products, poultry, red meat and fish) or taken as a supplement.
The benefits of L-arginine stem from its role in protein synthesis. It acts as a precursor to nitric oxide, a powerful vasodilator. Arginine is important for cellular function, muscle development, treatment of erectile dysfunction, high blood pressure and congestive heart failure.
Daily norm
It is believed that the body of a healthy person should have from 50 to 150 micromoles of arginine. This serving is easily obtained from animal protein products. Approximately 5.5 g of amino acid per day is consumed by people whose diet includes a sufficient amount of fish and meat. Vegetarians should take care of additional sources of amino acids.
Through experiments, the approximate daily dose of arginine was established. However, the dosage depends on many subjective factors and ranges from 6-30 g of the substance per day. Usually, there is a recommendation to take about 6 g of the substance for adults, for children - about 4 g.
Arginine is sometimes called a semi-essential amino acid, because although the body produces the substance, there are cases when additional sources may be required (foods rich in arginine, dietary supplements). Increased doses of amino acids are primarily needed by people with serious illnesses and injuries, and children. In addition, during the first months, the body of newborns is also not able to produce its own reserves of arginine, so this amino acid is also essential for babies. After 35 years, the production of amino acids in the body also slows down.
Recent studies have shown that arginine is extremely useful for people with diseases that suppress the immune system (oncology, AIDS and others). But in these cases, as well as during periods of intensive growth, it can be difficult to “cover” the daily requirement of amino acids exclusively from food and by the body’s efforts. At this time, you can resort to the use of dietary supplements.
Benefits and effects of Arginine
Arginine is considered a very valuable amino acid due to its effects. It is used in medicine, for the prevention of various diseases, and in sports. Most of the beneficial effects of Arginine have a serious scientific evidence base, but scientists continue to study the substance in depth. Therefore, every year the potential list of beneficial effects expands, which is facilitated by every major RCT.
The main effects of taking Arginine:
- Improving the supply of nutrients to muscles and other tissues;
- Nitric oxide donor;
- Accelerates the recovery of muscle tissue, improves the healing of injuries;
- Takes part in the metabolism of proteins and fats;
- Slight acceleration of fat burning in obesity and in people with impaired glucose tolerance;
- Increased endurance;
- Normalization of blood pressure.
Also, the use of L-Arginine is useful in old age, when protein synthesis and amino acid production in the body decrease. This serves as a prevention of cardiovascular diseases, as well as many problems associated with impaired blood flow to the brain and other organs.
Women need arginine to increase fertility and normalize sexual function. For men, the amino acid improves sexual function and prevents the development of prostatitis due to increased blood flow and vasodilation.
Possible contraindications
The potential benefits and harms of Arginine are considered to be sufficiently studied, therefore, based on current research, the supplement is considered completely safe. However, possible negative effects are only associated with non-compliance with recommended dosages. Side effects when dosages are exceeded:
- Nausea;
- Weakness;
- Diarrhea;
- Reduced blood pressure.
If any side effects occur, the dosage should be reduced to a level at which they disappear.
The only contraindications to Arginine include:
- For pancreatitis and problems with the pancreas;
- If kidney stones occur (may provoke their passage);
- In the case of the Herpes virus, the amino acid is used to create new viral cells, so consumption in increased quantities can cause an exacerbation.