What is dietary fiber?
Fiber is the so-called complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), slowly digestible components that are mainly contained in plant foods:
- mushrooms;
- vegetables;
- corn;
- legumes.
If you need to increase your fiber intake in your daily diet, you should replace processed grains and processed foods with foods higher in fiber, such as:
- brown bread;
- wholemeal paste;
- unpolished rice;
- breakfast cereal.
You should also eat as many fiber-rich vegetables as possible, such as:
- artichokes;
- green pea;
- White cabbage;
- parsnip;
- spinach;
- Jerusalem artichoke.
As a snack, it is better to give preference to dried fruits. At least once a week you need to prepare dishes from legumes (lentil porridge, pea soup, stewed beans) or add them to salads and snacks.
Beans can also be combined with desserts, yogurts, breakfast cereals, baked goods, cereals and fruits. It is better to prepare a sauce, gravy, or appetizer from vegetables. When purchasing a particular product, it is worth studying the label on the package to determine its fiber content.
The benefits of fiber for hemorrhoids
Eating foods rich in fiber (see the section above for a complete list) is especially important for hemorrhoids.
Hard dietary fiber, like a sponge, absorbs large amounts of moisture and softens stool, facilitating its passage through the rectum without irritating the mucous membrane.
The basis of the diet should be fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals, bananas, dried apricots, prunes and 60 grams of bran daily.
We still peel the avocado
You should adhere to the following nutritional rules:
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions
- Give preference to buckwheat, barley, pearl barley and oatmeal porridge
- Choose bread from wholemeal, bran and black flour
- Avoid baked goods and pasta
- Choose the right vegetables: beets, cauliflower, broccoli, cucumbers, zucchini, raw, stewed and steamed carrots
- Drink 1.5-2 liters of water per day
- Limit tea, coffee, alcohol
Steam vegetables
Forms of fiber
In total, 2 types of fibrous substances can be distinguished depending on their interaction with water.
Insoluble
Insoluble dietary fiber does not grow in volume when passing through the gastrointestinal tract, as it absorbs a minimum of moisture. By doing this, they activate the activity of the digestive system, thus stimulating the transit of toxins, waste and undigested food residues.
Insoluble fiber polysaccharides are found in large quantities in hard-skinned vegetables and fruits, as well as bran and whole grains. It has a more solid microstructure, almost does not transform during movement through the intestines, but can significantly increase the volume of processed mass.
Soluble
When soluble fiber enters the body, it begins to absorb liquid, then increases in volume and becomes a viscous and thick mass. A clearly similar process can be observed during the preparation of oatmeal.
By swelling, soluble fiber fills the stomach and causes a feeling of fullness.
Most of them are found in the following products:
- apples;
- carrots;
- potatoes;
- oranges;
- beans;
- oatmeal;
- barley;
- chia seeds.
Both groups of fibers significantly add bulk to the food you eat without increasing its calorie content. This is due to the fact that food enzymes are not able to break down fiber; this process is carried out by bacteria inhabiting the human intestines, and it is called fermentation.
The resulting products are absorbed by our body. These are mainly fatty acids, as well as butyric, formic and acetic acid. It is very difficult to determine the exact volume of residual products. Dietitians unanimously claim that the calorie content of 1 g of fiber is about 2 kcal.
Dietary fiber, greatly increased in volume, has a mechanical effect on the digestive system, thanks to which a person feels full. Lack of fluid while eating foods high in dietary fiber can cause constipation.
What foods contain soluble and insoluble fiber?
However, knowing the fiber content of a product is not enough. Dietary fibers vary in their physical and chemical properties. Accordingly, their effect on the human body also differs.
Insoluble fibers are represented by lignin and cellulose. Lignin has the property of binding bile acids. Thanks to it, cholesterol levels in the circulatory system are reduced. It also protects the gallbladder from stone formation. Cellulose accelerates the movement of food debris through the gastrointestinal tract.
When insoluble fiber enters our body with food, it plays the role of a kind of sponge that cleanses the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. With its deficiency, toxic substances accumulate in the intestines, and the population of pathogenic bacteria also increases, the waste products of which cause harm to the body.
Soluble dietary fiber does not form a “sponge”, but a “jelly”. In addition to their main role, improving intestinal motility, they interfere with the proliferation of putrefactive bacteria, thereby improving the condition of the microflora.
Some of the products listed in the tables above contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, while some contain only one of its types.
Types of fiber
In addition to water, fiber can interact with alkalis. Considering this factor and the amount contained in parts of plant foods, it is customary to distinguish 5 types of dietary fiber.
Cellulose
This substance is the main constituent of plant cell walls. Cellulose belongs to the group of insoluble types of polysaccharides.
It is a component in the following products:
- wholemeal wheat flour;
- bran;
- Brussels sprouts, white cabbage;
- beets;
- broccoli;
- radishes;
- young pea pods;
- tomatoes;
- peel of apples, sweet peppers, cucumbers.
Cellulose absorbs excess fluid, thereby activating the work of the colon. The daily intake of this substance is 19-38 g, depending on the age and gender of the person.
Hemicellulose
This type of complex carbohydrates predominates in the following foods:
- sprouted wheat;
- lentils;
- bran;
- apples;
- grain;
- mustard sprouts;
- corn;
- Brussels sprouts.
Almost all types of such polysaccharides can be dissolved. Hemicellulose absorbs liquid, thereby facilitating intestinal function.
Both types of this substance help quickly cleanse the gastrointestinal tract of processed food residues and prevent the following diseases:
- constipation – stool becomes more frequent;
- colitis – inflammation is relieved;
- spasms in both parts of the intestine;
- haemorrhoids;
- colon cancer.
The human body needs to consume 5-25 g of hemicellulose per day.
Lignin
This is another type of insoluble dietary fiber, which is found in significant concentrations in the following products:
- cereals;
- beans;
- eggplants;
- radishes;
- strawberries
Moreover, stale fruits and vegetables contain more lignin than freshly picked ones. The distinctive quality of this type of fiber is its special viscosity, which prevents the absorption of harmful substances and promotes the rapid removal of food debris from the intestines.
Moreover, due to the property of lignin to interact with the acids of the gallbladder, the level of cholesterol in the blood decreases. The body's daily requirement for the element is 5-6 g.
Comedy
This is a soluble type of polysaccharide that is part of tree sap. Since gum is a polymer of dietary fiber, it is found not only in the peel, but also in the pulp of vegetables and fruits.
Most gums are presented in the following products:
- oatmeal and other dishes made from oats;
- walnuts;
- dried beans;
- zucchini and pumpkin;
- potatoes;
- strawberries;
- barley;
- carrots.
Gums suppress appetite, lower cholesterol, are a source of vitamins and slow down the absorption of glucose, which is especially useful for patients with diabetes.
Pectin
Pectin is found in abundance in the following foods:
- citrus fruits;
- apples;
- carrots;
- green beans;
- cabbage;
- potatoes.
The element participates in the digestive process not only directly in the stomach, but also in the large intestine.
Beneficial properties of dietary fiber
Fiber is necessary for the body because it performs the following functions:
- promotes accelerated removal of food from the digestive tract. The longer fiber is digested by the gastrointestinal tract, the more difficult it is to eliminate it later. Usually this process is accompanied by bloating, flatulence and gas formation. Fiber stimulates such reactions in the body and promotes its natural cleansing. That is why people suffering from intestinal problems are recommended to introduce more fiber products into their diet;
- dietary fiber in combination with plenty of drinking normalizes intestinal motility, and the more fiber a person consumes, the more water he needs to drink daily;
- dietary fiber prevents the intestines from slowing down, which causes constipation, and inhibits its accelerated work, as a result of which a person suffers from diarrhea. This double effect is due to increased intestinal motility, the muscles of which actively contract, and also due to the flow of fluid, which increases the volume of stool;
- fiber slows down the digestion of food, controls appetite and the feeling of fullness;
- dietary fiber creates the basis for favorable intestinal microflora, so nutritionists note that fiber is involved in the prevention of many diseases, including the following:
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- diabetes;
- cancer;
- obesity;
- consuming fiber reduces the likelihood of developing infectious and inflammatory processes, since it has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system.
Recent nutritional research has highlighted the benefits of polysaccharides for humans, both in normalizing digestion by increasing the rate of waste elimination and in releasing waste and toxins.
This explains why many people adjust their diet and switch to “roughage”, which helps to get rid of excess weight and normalize the process of processing food by the body.
In addition to its adsorbing effect, fiber also has the following beneficial properties:
- gives a feeling of satiety, which is especially valuable when dieting;
- normalizes appetite;
- improves the secretory function of the stomach;
- reduces the risk of malignant tumors of the colon;
- saturates the body with vitamins, minerals and microelements;
- slows down the increase in blood glucose levels;
- reduces cholesterol levels;
- normalizes blood pressure.
Why is a lack of complex proteins dangerous?
A lack of polysaccharides in the daily diet can lead to disturbances in intestinal motility, which is the main cause of constipation. A prolonged lack of fiber in the diet increases the risk of developing quite serious diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Even in the presence of chronic digestive problems, for example, irritable bowel syndrome, it is recommended to continue consuming foods high in dietary fiber, with the only difference being that the patient’s individual intolerance to certain substances is taken into account.
Excessive consumption of polysaccharides does not lead to serious health consequences. However, too much of them in the body can cause unpleasant symptoms such as diarrhea and flatulence. It is worth noting that such cases are quite rare.
Why are deficits and surpluses dangerous?
Fiber deficiency is:
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - with a deficiency of fiber, the stomach and intestines are primarily affected;
- weight gain - soluble fiber monitors blood sugar levels, and the feeling of hunger is closely related to this. As soon as this level drops below normal, we become hungry again and overeat;
- the risk of developing serious diseases - without fiber, the level of “bad” cholesterol and glucose increases, and this is one of the causes of heart disease and diabetes.
Excess fiber in the diet is less common and only with a very large dosage - 70 g per day. Side effects can be caused by veganism, a high-fiber diet, and nutritional supplements.
- intestinal disorders (bloating, abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea) – the body does not absorb fiber, so its excess clogs the intestines;
- dehydration – soluble dietary fiber removes a large amount of fluid from the body;
- deficiency of valuable substances - studies show that a large amount of plant fiber interferes with the absorption of iron, zinc and other important elements.
Fiber requirement standards. Table by age
The daily fiber requirement is approximately 25-30 g, but most people have no more than 15 g of this substance in their diet.
For normal intestinal functioning, EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) recommends following the following consumption standards:
| Age | Floor | Daily requirement | |
| 1-3 years | boys and girls | up to 14 g | |
| 4-7 years | 17-19.5 g | ||
| 8-12 years | 22-25 g | ||
| 13-18 years old | boys and girls | 25-31 g | |
| 19-30 years old | 22-35 g | ||
| 30-50 years | men | 40 g | with a non-standard diet 14 g per 1,000 kcal |
| women | 25 g | ||
| over 50 years old | men | 30 g | |
| women | 21 g | ||
To prevent organ pathologies, as well as type 2 diabetes, it is necessary to include in the daily menu more dishes and foods rich in fiber - the volume of its consumption should be at least 30 g every day. Experts give a similar recommendation to people with cancer and obesity.
Restrictions
You can avoid the negative consequences of excess fiber entering the body if you consume it in moderation and not on an empty stomach. The best option is to combine foods with dietary fiber and some liquids.
For example, if beans are consumed at one meal, then at the same time you should eat soup or drink compote, water, or tea as the first course. Including foods rich in dietary fiber in your menu helps improve digestion.
Their excess leads to diarrhea, rotting, poor digestion and fermentation of food, constipation, which causes the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- intestinal obstruction;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdominal cavity;
- hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus.
If the listed symptoms appear, you should consult a physician or gastroenterologist about the advisability of continuing to consume fiber.
With caution, you should include fibrous foods in your daily menu in large quantities in case of diseases of the stomach or duodenum during exacerbation of diseases.
List of the best foods rich in fiber. Benefits and contraindications
In order not to harm your body, you need to know about the volume of this element in each product consumed.
Cereals and pasta
Dietary fiber in food products (the table includes background information on their content) in pasta and cereals is contained in different concentrations:
| Finished product | Volume of fiber per 100 g of raw materials | Part of the daily value for an adult (30 g) |
| barley | 14.5 g | 48 % |
| buckwheat | 14 g | 47 % |
| buckwheat | 11.4 g | 38 % |
| rice | 9.7 g | 32 % |
| oatmeal | 8 g | 27 % |
| pearl barley | 7.8 g | 26 % |
| corn noodles | 4.8 g | 14 % |
| whole wheat noodles | 4.8 g | 14 % |
| corn grits | 4.8 g | 16 % |
| wheat cereal | 4.6 g | 15 % |
| semolina | 3.6 g | 21 % |
| pasta | 1.8 g | 5,4 % |
| egg noodles | 1.2 g | 3,6 % |
| rice noodles | 1 g | 3 % |
Cereals and pasta are beneficial for the body due to the following effects:
- prolonged feeling of fullness;
- the protein contained in the composition stimulates cell growth and regeneration;
- contains antioxidants;
- help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract.
Contraindications for use - excess starch content can lead to weight gain.
Legumes
Legumes also contain fiber. Its volume is indicated in the table:
| Finished product | Volume of fiber per 100 g of raw materials | Part of the daily value for an adult (30 g) |
| beans | 12.4 g | 41 % |
| lentils | 11.5 g | 38 % |
| mung bean | 11.1 g | 37 % |
| peas | 10.7 g | 36 % |
| chickpeas | 9.9 g | 33 % |
| soya beans | 6 g | 18 % |
Positive aspects of eating legumes:
- high protein content;
- can be given to children from 8-9 months of age;
- legumes cleanse the body of cholesterol;
- due to the presence of nutrients in the composition, they are recommended for use during pregnancy;
- these products improve heart function and stabilize hormonal levels;
- the condition of the skin, hair, nails improves;
- legumes actively remove radionuclides and heavy metal salts from cells.
The possible harm that beans can cause to the body is expressed in the aggravation of pathologies such as:
- hepatitis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- tendency to constipation and gas formation in the intestines;
- gout;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- circulatory failure.
Vegetables
Dietary fiber in food (the table contains data on vegetables) helps the body cleanse itself, so it is important to include it in the diet in the required quantity:
| Finished product | Volume of fiber per 100 g of raw materials | Part of the daily value for an adult (approximately 30 g) |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 4.5 g | 15 % |
| cabbage | 2-4 g | 7-14 % |
| beet | 2.5 g | 8 % |
| carrot | 2.4 g | 8 % |
| radish | 2.1 g | 7 % |
| pumpkin | 2 g | 7 % |
| Sweet pepper | 1.9 g | 6 % |
| turnip | 1.9 g | 6 % |
| radish | 1.6 g | 5 % |
| garlic | 1.5 g | 5 % |
| potato | 1.4 g | 5 % |
| tomato | 1.4 g | 5 % |
| zucchini | 1 g | 3 % |
| cucumber | 1 g | 3 % |
Including vegetables in the daily menu benefits the body, which is reflected in the following effects:
- the composition contains trace elements and acids that have a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- vegetables are quickly digested, giving a person strength and vigor for the whole day;
- vegetables contain many vitamins that stimulate the nervous system;
- products free the body from toxins, carcinogens and toxins.
Vegetables can harm human health only in the case of individual characteristics of the body and chronic diseases. For example, white cabbage is not recommended for consumption if a person has increased gastric secretion or is diagnosed with pancreatitis.
Animal products
Animal products do not contain fiber, as it is an element of plant foods.
Berries and fruits
Dietary fiber in foods (the table contains a list of berries and fruits rich in fiber) is necessary for the body to function normally. When compiling a diet, you should take into account the concentration of fiber contained in foods:
| Finished product | Volume of fiber per 100 g of raw materials | Part of the daily value for an adult (approximately 30 g) |
| dried figs | 18.2 g | 61 % |
| dried apricots | 17.6 g | 59 % |
| dried peach | 14.9 g | 50 % |
| dried apples | 14.9 g | 50 % |
| rose hip | 10.8 g | 36 % |
| raisin | 9.6 g | 32 % |
| prunes | 9 g | 30 % |
| avocado | 6.7 g | 22 % |
| feijoa | 6.4 g | 21 % |
| cloudberry | 6.3 g | 21 % |
| dried pear | 6 g | 20 % |
| dates | 6 g | 20% |
| red rowan | 5.4 g | 18 % |
| black currant | 4.8 g | 16 % |
| chokeberry | 4.1 g | 14 % |
| durian | 3.8 g | 13 % |
| kiwi | 3.8 g | 13 % |
| raspberries | 3,7 | 12 % |
| quince | 3.6 g | 12 % |
| white currant | 3.4 g | 11 % |
| Red currants | 3.4 g | 11 % |
| cranberry | 3.3 g | 11 % |
| blueberry | 3.1 g | 10 % |
| blackberry | 2.9 g | 10 % |
| pear | 2.8 g | 9 % |
| cowberry | 2.5 g | 8 % |
| blueberry | 2.5 g | 8 % |
| fresh figs | 2.5 g | 8 % |
| orange | 2.2 g | 7 % |
| strawberries | 2.2 g | 7 % |
| apricot | 2.1 g | 7 % |
| peach | 2.1 g | 7 % |
| lemon | 2 g | 7% |
| sea buckthorn | 2 g | 7 % |
| mandarin | 1.9 g | 6 % |
| cherry plum | 1.8 g | 6 % |
| cherry | 1.8 g | 6 % |
| grapefruit | 1.8 g | 6 % |
| apples | 1.8 g | 6 % |
| banana | 1.7 g | 6 % |
| nectarine | 1.7 g | 6 % |
| papaya | 1.7 g | 6 % |
| grape | 1.6 g | 5 % |
| mango | 1,6 | 5 % |
| persimmon | 1.6 g | 5 % |
| plum | 1.5 g | 5 % |
| a pineapple | 1.2 g | 4 % |
| cherries | 1.1 g | 4 % |
| pomelo | 1 g | 3 % |
| pomegranate | 0.9 g | 3 % |
| melon | 0.9 g | 3 % |
| watermelon | 0.4 g | 1 % |
Berries and fruits bring great benefits to the human body, this is expressed by their effects:
- participate in cleansing the intestines;
- with increased consumption, berries and fruits do not harm the figure;
- these products stimulate cell regeneration and prevent moisture evaporation;
- pectin normalizes sugar levels and removes carcinogens;
- fruits and berries contain vitamins and microelements.
- If these products are consumed unbalanced, they can harm the body:
- cause an allergic reaction;
- Peaches and apricots take a long time to digest and can cause a feeling of heaviness;
- consuming large amounts of sweet varieties can lead to the development of varicose veins;
- exotic fruits, plums and grapes relax the intestinal muscles and can cause diarrhea.
What fibrous foods are allowed during pregnancy?
Dietary fiber in food consumed daily brings undeniable benefits to the body. This is especially important for women carrying a child. It is important for them to compose their menu in accordance with the tables of fiber content in products so that it is as balanced as possible.
The daily diet of pregnant women must include fresh fruits and vegetables.
They help normalize stool and regular bowel movements, and also help maintain stable blood glucose levels. They are recommended to eat up to 2 kg of vegetables and fruits daily. At the same time, apples, pears, apricots and peaches should be consumed with the peel, since it contains the most dietary fiber.
The main sources of fiber for pregnant women are whole grain products. Rice, rye and wheat bran are high in dietary fiber. However, their excess in the body prevents the normal absorption of other nutrients obtained from their food.
In addition, nutritionists recommend adding peas and lentils to your diet. In addition to their high dietary fiber content, they are sources of iron, calcium, zinc, and phosphate.
It is especially useful to enrich the diet with foods rich in fiber for pregnant women in the last trimester. During this period, the fetus begins to put pressure on the organs of the digestive system, which causes problems with digestion of foods.
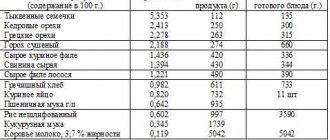
1-4: Seeds and nuts
Almost all seeds and nuts are high in dietary fiber. In addition, nuts have a special set of beneficial properties: prevention of diabetes and atherosclerosis, improvement of metabolism and microcirculation. American studies have also shown that nuts help prevent the development of fatal cardiovascular complications.
Chia seeds (33.4%)
Fiber: 34.4 grams per 100 grams.
Chia seeds contain the most dietary fiber on the planet.
They also contain a lot of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which have a beneficial effect on the health of the heart and blood vessels, preventing the development of atherosclerosis and the formation of parietal blood clots.
Pumpkin seeds (18.0%)
Fiber: 18.0 grams per 100 grams.
Pumpkin seeds are the main suppliers of valuable polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, magnesium, zinc, arginine, as well as vitamins A and E.
When consumed, there is an improvement in the aesthetic properties of the skin (increased smoothness and elasticity), a decrease in blood pressure and glucose levels in the blood plasma.
Almonds (12.5%)
Fiber: 12.5 grams per 100 grams or 0.25 grams per medium sized nut.
Almonds are the most popular type of nut. Almonds contain valuable fats, manganese, magnesium and vitamin E in large quantities. They help cleanse blood vessels, reducing the level of total cholesterol in the blood. With systematic consumption, a decrease in body weight is observed.
Bulgur wheat (4.5%)
Fiber: 4.5 grams per 100 grams.
It is a whole grain product popular in Middle Eastern countries. Used as an alternative to the usual rice in salads.
Products with dietary fiber and rules for reasonable weight loss
Regular consumption of foods high in fiber helps you lose extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. A sufficient amount of dietary fiber can speed up metabolism at rest, that is, when a person burns some calories without engaging in sports or other physical activity.
Most foods high in fiber (fruits, vegetables, greens) are low in calories. Those who want to lose weight need to eat more of these foods to feel and look healthy. They quickly saturate the body, which helps eliminate excess weight and maintain excellent physical shape.
The rules for losing weight with dietary fiber dictate the following points:
- You need to consume 20 g of fiber daily. This volume is provided by 800 g of vegetables and fruits eaten with peel;
- pearl barley, buckwheat, oatmeal, as well as brown rice will provide up to 5-7 g of fiber in the diet;
- 100 g of whole grain bread contains up to 6 g of dietary fiber;
- 2 times a week it is necessary to introduce into the diet dishes prepared with the addition of lentils, beans or peas;
- Every day you need to consume up to 6 tbsp. l. steamed bran;
- confectionery sugar must be replaced with dried fruits;
- During snacking periods, you should eat nuts or seeds.
To lose weight, you need to eat fiber-rich foods in the morning. Also, nutritionists do not recommend drinking water with food.
The menu should be compiled according to the following principle:
- salads – 25% of the diet;
- fruits – 25% of the diet;
- fresh or cooked vegetables - 25% of the diet;
- cereals and legumes – 10% of the diet;
- nuts – 10% of the diet;
- vegetable fats – 5%.
Most products of plant origin contain dietary fiber, but the following are considered the best (in descending order of the amount of fiber they contain per 100 g of product):
- Wheat bran – 46.6 g.
- Chia seeds – 34.4 g.
- Flax seeds – 27.3 g.
- Dried porcini mushrooms – 26.2 g.
- Poppy seeds – 19.5 g.
- Buckwheat grain – 14.0 g.
- Beans – 12.4 g.
- Lentils – 11.5 g.
Dietary fiber is an essential part of a healthy human diet. When calculating the daily menu, it is advisable to use a table of the content of these substances in food products. In this case, it will be possible to say with confidence that the body will receive a sufficient amount of fiber for its normal functioning.
Chia seeds
Despite their small size, chia seeds are rich in certain nutrients.
In addition to being high in fiber, protein, and a range of vitamins and minerals, chia seeds are one of the best-known plant sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
Chia seeds can be sprinkled on top of salads and yogurt or added to smoothies.
They also absorb liquid well, turning into a gel that can be used as a vegan egg replacer or as a thickener for sauces and jellies.
Two tablespoons (30 grams) of chia seeds contain 11 grams of fiber and 2 grams of net carbs (16).