Most people who have tried to change their figure know that the process of losing weight can be difficult and lengthy. However, while losing extra pounds is quite possible, maintaining the result is much more difficult. This is primarily due to the launch of a number of adaptive mechanisms in the body, which are aimed at minimizing weight loss.
This article does not try to attribute everything to physiology and genetics and downplay the role of personal involvement in the process, motivation to achieve results and the desire to maintain them. Rather, understanding the processes and genetic component of excess weight will help not to give up when faced with difficulties that can be explained by the physiology of the processes and, perhaps, will be able to debunk the prejudice that extra pounds are solely a consequence of overeating and incontinence in nutrition.
| Our goal is to lead to maximum understanding of all the processes occurring in our body, because only in this way will the changes become long-term, and the path to them and leading a healthy lifestyle will be conscious. |
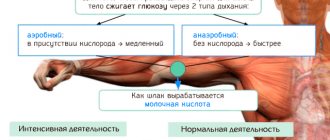
Metabolism
Every living organism requires energy to perform daily functions aimed at survival. Body weight is determined by energy intake and expenditure, and any imbalance leads to weight fluctuations.
The efficiency of this metabolism depends on how productively existing or available energy is used to maintain basic metabolism, and how effectively energy is extracted and absorbed from food .
This indicator is individual for each person. This fact is counterintuitive, but generally a person with an efficient metabolism will be prone to gaining weight. Why? Because it efficiently extracts energy from food, uses it sparingly for daily functions, and stores excess energy very efficiently. This is probably the only case when you really don’t want to be so effective.
Who is an example of an inefficient metabolism? People of thin build, for whom everything happens the other way around: energy is not extracted from food so well, and a lot of it is required to function - accordingly, little remains in the black.
The physiology of efficiency is very logical in the context of evolution, since such a metabolism helps to survive during long periods of hunger and quickly stock up during periods of abundance. But when a person is in abundance all the time, this is where problems arise.
Two reasons why there is less adipose tissue, but the scale shows the same number
Muscles increase in volume
If the strength training program is designed correctly, then muscles will inevitably begin to grow from exercise. Up to a certain point, excess fat will disappear and weight will decrease, but with the gradual growth of muscle tissue, the arrow on the scale will stop or even creep up. In this case, the person will feel better and look slimmer, but will experience some discomfort from the number on the scale. What to do?
Measure volumes, not weights. Centimeters, unlike kilograms, will not deceive you: with regular training and proper nutrition, it will very quickly become noticeable that your waist and hips have decreased in volume. You can record these metrics once a week to track your progress. It is better to weigh yourself on a smart scale that shows changes in the percentage of muscle, water and fat in the body.
Fluid is retained in the body
If a person not only works out hard on exercise machines or swims in the pool, but also seriously limits himself in the number of calories, a hormonal imbalance may occur. Such stress leads to increased production of the hormone cortisol. The main signs of this are belly fat that won't go away, and swelling of the arms and legs due to fluid retention in the body. But an accurate diagnosis can only be made by taking a test.
Fluid in the body can also be retained due to a large amount of salt. Inexperienced bodybuilders sometimes try to increase the amount of protein by eating sausage, fatty salty cheese and similar products. Yes, there really is more protein in the diet, but excess salt leads to dangerous stress on the kidneys, blood vessels and heart. It is very important to select nutrition from a line of high-quality sports proteins and assess the amount of fluid in the body on the same smart scales.
The tendency to gain weight as a genetic component
Undoubtedly, lifestyle (sedentary or active) affects weight, but a considerable amount of research indicates that genetics may also be a reason for the tendency to gain extra pounds. In rare cases, it all comes down to changes in just one single gene associated with regulating feelings of satiety and hunger. Many studies (mostly conducted on twins) have clearly shown the importance of genetic factors in weight gain.
For example, a study on the relationship between weight gain and environment conducted with adopted twins found that the weight of adoptive parents and children may differ significantly, while a direct relationship was observed between the weight of children and their biological parents. Another study, also conducted on twins, showed that if several pairs of twins are fed the same food for 3 months, then the weight gain between brothers or sisters will be almost the same, and between pairs there can be a huge spread of two to ten kilograms. Similar results were found in weight loss studies.
There is also a body of evidence for differences in basal metabolism between people from different ethnic groups, which further demonstrates the importance of genetics in weight gain, loss and maintenance.
Body weight is controlled by a myriad of metabolic pathways and feedback circuits, coordinated at the molecular and hormonal level.
The amount of food consumed is regulated by the central nervous system through a series of interconnected neuroendocrine feedback loops. Energy expenditure is regulated by the autonomic nervous system and a number of hormones, the most important of which are thyroid hormones. But hormones such as insulin, leptin, ghrelin and many others also play an important role in the process.
| The scientific literature has documented many examples of successful weight loss, but the main problem is that most people are unable to maintain their new weight in the long term. |
The plateau effect: how long does it last?
Freezing of weight on one “step” can last from several days to two to three weeks and up to 5 months. At the same time, you need to understand that a plateau is not always bad. For example, there is a so-called imaginary plateau, in which fat mass in the body decreases, as before, but fluid is retained or accumulated. This usually happens in women during the second phase of the menstrual cycle. At the same time, everything that happens in the body turns out to be natural, and this is associated with changes in hormonal levels. This fluid retention can reach 2-3 liters, and there is certainly no need to panic.
Continue your efforts. If you notice that your appetite has increased, you can slightly expand your diet by including new foods (but not fat-containing ones). In the first few days of the new cycle, you will notice that the weight has moved from its “dead point”.
The plateau effect when losing weight, lasting from a couple of days to a couple of weeks, is also a kind of “fuse”. This delay in weight loss may mean that your body is preparing the ground for further weight loss. The body needs this time to regroup and prevent prolapse of the internal organs (after all, there are fatty layers inside).
In this case, you don’t have to think about how to overcome the plateau when losing weight, but just continue in the same mode, and your body will thank you.
But in some cases, a plateau occurs for completely different reasons:
- illnesses,
- stressful state,
- critical days,
- chronic lack of sleep,
- stool retention,
- excessive addition of salty foods, even to the diet for just one day.
In order for weight to begin to decrease again, you need to overcome all these factors.
It is also important to look not at the duration of the plateau, but at how many weeks after starting the diet this effect began. If the wrong fat burning program is chosen, then the weight can stop falling down after just 2 weeks. And the reason for it all is the inadequacy of the weight loss program.
- A diet that is too strict means too few calories that your body does not have enough for normal metabolism.
- Proteins and fats are completely cut out of the diet. So, you need at least 0.5 grams of pure protein per kilogram of your weight and 40 grams of healthy lipids.
- Those who adhere to a mono-diet often try to overcome a dietary plateau, and unsuccessfully. You can’t just sit on apples, buckwheat, or anything else.
By the way, it is for these reasons that many diets are designed for 2 weeks, sometimes three. And this is a sign that a dietary plateau, sometimes protracted, cannot be avoided. And the most correct thing to do is not choose a diet, but a reasonable nutrition program that can be followed without harm, but on the contrary, only with health benefits, for the rest of your life.
However, the hudeem-bez-problem.ru portal can recommend you several strategies.
"Set point"
One possible explanation is the “set point” theory: a “weight set point” is the weight range within which all body systems function optimally. According to this concept, weight is regulated at a given value and the body resists a strong deviation from this value. The hypothesis about the presence of a certain weight constant has been promoted for many years, and over the years of research it has been confirmed by a large number of experimental results.
| First, the weight of all mammals, including humans, fluctuates in response to overeating or underfeeding and usually returns to its original level when normal eating patterns are restored. |
| Secondly, metabolism changes significantly when you gain or lose weight. |
So, when people gained 10% of their initial weight, as expected, there was an increase in energy expenditure, but the most interesting thing is that it was not the basic metabolism that changed, but the energy requirement of skeletal muscles. That is, one of the mechanisms to prevent further weight gain was an increase in energy consumption. Similar observations were made with weight loss, i.e. energy expenditure dropped significantly to prevent further weight loss.
These mechanisms fully explain why it is difficult for people to lose “the last couple of kilograms” and why the weight is so easily gained again if you return to your previous diet, because now the body is more economical in its needs. At this stage, the duration of reduced energy requirements after weight loss is unclear, but there is evidence of normalization of metabolism and restoration of its original level.
What is the plateau effect?
This is the so-called “plateau effect” - from the French word that translates as “plain”: if you depict the process of weight loss in the form of a graph, where days are marked on the horizontal and weight on the vertical axes, then the weight change curve during the plateau effect will run parallel to the bottom axis of the graph for a long time, like a plain on the ground.
Of course, when a person restricts himself in nutrition, plays sports and at the same time does not observe at least any results in weight loss for a long time, then this situation is very demoralizing and reduces motivation, even if the plateau effect lasts only a couple of weeks.
In order to prevent the plateau effect from occurring or quickly overcome this state of the body, you need to know about its causes. Depending on them, they choose ways to combat this unpleasant phenomenon.
Hormones and their effect on weight
In addition to slowing your metabolism, weight loss is associated with increased appetite. After eating, satiety signals from the gastrointestinal tract reach the brain. Various mechano- and chemoreceptors in the intestines detect the presence of nutrients and release a series of hormones. All of these hormones regulate satiety (when to stop eating), satiety (lack of hunger between meals) and hunger. But this is only physiological regulation of energy balance.
| There is also hedonic regulation, which is based on the attractiveness of food and pleasure. This system is able to stimulate food intake even in the absence of energy needs. |
Many people who have lost weight notice a more pronounced desire to eat between meals, a sharper feeling of hunger, and an increase in the amount of food eaten. Physiologically, these processes are attributed to increased levels of cortisol (stress hormone).
Another hormone that can affect weight retention is ghrelin . This hormone is secreted by the walls of the stomach and pancreas. Its levels rise before eating, causing hunger, and fall during and after eating, causing a feeling of fullness. Moreover, experiments have shown that constantly elevated levels of this hormone lead to a slowdown in metabolism and stimulation of the deposition of fat reserves.
| Thus, increased ghrelin levels in the period after weight loss can lead to the opposite effect - weight gain through increased appetite and slower metabolism. |
leptin is also an important player and is produced by adipose tissue. With weight loss, its level in the blood drops, which stimulates hunger and an increased need for energy.
It would seem that all these physiological, hormonal changes are the sole culprits in weight gain, and some studies indicate this, however, many others do not trace a direct connection. Of course, decreased leptin levels and increased ghrelin levels can be harbingers of such an outcome, but this, again, is not clear.
| Proper weight loss is a long and demanding process, the most important factor of which is changes in habits. |
Changes in approach to nutrition and physical activity are an integral part of the process and are what contribute to successful weight loss and maintenance of the achieved results in the long term.
Many studies that are based on monitoring people in the maintenance phase, that is, after weight loss, indicate a number of important rules:
- change the composition of macronutrients (especially their protein component);
- Choose a filling breakfast that contains complex carbohydrates or complex carbohydrates and protein;
- move;
- avoid low-calorie diets - the body will compensate for everything in the future and will not allow you to maintain weight;
- watch for changes - it doesn't have to be a scale or a centimeter, but pay attention to changes in your parameters.
| A number of studies show that all people who have managed to lose weight and maintain their new shape have a number of similarities, the first of which is an active (moving) lifestyle. |
Despite thousands of ongoing studies of the physiological component of weight loss, nutritionists and scientists are beginning to agree on one thing - it is necessary to change habits, eat consciously and monitor changes. To a large extent, everything is related to lifestyle, although physiology cannot be ignored.
Scientific hypotheses about the causes of weight loss
The few studies devoted to studying the causes of the phenomenon come down to three main points:
#1 Stopping weight loss is due to the body adapting to stress
Yes, any diet, like increased physical activity, is stressful for the body. And we have a colossal supply of resources in reserve to adapt to any stress. For example, if you find yourself in conditions of limited oxygen, the body will immediately increase the production of red blood cells in response; there is a need for increased physical activity - muscle mass increases; little energy comes from food - the body will cut down on consumption and conserve reserves by slowing down metabolism.
Thus, the first reason for weight loss is metabolic adaptation (research). Simply put, after a month, two, three (these periods vary greatly), your body was finally convinced that there would be so much food and not a gram more and decided to reduce metabolism in order to stop weight loss.
This mechanism was described in four independent studies conducted by the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (research).
They also identified the second mechanism for the appearance of a “weight plateau.”
#2 Hidden mistakes in diet
According to American researchers, periodic diet violations, often subtle, are a common reason for stopping weight loss. This also includes errors in calculating the calorie content of food in the direction of decrease and, conversely, an inflated idea of the real level of one’s own activity.
Well, everything is simple here: discipline, discipline and more discipline.
#3 Imaginary plateau
In this case, everything goes according to plan, although the scales say otherwise. Nevertheless, fat mass is steadily decreasing, but weight remains the same due to fluid retention in the body . The phenomenon is temporary, most often occurring in women in the second phase of the menstrual cycle due to an increase in progesterone production.
Up
Plateau phenomenon. Comment by Elena Degtyar
One of the most important goals of this article is to try to explore the plateau phenomenon that almost all people with a high BMI experience when trying to lose weight. Very often, maximum weight loss is achieved by six months of the diet, and after that the weight is either maintained or begins to creep back up. Unfortunately, there are no detailed descriptions of this phenomenon in the scientific literature.
Searching among popular and respected resources on the international Internet network, I personally was very surprised, because it all often came down to the following:
- Most likely, people themselves are to blame for this, because they stop adhering to the regime;
- they think they are making an effort, but in reality they are not working hard enough;
- Those losing weight who are faced with a plateau are asked to cut the calorie content of their diet even more (without falling below 1200 kcal). If a person has been eating in this range for a long period of time, then it turns out that everything is lost.
- They try to convince those who are losing weight that, most likely, they have inflated expectations and, perhaps, they are already at their ideal weight, without knowing it.
However, experience and communication with people show that often all the rules are followed and there are extra pounds, but the weight is worth it. Having dug deeper, I still managed to find some advice that was consistent with my personal opinion regarding this situation.
Often, those who are trying to lose weight build a clear, specific system of nutrition and training. At first, this system gives results and, inspired, the person continues to follow the chosen direction, fearing to deviate from the established scheme.
But the most beautiful and at the same time annoying quality of the body is its ability to adapt.
The body can adapt to altitude by producing more red blood cells; to physical activity, starting to build muscles; to a small amount of energy, cutting costs to a minimum and strictly conserving reserves.
| Having driven oneself into certain limits, especially those that imply restrictions and stress, a person will be stressed. |
Therefore, the first thing you need to do when you see that progress has stopped is to relax and understand that this is normal. Moreover, it is even wonderful, because you know that you have undergone dramatic changes and your efforts were not in vain. In this situation, it is advisable to continue to adhere to the chosen regime for some time and see what happens. Are there any changes in sensations? What's going on emotionally?
Nutritionists and scientists rarely pay attention to the emotional background, and since the plateau phenomenon is not studied at all, then to the emotions of a person whose efforts are now being wasted, as he believes, even more so. However, experience shows that often in a plateau state a person begins to experience fear or despair. Fear, because it is not clear what to do now to restart the system, and despair, the desire to give up everything, because if the efforts are in vain, then you can give up the whole idea.
But you shouldn't throw anything away. On the contrary, you need to be patient and perceive the situation as a quest. Imagine that you need to get out of a locked room by collecting the required number of clues and finding the key to the door.
Exercise stress
Try to figure out if you have overtrained. Rest is an important component of progress.
| Regular intense physical activity is a certain kind of stress for the body from both a physiological and psychological point of view. In professional athletes, symptoms of overtraining manifest themselves in changes in hormonal levels in the blood and general fatigue. |
You may not be a professional athlete, but it is clear that prolonged effort at a high level of functionality in other areas of life leads to fatigue.
So make sure you get enough rest. If you feel that you have found a balance between exercise and rest, then just try changing the type of physical activity.
What can be changed? For example, if you've been going to the gym and focusing on strength, start running or doing some other cardio exercise.
If you've been balancing between cardio and strength training, try yoga, callanetics, Pilates or stretching. Start doing short interval training or choose more challenging exercises, focusing on technique and effort rather than length of workout. The amount of scientific literature confirming the high effectiveness of interval training is only growing.
Nutrition
Don’t immediately think that you now need to eat even less and start looking for an even lower-calorie diet.
Yes, your body has adapted to your diet. You have lost weight, you now need less energy than at the beginning of your journey. But this does not mean that it is necessary to remove something and cut down the diet even more. If you carefully read the article, you could see that adaptation occurs not only in this vein: “less weight - less energy expenditure,” but also in the regulation of metabolism and its efficiency. Also, if you read an article about the physiology of weight loss, then you know that along with fat, the body loses muscle mass, and these are the tissues that are usually the most demanding in terms of energy consumption. So in the case of a plateau, you have three very interesting possibilities:
| 1. Set up an energetic swing. Eat a couple of days more than usual, and then one day less than usual, then again more and again less. Thus, by maintaining energy balance over a week or month, but varying it from day to day, you can take the body out of its usual function and cause it to “lose” its metabolism. 2. Try changing your diet. If you have been eating 3 times a day so far, reduce your portions, but eat 5 times a day. Or focus on your main daily caloric intake in the first half of the day and reduce the amount of food in the second half. 3. Play with your macronutrient spread. Increase the amount of protein at the expense of fats or fats at the expense of carbohydrates, try to shift the usual alignment so that the body begins to launch mechanisms for using alternative fuel. |
Don't be afraid to experiment! A plateau is a kind of stagnation, stagnation, and in order to re-enter the path of progress, a shake-up is needed. But a shake-up does not mean less food, more exercise, and fears and stress for dessert. No! This means research and change, which means new discoveries and new progress.
Author: Elena Degtyar, PhD, head of the scientific department #SEKTA
Literature:
1. Anastasiou CA, Karfopoulou E., Yannakoulia M (2015) Weight regaining: From statistics and behaviors to physiology and metabolism Metabolism, clinical and experimental [0026-0495, 1532-8600], yr: 2015 vol: 64 iss:11 pg:1395-407 2. Harrold JA TM Dovey, JE Blundell, JC Halford CNS regulation of appetite Neuropharmacology, 63 (2012), pp. 3–17 3. Greenway FL. (2015) Physiological adaptations to weight loss and factors favoring weight regain International Journal of Obesity 39, 1188–1196 4. Urhausen A., Gabriel H., Kindermann W. (1995) Blood Hormones as Markers of Training Stress and Overtraining Sports Medicine 20 (4) 251-276
What you need to know about the plateau effect when losing or gaining weight
What is the plateau effect?
Typically, weight loss is most noticeable in the first few months.
“The plateau effect is a period of stagnation: when you don’t eat anything harmful, but still don’t lose weight, when you work out just as hard, but the muscles don’t grow. In the first month, excess fluid usually disappears, so it seems that we are losing weight very quickly,” explains Alena Zlobina, founder and ideological inspirer of the “Taste & Color” project. “This phenomenon can be observed both during mass gain (lack of progress in the growth of muscle mass) and during fat burning (the weight loss process stops),” explains Anton Bengardt, master trainer at the gym of the Crocus Fitness network of fitness clubs.
What happens in the body?
“Physiologically, the plateau effect is based on metabolic adaptation. For example, you consumed 1800 kcal daily, while your weight remained stable or changed slightly. This means that calorie consumption was approximately equal to consumption and was also about 1800 kcal. If you reduce your consumption, for example, to 1400 kcal, then the body perceives this restriction as temporary, and by inertia continues to spend 1800 kcal, covering the lack of calories with internal reserves. At this time, active weight loss is underway. After 2-4 months, the body understands that the restriction was not temporary, and reduces consumption to adequate intake - up to 1400 kcal. Weight loss stops,” adds Alisa Shabanova, ideologist and developer of the original GrinDin menu, a service for delivering tasty and healthy food throughout the day.
Why does the plateau effect occur?
The plateau effect usually occurs 3-4 months after starting weight loss. If there is a lot of excess weight, then it may occur later - after six months or even a year. If there is not enough excess weight, a little earlier, after 2 months. “After a period of caloric restriction, fat burning slows down. This is due to the fact that the body, in anticipation of more “hungry” days, will strive to preserve at least some reserves. This process is completely normal and natural. Another reason is that the caloric content of the diet is too low. With a daily calorie content of 700–800 kcal, the speed of the thyroid gland and metabolism in general decreases. Of course, not a single nutritionist will recommend such an energy value of the diet, but people who lose weight on their own often think that the stricter the restrictions, the more effective the weight loss will be, says Mikhail Gavrilov, a psychotherapist, author of a patented method for correcting eating behavior and reducing weight, member of the Institute of Functional Medicine (IFM, USA). - Also, the plateau effect can be caused by constant physical activity. If you involve sports in losing weight, it is important to understand that the load needs to be changed in accordance with your progress. Otherwise, it will simply be ineffective.”
What other reasons could there be?
Anton Bengardt, master trainer at the Crocus Fitness fitness club chain, says that, among other reasons for the plateau effect, there may be overtraining, lack of a training diary and a well-designed training program, genetics, and incorrect and ineffective exercise technique.
Training is stressful, so the body needs time to restore resources after exercise. Muscles recover quite quickly, but the central nervous system takes much longer. This is why you should not do strength training more than 3 times a week. In addition, the training diary allows you to control working weights, number of repetitions and approaches. We must not forget that women have peculiarities of the hormonal system, due to which muscle mass grows for a long time and little by little: the body does not allow hypertrophy. At some point, muscle growth stops.
How to overcome the plateau effect?
Under no circumstances should you reduce your caloric intake further and further. This will lead to a further drop in the level of exchange and inevitable disruptions in the future. An effective way is a “swing”, which can be arranged either within a week or over a longer period. “A small swing means adding fasting days, one or two per week. The calorie content of a fasting day should not be less than 800–900 kcal, and you can arrange it on your favorite foods: vegetables and fish, fruits and cottage cheese, fermented milk and dairy products, explains Alisa Shabanova. - Big swing - changes in caloric intake during the week up or down. Such fluctuations make it possible to shake up the exchange and move it from a dead point.”
Alena Zlobina recommends allowing the body to rest by including several favorite foods in the diet and giving up sports for a while. And then increase physical activity or change it by adding something new. The expert also advises increasing the amount of protein. Digesting protein is a very energy-intensive process that can burn 20-30% more calories each day.
What is carbohydrate cycling?
“Interval training works great for accelerating metabolism, but it is suitable for trained people. And if, for example, you are just walking, then change the pace of walking from slow to medium, from medium to fast. If there are no contraindications, you can alternate running at an average pace with walking. You can alternate days with normal calorie content and days with a high carbohydrate load, when the daily energy value of the diet increases by 50% due to carbohydrate foods. But such days should only be practiced by relatively healthy people,” advises Mikhail Gavrilov.
What is the point of carbohydrate rotation? On days with normal calories and carbohydrates, we improve cell sensitivity to insulin and lipid profile. And on days with a high amount of carbohydrates, we increase the level of thyroid hormones, testosterone (it also activates fat burning) and leptin (a hormone that regulates satiety and energy metabolism). It turns out to be a kind of deception of the body from the series “no, there are no restrictions, so I fed you normally.”