Weight training and other types of exercise that help strengthen the muscles of the buttocks, thighs and legs will help pump up your legs while doing fitness and sports in order to lose weight and build muscle mass. If desired, you can perform them at home. In a month, the first results will be noticeable.
To achieve weight loss and pump up your legs, a man should pay attention to problem areas in each workout and carefully work on them.
- Lateral, or to the side
- Regular
- "Gluteal Bridge"
Muscles that need to be worked
Before starting classes, it is necessary to determine those areas that need to be pumped up in order to obtain a beautiful and correct shape. Usually pay attention to the following areas of the lower extremities:
- the inner side of the thigh, where it is quite difficult to pump muscles;
- the front surface of the thigh, which gives the correct shape to the legs;
- back of the thigh;
- gluteal muscles;
- calves, or shins, which are not so difficult to pump up.
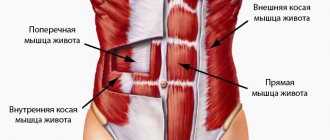
One of the important muscles for the formation of a beautiful relief of the muscles on the front surface of the thigh is the quadriceps (quadriceps). It is responsible for flexion and extension of the leg at the knee joint and forms the patella region. If this muscle is weak and untrained, leg shape and strength will deteriorate.
Briefly about the anatomy of the legs
In this block we will talk mainly about the quadriceps (quadriceps = Quadriceps), and their complex muscle structure. The quadriceps femoris muscle occupies the entire front and part of the lateral surface of the thigh. Consists of four heads:
- Rectus muscle
- Intermediate wide
- Medial wide
- Lateral wide
Each of the heads has its own beginning, but, approaching the knee area, they all pass into a common tendon, which covers the patella and attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
Rectus femoris muscle
The rectus femoris muscle is the longest of all muscle heads. Occupies the anterior surface of the thigh. It goes down and passes into a narrow tendon, which is part of the common tendon of the quadriceps muscle. Having reached the tibia, the tendon attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
Vastus medialis muscle
The vastus medialis muscle (lat. Musculus vastus medialis) occupies the anteromedial surface of the lower half of the thigh. The muscle originates from the medial lip of the linea aspera of the femur and, moving downwards, passes into the broad tendon, which is partially woven into the broad tendon along with the rectus muscle, and partially attached to the medial edge of the patella, forming the medial suspensory ligament of the patella.
Thus, the bundles that form the muscle are directed obliquely from top to bottom and from the inside to the front.
Vastus lateralis muscle
The vastus lateralis muscle (lat. M.vastus lateralis) occupies almost the entire anterolateral surface of the thigh.
From above it is somewhat covered by the muscle that strains the fascia lata, and in front by the rectus femoris muscle. The muscle starts from the greater trochanter, the intertrochanteric line and the lateral lip of the broad line of the thigh.
Heading down, the muscle passes into the broad tendon, which is part of the common tendon of the quadriceps muscle and is involved in the formation of the lateral suspensory ligament of the patella.
Vastus intermedius muscle
The vastus intermedius muscle (lat. M.vastus intermedius) is located on the front surface of the thigh between the medial and lateralis muscles, directly under the rectus femoris muscle.
It is the weakest among the other heads. It begins on the anterior surface of the femur - from the intertrochanteric line and, going down, passes (almost half its length) into the broad tendon, which in the distal part joins the tendon of the rectus femoris muscle, passing into the common tendon of the quadriceps muscle.
General recommendations
Simple rules that must be followed by beginners and advanced athlete will help increase the effectiveness of home training:
- Moderation. It is the main condition for the effectiveness and safety of training. You shouldn’t load your body with heavy exercises and loads on the first day, especially if the guy or man has never trained before that day. This will lead to injury or strain to the muscles and ligaments.
- Regularity. There will be no benefit from training once a month, and the muscles from such a rare load will not grow and will become very sore. The optimal training regimen is 3 sessions per week lasting 1.5-2 hours for advanced athletes and 30-60 minutes for beginners. It is important to listen to your body and stop when your strength is running low. Excessive exercise will not lead to the desired result, but can harm the body.
- The need to warm up before each lesson. It will prepare the muscles for the upcoming loads and prevent injury. For warming up, you should choose simple rhythmic exercises that will allow you to get ready for further training.
- The need for a cool down. The session should end with some kind of muscle stretching exercise.
Beginners are not recommended to start with heavy loads and use weights of more than 3 kg each. For experienced athletes, the weight of each dumbbell can reach 10-15 kg.
For training, you should choose a spacious room, ventilate it, wear comfortable sportswear and take weights in accordance with your level of physical fitness.
Warm-up
It is recommended to perform simple exercises:
- Jumping rope for 5-7 minutes. You can choose the pace yourself. You should not jump quickly; it is important to feel the warming up of each muscle at a moderate pace. You are allowed to jump on two legs or alternately, it doesn’t matter.
- Swing your legs forward . They must be performed in a standing position, raising straight legs one at a time to chest level for 2-3 minutes. Keep the rhythm moderate.
A similar warm-up for 10 minutes will help warm up your muscles and prepare for the upcoming loads. Instead of jumping rope, you can run in place or quickly walk around the room. This option is suitable for beginners and those who begin classes after severe injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
Dumbbell workout
Exercises with dumbbells will be the first step for those who want to build up their legs. They are effective, bring quick results, and the weight of the weights can be chosen taking into account the degree of preparedness. This allows them to be used for training beginners and professionals.
The following exercises will be the most effective and easiest to perform.
Jumping
They help pump up all the thigh muscles.
Exercise technique:
- Take the starting position - standing with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Take a dumbbell in each hand.
- Squat with them and jump as high as possible.
- Repeat 10 times.
For advanced athletes, the number of repetitions increases to 25 times. The weight of each dumbbell for a beginner is from 1 to 2 kg, for a professional - up to 5 kg.
Holding on one leg
You will also need a dumbbell for this exercise. It helps strengthen and pump up the front muscles of the thigh, lower leg and buttocks.
Technique:
- Take the starting position - standing, holding your hands on a wall or chair.
- Place a round dumbbell on the toes of one foot.
- Raise your leg 10 cm from the floor.
- Hold for at least 20 seconds.
- Repeat for the second leg.
For each leg you need to do at least 3 approaches.
The weight of the weight for a beginner should not exceed 2 kg, for professionals 4-5 kg is allowed. For those who want to complicate the execution, they are allowed not to hold on with their hands, but to try to maintain balance without support.
Scheme No. 3. First level.
Barbell squats can be a challenging exercise for many to learn the technique. So the simpler version of the goblet squat can be a good place to start learning the biomechanics of the squat before doing it with a heavy barbell on your back.
This workout is heavily machine-based, allowing for a smoother, more controlled approach to free weight training.
As your coordination improves and your muscles become stronger, progress to more complex movements with free weights and heavier loads.
Note:
- Before performing working sets, do 2-3 warm-up sets with a gradual increase in weight, but not to the point of muscle failure.
- Choose a weight that will allow you to perform the exercises with the prescribed number of sets and repetitions.
- Start your workout with multi-joint exercises, then move on to isolation movements on machines.
Read also: How to pump up your legs: 2 training programs.
Beginner level leg training.
1. Goblet squats – 3 sets of 10-12 reps.
2. Leg press – 3 sets of 10-12 reps.
3. Leg extension in the simulator - 3 sets of 10-12 repetitions.
4. Leg curls while sitting in a machine - 3 sets of 10-12 repetitions.
5. Standing calf raises in the simulator - 3 sets of 15 repetitions.
Rest between sets is 60 seconds, between exercises - 1.5 minutes.
Lunges
Lunges will be the most effective exercise for the muscles of the buttocks and thighs, will help to form a beautiful relief and eliminate fat in these areas. Suitable for beginners and advanced athletes.
There are several ways to perform lunges that are equally effective for targeting problem areas.
Lateral, or to the side
This is the simplest option to work on problem areas of the legs.
Technique:
- Take the starting position - standing on the floor with your legs previously spread, shoulder-width apart.
- Lunge with one leg to the side. The second leg should be straightened and the foot should be on the floor.
- Hold the position for 10 seconds.
For each leg you need to perform 3 approaches.
Beginners should not use weights; professionals are allowed to take dumbbells weighing up to 5 kg in each hand.
Bulgarian
This version of lunges is performed with minor complications.
Technique:
- Take a standing position on the floor with your feet shoulder-width apart. A chair or bench should be placed at the back.
- Place one leg on the bench, pre-bent at the knee.
- Lunge on the other leg.
For each leg, repeat the exercise at least 10 times for beginners. Advanced athletes are allowed to use weights up to 4 kg in each hand and do at least 20 repetitions for each limb.
Low
This version of lunges is performed forward and allows you to pump the quadriceps of each leg, buttocks, and lower legs.
Technique:
- Take a standing position on the floor with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Lunge forward with one limb so that the knee of the other touches the floor.
- For each leg, perform 10 times.
Beginners are advised to place their hands on their sides when performing the exercise. Trained men should take a weighting device weighing up to 4 kg in each hand.
Cross
This is a complicated version of lunges that allows you to pump all the muscles of the thighs, legs and buttocks.
Technique:
- Take the starting position - standing on the floor with your legs apart, shoulder-width apart.
- Lunge forward so that both limbs form one line.
For each leg you should do at least 10 repetitions. Beginners should not use weights, as it is quite difficult to maintain balance when performing lunges. Trained people are allowed to take a dumbbell in each hand. The weight of each should not exceed 2-3 kg.
Scheme No. 4 Isolated training of quadriceps.
Since multi-joint exercises work your legs from top to bottom, front and back, that is, from different angles, it is impossible to completely isolate one muscle group from another (quads from hamstrings)
However, it is quite possible to do this by increasing the range of motion of the knee joint to a greater extent and at the same time limiting the movements in the hip joint.
One way to do this is to change the position of your legs when squatting in a hack machine, placing them on the bottom of the platform. You can also perform a couple of additional movements with a heavier weight for 6 repetitions only at half the amplitude, performing partial repetitions.
Front squats also place the load on the quadriceps more than back squats.
The training is performed according to the reverse pyramid principle. As the number of repetitions increases, reduce the weight of the apparatus proportionately.
Please note that this training load only covers the quadriceps. If you wish, you can add one exercise each for the hamstrings and calf muscles.
Note:
- Before performing working sets, do 2-3 warm-up sets with a gradual increase in weight, but not to the point of muscle failure.
- Choose a weight that will allow you to perform the exercises with the prescribed number of sets and repetitions.
Isolated quadriceps workout.
1. Front squats – 4 sets of 6, 8, 10, 12 reps.
2. Hack squats - 3 sets of 8, 10, 12 reps (leg position - lower part of the platform) 2.3 sets of 6 reps (partial reps)
3. Leg extensions in the simulator - 3 sets of 10, 10, 12 repetitions.
Rest between sets 60 seconds, between exercises 1.5 minutes.
Squats
Squats are considered the most effective exercise for working the muscles of the lower extremities, buttocks and building muscle mass in these areas. It is for this reason that every training program should have it.
The following types of squats are considered the most effective for pumping up your legs.
Regular
This is a simple and effective exercise for pumping up muscle mass not only in the legs, but also in the buttocks area.
Technique:
- Take the starting position - standing on the floor with your feet shoulder-width apart. Place your arms freely at your sides or extend them forward.
- Squat without lifting your heels from the floor, without rounding your back, without lowering your head.
Completion time for beginners is 1 minute, for trained ones - up to 3 minutes at a moderate pace.
On one leg
This option is more suitable for professionals, as it requires increased concentration and the ability to accurately maintain balance.
Technique:
- Take a starting position similar to the previous exercise.
- Raise one pre-straightened leg parallel to the floor.
- On the other, do squats.
Do 20 repetitions for each leg. A beginner should start with 5 repetitions, gradually increasing this number.
With weights
The exercise is suitable for trained men and those who are just starting to exercise. It is performed similarly to regular squats, but a dumbbell is taken in each hand during the execution.
Weight for experienced athletes is from 3 to 6 kg, for beginners 1-2 kg is enough.
You should start with 10 repetitions, gradually increasing this number to 20-30 times per workout. Weight also needs to be increased gradually, especially for untrained people and young guys.
Shifting weight forward
The exercise is performed similarly to the previous one. The difference is that the hands with dumbbells should be held as close to the chest as possible so that all their weight falls on the shoulders and arms. This will create additional tension in the buttocks, thighs and legs, which will be involved in maintaining the balance of the whole body.
You should do up to 20 squats. The weight of weights for beginner athletes should not exceed 3 kg; for professionals, up to 5 kg in each hand is allowed.
How to pump up your thighs at home
Pumping legs at home for men cannot do without working out the thigh muscles. In order to get them in shape, simple leg exercises at home are also suitable, which, if performed correctly, bring good results.
You need to start training your hips with squats . We stand straight, placing our feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Toes point forward, heels do not leave the ground while performing. When performing squats, do not try to squat as low as possible. If you use additional weight in the form of a barbell or dumbbells, it can damage your knee joints. Try to squat until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
Remember, keep your back straight and your heels on the floor. By lifting your heels off the floor, you will shift your center of gravity and redistribute the load. The necessary muscles will not be fully loaded, and the exercise will become more difficult.
Cardio exercises
Cardio exercises are an addition to the main training complex. Running is considered the most effective form of exercise. It trains the muscles of the legs and buttocks, eliminates excess fat in this area and builds muscle mass.
The optimal time for a beginner is 20 minutes at a moderate pace. A trained person can increase this period to 1 hour. The frequency of training is 2-3 times a week. If it is not possible to run outdoors, it is allowed to replace the session with training in the gym on a treadmill or on an orbit track.
Combining such activities with weight training exercises will allow you to achieve noticeable results in a short time.
Scheme No. 6. Isolated hamstring workout.
The hamstrings should not be the lagging leg muscles, and not only for aesthetic reasons, they support the integrity of the knee joint.
For this, there is a whole family of movements (leg bending), which can be performed lying down, sitting, standing alternately, first bending one leg, then the other.
Don't forget to also do the Romanian deadlift, which targets your hamstrings and glutes.
The Romanian deadlift is often confused with the stiff-legged deadlift, which focuses on the lower back, or even the classic deadlift.
In this type of deadlift (Romanian deadlift), the knees are slightly bent as you lower the weight, the back is straight, and the plates do not touch the floor.
Proper technique is critical for the hamstrings. Keep your back straight throughout the exercise and never try to achieve an excessive range of motion if it causes your back to round.
Don't forget that your hips also work when you squat deeply and control the speed of the movement in the negative phase.
However, this amount of work is not enough to avoid doing special, isolating exercises for the hamstrings.
If you decide to split your quads and hamstrings workouts into two training days, leave at least 48 hours in between to ensure full recovery.
This workout again follows the reverse pyramid protocol. As the number of repetitions increases, reduce the weight of the apparatus proportionately.