Share:
Parboiled rice stands out on store shelves with an unusual creamy, yellowish or golden hue. It relatively recently appeared in our kitchens among its round and long-grain counterparts. Steamed rice has confidently entered the diet of adherents of a healthy lifestyle and athletes, as a champion among types of rice in terms of beneficial properties.
Rice dishes occupy a leading position among grain crops, actively competing with wheat. They are especially popular in China and Southeast Asia. National dishes are prepared from rice: pilaf, paella, flatbreads, noodles, risotto - you can’t list it all. More than 95% of the world's population over one year old is familiar with products based on it. Recently, classic white rice has been losing its position to grains that have undergone preliminary preparation. Why this happens, and what are the differences between steamed rice and ordinary rice, you will learn from this article.
How do you get steamed rice and what is its difference from regular rice?
After ripening, the rice grain is peeled from all layers of the shell. When grinding it, the embryo is cut off. The result is a beautiful, white grain that, as a result of refining, has lost up to 85% of oils, up to 70% of cellulose and minerals, up to 65% of niacin, 50% of riboflavin and about 10% of protein. While rice acquires an attractive appearance, it loses its beneficial properties. The more polished the rice, the less biologically active substances it contains.
After repeated attempts to preserve the beneficial properties of grain during cleaning, manufacturers finally found the optimal way to pre-treat it.
Process of making parboiled rice:
- The grains in the shell are winnowed.
- Unrefined rice grains are washed to remove dirt and dust.
- Film-coated grains are soaked in water. At the same time, useful elements found in the peel and germ become more accessible.
- The prepared raw materials are steamed under pressure. At the same time, vitamins, microelements and oils (up to 80%) located in the surface layers penetrate into the central part of the grain. The starch is destroyed and the grain becomes denser and glassy.
- The rice is dried.
- The grain is dehulled (cleaned) by removing the kernels and removing the bran.
- The resulting grains of rice are sorted and polished. The shell removed in this case no longer contains more than 20% of useful components. Biologically active substances remain in the grain.
After this treatment, the rice acquires a characteristic color and appears more transparent than ordinary rice. It is easy to distinguish by appearance.
But if in doubt, check the information on the cereal packaging.
Recipe for boiled rice with butter. Calorie, chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “boiled rice with butter.”
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 150.8 kcal | 1684 kcal | 9% | 6% | 1117 g |
| Squirrels | 2.2 g | 76 g | 2.9% | 1.9% | 3455 g |
| Fats | 3.4 g | 56 g | 6.1% | 4% | 1647 g |
| Carbohydrates | 27 g | 219 g | 12.3% | 8.2% | 811 g |
| Water | 65.3 g | 2273 g | 2.9% | 1.9% | 3481 g |
| Ash | 2.076 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 19.7 mcg | 900 mcg | 2.2% | 1.5% | 4569 g |
| Retinol | 0.017 mg | ~ | |||
| beta carotene | 0.013 mg | 5 mg | 0.3% | 0.2% | 38462 g |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.154 mg | 1.5 mg | 10.3% | 6.8% | 974 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.02 mg | 1.8 mg | 1.1% | 0.7% | 9000 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.372 mg | 5 mg | 7.4% | 4.9% | 1344 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.055 mg | 2 mg | 2.8% | 1.9% | 3636 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 92.813 mcg | 400 mcg | 23.2% | 15.4% | 431 g |
| Vitamin D, calciferol | 0.057 mcg | 10 mcg | 0.6% | 0.4% | 17544 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.044 mg | 15 mg | 0.3% | 0.2% | 34091 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 1.4084 mg | 20 mg | 7% | 4.6% | 1420 g |
| Niacin | 0.004 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 25.86 mg | 2500 mg | 1% | 0.7% | 9667 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 8.89 mg | 1000 mg | 0.9% | 0.6% | 11249 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 7.93 mg | 400 mg | 2% | 1.3% | 5044 g |
| Sodium, Na | 726.47 mg | 1300 mg | 55.9% | 37.1% | 179 g |
| Sera, S | 3.73 mg | 1000 mg | 0.4% | 0.3% | 26810 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 33.7 mg | 800 mg | 4.2% | 2.8% | 2374 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 1119.19 mg | 2300 mg | 48.7% | 32.3% | 206 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Iron, Fe | 1.432 mg | 18 mg | 8% | 5.3% | 1257 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 0.281 mcg | 10 mcg | 2.8% | 1.9% | 3559 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.3396 mg | 2 mg | 17% | 11.3% | 589 g |
| Copper, Cu | 72.84 mcg | 1000 mcg | 7.3% | 4.8% | 1373 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 2.062 mcg | 70 mcg | 2.9% | 1.9% | 3395 g |
| Selenium, Se | 7.031 mcg | 55 mcg | 12.8% | 8.5% | 782 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.3928 mg | 12 mg | 3.3% | 2.2% | 3055 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 0.1 g | max 100 g | |||
| Essential amino acids | 0.015 g | ~ | |||
| Arginine* | 0.186 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 0.137 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 0.054 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.097 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 0.186 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 0.082 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.053 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.001 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.081 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.027 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 0.12 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 0.003 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | 0.021 g | ~ | |||
| Alanin | 0.13 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.211 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.102 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 0.437 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 0.106 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 0.119 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 0.076 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.045 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Cholesterol | 7.44 mg | max 300 mg | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 2.1 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| 4:0 Oil | 0.118 g | ~ | |||
| 6:0 Kapronovaya | 0.054 g | ~ | |||
| 8:0 Caprylic | 0.029 g | ~ | |||
| 10:0 Kaprinovaya | 0.066 g | ~ | |||
| 12:0 Lauric | 0.075 g | ~ | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 0.348 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 1.009 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 0.301 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 1.019 g | min 16.8 g | 6.1% | 4% | |
| 14:1 Myristoleic | 0.067 g | ~ | |||
| 16:1 Palmitoleic | 0.102 g | ~ | |||
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 0.842 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.09 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 0.8% | 0.5% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.078 g | ~ | |||
| 18:3 Linolenic | 0.012 g | ~ | |||
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.1 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 2.1% | 1.4% |
The energy value of boiled rice with butter is 150.8 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Composition of parboiled rice
The popularity of rice on Earth is not accidental. It is rich in microelements, vitamins, and dietary fiber. Their quantity varies significantly depending on the type, variety, processing method and area in which the plant was grown. See here for detailed ingredients of white rice.
The grain contains amino acids: arginine, choline, histidine, tryptophan, cysteine, methionine, lysine.
Nutritional value of parboiled rice:
| Substance | Quantity | Units |
| Squirrels | 6,1 – 14 | G |
| Fats | 0,4 – 2,2 | G |
| Carbohydrates | 71,8 – 79,5 | G |
| Energy value | 123 – 135 | Kcal |
Here you will see the composition of classic rice.
Preliminary preparation of cereals leads to the destruction of starch. This reduces the glycemic index (GI) from 70 to 38-40 units.
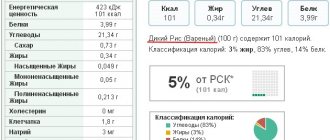
Calorie content Steamed rice. Chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Parboiled rice”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 321 kcal | 1684 kcal | 19.1% | 6% | 525 g |
| Squirrels | 7 g | 76 g | 9.2% | 2.9% | 1086 g |
| Fats | 1 g | 56 g | 1.8% | 0.6% | 5600 g |
| Carbohydrates | 71 g | 219 g | 32.4% | 10.1% | 308 g |
| Alimentary fiber | 3 g | 20 g | 15% | 4.7% | 667 g |
| Water | 14 g | 2273 g | 0.6% | 0.2% | 16236 g |
| Ash | 0.7 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.08 mg | 1.5 mg | 5.3% | 1.7% | 1875 |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.04 mg | 1.8 mg | 2.2% | 0.7% | 4500 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 78 mg | 500 mg | 15.6% | 4.9% | 641 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.4 mg | 5 mg | 8% | 2.5% | 1250 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.2 mg | 2 mg | 10% | 3.1% | 1000 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 19 mcg | 400 mcg | 4.8% | 1.5% | 2105 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.4 mg | 15 mg | 2.7% | 0.8% | 3750 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 3.5 mcg | 50 mcg | 7% | 2.2% | 1429 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 3.3 mg | 20 mg | 16.5% | 5.1% | 606 g |
| Niacin | 1.6 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 100 mg | 2500 mg | 4% | 1.2% | 2500 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 8 mg | 1000 mg | 0.8% | 0.2% | 12500 g |
| Silicon, Si | 100 mg | 30 mg | 333.3% | 103.8% | 30 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 50 mg | 400 mg | 12.5% | 3.9% | 800 g |
| Sodium, Na | 12 mg | 1300 mg | 0.9% | 0.3% | 10833 g |
| Sera, S | 46 mg | 1000 mg | 4.6% | 1.4% | 2174 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 150 mg | 800 mg | 18.8% | 5.9% | 533 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 25 mg | 2300 mg | 1.1% | 0.3% | 9200 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Bor, B | 120 mcg | ~ | |||
| Iron, Fe | 1 mg | 18 mg | 5.6% | 1.7% | 1800 g |
| Yod, I | 1.4 mcg | 150 mcg | 0.9% | 0.3% | 10714 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 1 mcg | 10 mcg | 10% | 3.1% | 1000 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 1.25 mg | 2 mg | 62.5% | 19.5% | 160 g |
| Copper, Cu | 250 mcg | 1000 mcg | 25% | 7.8% | 400 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 3.4 mcg | 70 mcg | 4.9% | 1.5% | 2059 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 2.7 mcg | ~ | |||
| Selenium, Se | 15.1 mcg | 55 mcg | 27.5% | 8.6% | 364 g |
| Fluorine, F | 50 mcg | 4000 mcg | 1.3% | 0.4% | 8000 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 1.7 mcg | 50 mcg | 3.4% | 1.1% | 2941 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 1.42 mg | 12 mg | 11.8% | 3.7% | 845 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Starch and dextrins | 72.9 g | ~ | |||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 0.7 g | max 100 g | |||
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.09 g | ~ | |||
| Maltose | 0.17 g | ~ | |||
| Sucrose | 0.39 g | ~ | |||
| Fructose | 0.07 g | ~ | |||
| Essential amino acids | |||||
| Arginine* | 0.51 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 0.42 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 0.17 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.33 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 0.62 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 0.26 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.16 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.3 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.24 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.1 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 0.37 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 0.66 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | |||||
| Alanin | 0.39 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.54 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.32 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 1.2 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 0.33 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 0.33 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 0.29 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.14 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| beta sitosterol | 20 mg | ~ | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 0.3 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 0.01 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 0.18 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 0.04 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.32 g | min 16.8 g | 1.9% | 0.6% | |
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 0.32 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.19 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 1.7% | 0.5% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.19 g | ~ | |||
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.19 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 4% | 1.2% |
The energy value of steamed rice is 321 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Benefits of Parboiled Rice
Technological features of cereal preparation preserve biologically active substances in it as much as possible. Having a low GI, steamed rice is recommended for dietary nutrition. It is allowed for athletes and patients suffering from metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
Benefits of parboiled rice:
- normalizes metabolic processes;
- activates brain activity, regulates the intensity of processes in the nervous system;
- has a beneficial effect on the heart muscle;
- saturates the athlete with biologically active substances;
- breaks down slowly and does not lead to critical fluctuations in blood sugar levels;
- supplies the body with energy for a long time;
- has a positive effect on water-salt metabolism;
- has an enveloping effect;
- reduces acid production in the stomach;
- slows down the activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Rice is actively used in dietetics. It is especially useful for athletes with a tendency to stomach upsets and diseases of the digestive system. It is recommended to include it in the diet of athletes during pregnancy against the background of gestational diabetes.
Rice does not contain gluten and is suitable for sports nutrition even for young athletes.
What harm can it do?
Rice cereal is balanced in composition. It has a neutral taste and has a gentle effect on the athlete’s body. But it can also have a negative impact.
In particular, the harm of parboiled rice manifests itself in constipation. They appear in athletes with slow intestinal motility. This side effect occurs when excessive consumption of rice-based dishes, a decrease in the athlete’s physical activity, for example, due to injuries, or when drinking insufficient amounts of water.
Please note that constipation becomes more frequent due to increased sweating. This happens in the summer and with increased physical activity. Usually you can get rid of them by changing your drinking diet.
Also, steamed rice is not recommended for athletes with individual intolerance. It is extremely rare. Rice is a hypoallergenic dietary product and usually does not cause side effects.
Features of steamed rice
Steamed rice has not only an improved composition, but also some culinary features:
- When heat treated, its color changes from amber to white.
- The grains are denser. They do not stick together or become soft, retaining their shape even after reheating.
- The cooking time for this type of cereal is longer (about 30 minutes).
- It is advisable to leave the finished rice in a warm place for another 15 minutes to evenly distribute moisture and add fluffiness. This makes digestion easier.
- The finished dish is almost 2 times larger compared to unprocessed rice of the same variety and quality.
Knowing these features, it is easy to prepare a tasty and healthy dish for an athlete.
In weight loss diets
Parboiled rice is often used in dietetics. It is suitable for weight loss diet. On the one hand, rice suppresses hunger well, and on the other, it has a reduced calorie content.
The maximum weight loss effect is achieved by a mono-diet. For 3 days, the diet consists of only boiled steamed rice, herbal teas and water. The diet is effective, but difficult psychologically and physically. Few people can stick to such a diet for a long time. And rice days according to this plan are good for fasting and are well tolerated.
Rice goes well with vegetables, fruits, and animal products, becoming a complete component of combined diets. There are many dietary rice dishes. The general requirement is to cook the grain until fully cooked without adding salt. Porridges, salads, puddings, noodles using rice cereal are an excellent basis for long-term weight loss courses.
For diabetics
The main problem with carbohydrate metabolism disorders is a complete change in diet on an ongoing basis. In diabetes, glucose cannot get from the patient’s blood into the cells due to the lack of insulin (type I) or due to tissue insensitivity to it (type II). Therefore, for the diet, foods are chosen that do not cause a sharp increase in blood sugar. These include parboiled rice. It contains a small amount of fast carbohydrates. Slow carbohydrates are absorbed gradually, without causing glycemic spikes.
When glucose metabolism is impaired, obesity (type II) is often observed. In this case, the diet is aimed at weight loss, which is also facilitated by rice dishes.
Calorie content of steamed boiled rice per 100 grams
Calorie content of steamed boiled rice per 100 grams is 96 kcal. In 100 g of product:
- 2.09 g protein;
- 0.14 g fat;
- 21.5 g carbohydrates.
Recipe:
- 100 g of steamed rice is washed until the water becomes clear;
- pour rice into 250 ml of boiling water and cook for 15 minutes;
- For the last 5 minutes of cooking, the rice is simmered under a closed lid over low heat;
- salt is added to taste.
Read: Calorie content of ketchup in 1 tablespoon
The calorie content of boiled steamed rice with butter is 113 kcal. A 100-gram serving contains 1.71 g protein, 3.58 g fat, 17.9 g carbohydrates.
Recipe:
- 100 g of steamed rice are thoroughly washed, poured into a pan and poured with 300 ml of water;
- add salt to the dish (to taste);
- Cooking rice lasts 25 minutes. After the water has boiled, turn the heat to low;
- Add 15 g of sunflower oil to the finished dish.