Related Products
Chili soup (57 cal) Carrot coriander soup (100 cal) Lentil soup (54 cal) Vegetable soup (41 cal) Clear soup (8 cal) Chicken soup (60 cal) Potato soup (63 cal) ) Mushroom soup (51 kcal.) Tomato soup (43 kcal.) Bean soup (74 kcal.) Fish soup (ear) (16 kcal.) Turtle soup (53 kcal.) Onion soup (44 kcal.) Noodle soup ( 35 cal) Beef soup (50 cal) Vegetable pasta soup (44 cal) Broccoli soup (60 cal) Homemade soups (22 cal) Turkey soup (38 cal) Cream soups (52 kcal.) Meat soup (50 kcal.) Oyster stew soup (40 kcal.) Chinese soup (33 kcal.) Shark fin soup (46 kcal.) Cheese soup (76 kcal.)
How many calories are in a bowl of pea soup?
Peas themselves are not the most high-calorie product. 100 g of fresh green peas contains only 55 kcal, canned peas contain even less - 40 kcal, but they can be saturated with sugar. But dried whole grains, from which soup is mainly made, already contain 298 kcal in a 100-gram serving. However, they are used relatively little, since in the process the grains swell and become larger. Plus, proper pea soup still has a fair amount of broth.
Classic pea soup usually contains potatoes, so it has a considerable calorie content, and at the same time, it also contains starch. 100 g of soup contains approximately 65 kcal. If you want to get a dietary dish, remove potatoes from the food list. There will be about 40-45 kcal left.
If you prepare soup exclusively with peas with potatoes, onions, herbs and carrots, you get a vegetable composition that has a relatively low energy value: about 60-70 kcal per 100 g. The indicator is relevant for the ratio of water and food - 2:1. If there is less broth, the serving will have more calories.
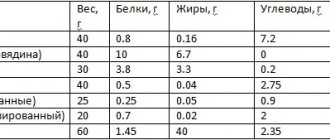
Composition of nutrients, BJU
Pea soup
| For quantity: 100 grams | ||
| Calories — 67 | Calories from fat - 14 | |
| BJU | ||
| Total fat content | 1.5g | |
| Saturated | 0.7g | |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.16g | |
| Monounsaturated | 0.53g | |
| Cholesterol | 2mg | |
| Total carbohydrate content | 10.54g | |
| Dietary fiber | 2g | |
| Sugar | 3.53g | |
| Squirrels | 3.34g | |
| Vitamins and microelements | ||
| A - 3 µg | C - 0.57 mg | |
| B-6 – 0.03 mg | B-12 - 0.06mcg | |
| D - 0mcg | E - 0.09 mg | |
| Calcium 29mkg | Iron 0.81 mg | |
| Magnesium 17.33 mg | Zinc 0.66mg | |
| Potassium 97 mg | Sodium 212 mg | |
Distribution of calories for BJU:Carbohydrates (61%) Fats (20%) Proteins (19%) | ||
How many calories does it have?
Here's how much:
Today there are many different recipes for making pea soup. Including those that allow you to minimize the number of calories in a dish. For example, if you want to prepare a dietary soup, then you definitely should not add smoked meats to it.
Now let's clarify what nutritional value pea soup has. Its calorie content cannot but please all those who adhere to a diet.
The calorie content of pea soup with water, per 100 grams, is:
Pea soup in dietetics
Who among us did not eat rich pea soup as a child? So tasty, filling and high in calories. The classic soup recipe is prepared with fatty broth, so it is contraindicated for those who dream of a slim figure. Although my grandmother said in childhood that it was so healthy and that we definitely need to eat it at least sometimes. And she was right.
Peas contain a lot of vegetable protein, which promotes muscle growth, as well as B vitamins, and. It has a lot of potassium, magnesium, zinc, which contribute to the normal functioning of the digestive system, strengthens muscles and the nervous system, and even helps with insomnia.
Nutritionists advise that you do not need to exclude this soup from your diet, you just need to adjust its recipe a little to reduce the level of fat and calorie content. Therefore, below are recipes for making pea soup with different calorie content: without meat, with chicken and with smoked meats. Try them all or choose one, they are all delicious and good for your health.
Benefits of pea soup
Pea soup contains all the vitamins and nutrients that peas contain. These are, first of all, B vitamins, as well as vitamin E, which allows you to preserve beauty and youth for a long time, and vitamin C, which is necessary to strengthen the immune system. These vitamins also help normalize metabolism, effectively fight depression and have a beneficial effect on cardiovascular diseases. Despite the fairly high calorie content of pea soup, it is recommended to consume it regularly to replenish the reserves of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the body. In pea soup, proteins make up 23%, fats 1.2%, and carbohydrates 52%.
Pea soup for weight loss:
Not every diet is healthy. The effect of losing weight is often accompanied by general exhaustion of the body and a lack of nutrients.
It is not surprising that nutritionists recommend using weight loss programs that, using gentle methods, make it possible to get rid of excess weight, while maximizing the supply of the body with the necessary vitamins, microelements and other beneficial substances, especially protein. This is why plant foods that have a high percentage of protein are favored by them for weight loss. Having no fat, unlike protein products of animal origin, they saturate the body with protein, and dishes prepared from them are light and dietary.
The leader among plant products in terms of protein content is peas (22.4% protein by dry weight). Therefore, nutritionists believe that dishes made from it, prepared accordingly, will help those who want to lose weight, since they are low in calories and at the same time nutritious. But such a diet should be applied no more than once a year, since frequent consumption of peas can cause increased flatulence and worsen health. Therefore, in order not to burden the body by repeating such a diet, you can regularly arrange different fasting days once a week - on apples, on water, or on green tea, which will make it possible to constantly maintain normal weight.
Recipe Pea soup. Calorie, chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Pea soup”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 34.3 kcal | 1684 kcal | 2% | 5.8% | 4910 g |
| Squirrels | 1.9 g | 76 g | 2.5% | 7.3% | 4000 g |
| Fats | 0.4 g | 56 g | 0.7% | 2% | 14000 g |
| Carbohydrates | 5.9 g | 219 g | 2.7% | 7.9% | 3712 g |
| Alimentary fiber | 1.2 g | 20 g | 6% | 17.5% | 1667 g |
| Water | 89.8 g | 2273 g | 4% | 11.7% | 2531 g |
| Ash | 0.372 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 62.7 mcg | 900 mcg | 7% | 20.4% | 1435 g |
| beta carotene | 0.376 mg | 5 mg | 7.5% | 21.9% | 1330 g |
| Lutein + Zeaxanthin | 0.052 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.049 mg | 1.5 mg | 3.3% | 9.6% | 3061 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.024 mg | 1.8 mg | 1.3% | 3.8% | 7500 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 15.86 mg | 500 mg | 3.2% | 9.3% | 3153 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.165 mg | 5 mg | 3.3% | 9.6% | 3030 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.056 mg | 2 mg | 2.8% | 8.2% | 3571 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 1.431 mcg | 400 mcg | 0.4% | 1.2% | 27952 g |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 1.4 mg | 90 mg | 1.6% | 4.7% | 6429 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.127 mg | 15 mg | 0.8% | 2.3% | 11811 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 1.324 mcg | 50 mcg | 2.6% | 7.6% | 3776 g |
| Vitamin K, phylloquinone | 0.6 mcg | 120 mcg | 0.5% | 1.5% | 20000 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 0.7207 mg | 20 mg | 3.6% | 10.5% | 2775 g |
| Niacin | 0.315 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 156.62 mg | 2500 mg | 6.3% | 18.4% | 1596 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 14.73 mg | 1000 mg | 1.5% | 4.4% | 6789 g |
| Silicon, Si | 10.707 mg | 30 mg | 35.7% | 104.1% | 280 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 13.01 mg | 400 mg | 3.3% | 9.6% | 3075 g |
| Sodium, Na | 11.79 mg | 1300 mg | 0.9% | 2.6% | 11026 g |
| Sera, S | 22.18 mg | 1000 mg | 2.2% | 6.4% | 4509 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 35.6 mg | 800 mg | 4.5% | 13.1% | 2247 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 21.25 mg | 2300 mg | 0.9% | 2.6% | 10824 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Aluminium, Al | 172 mcg | ~ | |||
| Bor, B | 66.6 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vanadium, V | 25.74 mcg | ~ | |||
| Iron, Fe | 0.65 mg | 18 mg | 3.6% | 10.5% | 2769 g |
| Yod, I | 0.87 mcg | 150 mcg | 0.6% | 1.7% | 17241 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 1.832 mcg | 10 mcg | 18.3% | 53.4% | 546 g |
| Lithium, Li | 6.576 mcg | ~ | |||
| Manganese, Mn | 0.1461 mg | 2 mg | 7.3% | 21.3% | 1369 g |
| Copper, Cu | 79.74 mcg | 1000 mcg | 8% | 23.3% | 1254 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 8.12 mcg | 70 mcg | 11.6% | 33.8% | 862 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 17.375 mcg | ~ | |||
| Tin, Sn | 1.1 mcg | ~ | |||
| Rubidium, Rb | 54.5 mcg | ~ | |||
| Selenium, Se | 0.878 mcg | 55 mcg | 1.6% | 4.7% | 6264 g |
| Strontium, Sr | 6.47 mcg | ~ | |||
| Titanium, Ti | 12.25 mcg | ~ | |||
| Fluorine, F | 76.16 mcg | 4000 mcg | 1.9% | 5.5% | 5252 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 1.59 mcg | 50 mcg | 3.2% | 9.3% | 3145 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.324 mg | 12 mg | 2.7% | 7.9% | 3704 g |
| Zirconium, Zr | 1.01 mcg | ~ | |||
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Starch and dextrins | 4.769 g | ~ | |||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 1.1 g | max 100 g | |||
| Galactose | 0.06 g | ~ | |||
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.302 g | ~ | |||
| Maltose | 0.05 g | ~ | |||
| Sucrose | 0.595 g | ~ | |||
| Fructose | 0.198 g | ~ | |||
| Essential amino acids | 0.125 g | ~ | |||
| Arginine* | 0.135 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 0.089 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 0.037 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.09 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 0.136 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 0.13 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.019 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.04 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.075 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.023 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 0.086 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 0.149 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | 0.217 g | ~ | |||
| Alanin | 0.081 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.197 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.083 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 0.275 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 0.061 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 0.078 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 0.062 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.022 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Cholesterol | 0.16 mg | max 300 mg | |||
| beta sitosterol | 3.659 mg | ~ | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 0.1 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 0.001 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 0.043 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 0.012 g | ~ | |||
| 20:0 Arakhinovaya | 0.001 g | ~ | |||
| 22:0 Begenovaya | 0.001 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.101 g | min 16.8 g | 0.6% | 1.7% | |
| 16:1 Palmitoleic | 0.005 g | ~ | |||
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 0.097 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.158 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 1.4% | 4.1% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.146 g | ~ | |||
| 18:3 Linolenic | 0.02 g | ~ | |||
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.1 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 2.1% | 6.1% |
The energy value of pea soup is 34.3 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Benefits of pea soup without meat
The benefits of pea soup without meat are as follows:
- such soups are characterized by low calorie content and a small amount of fat, therefore they are an indispensable component of dietary nutrition;
- with regular consumption of pea soup, metabolism is stimulated and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract improves;
- the vitamins contained in the soup are beneficial for the health of the heart and blood vessels;
- The richness of pea soup with B vitamins makes it indispensable for stress, headaches, and mental stress;
- soup made from peas is indicated for hypertension;
- The minerals contained in the soup improve the condition of hair and nails and stimulate blood circulation.
Pea soup with smoked meats
Cooking time: 25-30 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 350 g peas.
- 350 g potatoes.
- 2 pieces of sweet pepper.
- 160 g onions.
- 120 g carrots.
- 200 g raw smoked sausage.
- 100 g hunting sausages.
- Pure water.
- Vegetable oil.
- Spices.
Cooking process:
First stage: peas, potatoes. Pour 1.5 liters of water into a saucepan and add the pre-soaked peas. Cook for 10-15 minutes. Cut the potatoes into pieces and add to the peas. Salt the water.
Second stage: carrots, peppers, onions, smoked meats. Finely chop the onion and pepper, grate the carrots. Lightly fry all vegetables in vegetable oil. Cut the sausage into cubes and add to the vegetables. Fry for another 8-10 minutes.
Third stage: peas, potatoes, frying. Add the fried vegetables and sausage to the peas and cook for another 10 minutes. Turn off the gas and let the soup brew for another 20-25 minutes. Now you can serve it to the table.
Calorie content of pea soup with smoked meats is 119 kcal per 100 g.
Pea soup with chicken broth
This is one of the options for pea soup with meat broth , in which the calorie content per serving is 240-250 kcal.
The calorie content of pea soup with chicken is 50-60 kcal lower than with pork or beef.
Ingredients:
- Chicken fillet – 200-300 g.
- A glass of peas.
- 5 liters of water.
- One onion.
- Two carrots.
- Salt pepper.
Cooking process:
Stage one: peas. Wash and soak the peas overnight. In the morning, drain the excess water, pour clean water into the pan and cook the peas until tender.
Stage two: chicken, vegetables. Wash the fillet and cut into pieces. Pour about 5 liters of water into a pan and cook the meat in it. Don't forget to add salt. The broth will take approximately 20-25 minutes to cook. Then add finely chopped vegetables to it and cook for another 15 minutes.
Stage three: boiled peas, spices. Add boiled peas and spices to taste to the soup, stir and leave for another 12 minutes. You can add greens and rye crackers to the soup.
Pea soup in chicken broth with meat has a calorie content of 80-85 kcal per 100 grams.