Related Products
Chili soup (57 cal) Carrot coriander soup (100 cal) Lentil soup (54 cal) Vegetable soup (41 cal) Clear soup (8 cal) Chicken soup (60 cal) Potato soup (63 cal) ) Mushroom soup (51 cal) Tomato soup (43 cal) Bean soup (74 cal) Turtle soup (53 cal) Onion soup (44 cal) Noodle soup (35 cal) Beef soup (50 cal) .) Pea soup (67 cal) Vegetable pasta soup (44 cal) Broccoli soup (60 cal) Homemade soups (22 cal) Turkey soup (38 cal) Cream soups (52 cal) Meat soup (50 cal) Oyster stew soup (40 cal) Chinese soup (33 cal) Shark fin soup (46 cal) Cheese soup (76 cal)
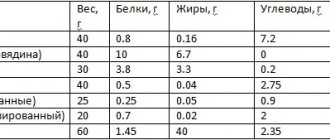
Calorie content of first courses with fish
Some versions of fish soup may be dietary. The calorie content of different fish soups is presented in the table.
| Dish | Serving Size | KBZHU |
| Fish soup with small fish, potatoes and millet | 100 g | Calories - 58 kcal, proteins - 8.2 g, fats - 1.3 g, carbohydrates - 3.4 g |
| Soup with rice and fish on an electric stove | 100 g | Calories - 53 kcal, proteins - 4 g, fats - 1.6 g, carbohydrates - 7.5 g |
| Homemade river fish chowder with tomatoes | 100 g | Calories - 49 kcal, proteins - 4 g, fats - 2.1 g, carbohydrates - 5 g |
Many people don’t cook fish soup because they don’t like to cut fish. Small specimens can be boiled whole, and the finished broth can be strained. From small fish, the stew turns out rich and very aromatic.
Composition of nutrients, BJU
Fish soup (ear)
| For quantity: 100 grams | ||
| Calories — 16 | Calories from fat - 7 | |
| BJU | ||
| Total fat content | 0.81g | |
| Saturated | 0.2g | |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.14g | |
| Monounsaturated | 0.24g | |
| Cholesterol | 1mg | |
| Total carbohydrate content | 0g | |
| Dietary fiber | 0g | |
| Sugar | 0g | |
| Squirrels | 2.17g | |
| Vitamins and microelements | ||
| A - 2 µg | C - 0.1 mg | |
| B-6 – 0.04 mg | B-12 - 0.69mcg | |
| D - 0mcg | E - 0.17 mg | |
| Calcium 3µg | Iron 0.01 mg | |
| Magnesium 7 mg | Zinc 0.06mg | |
| Potassium 144 mg | Sodium 156 mg | |
Distribution of calories for BJU:Carbohydrates (1%) Fats (45%) Proteins (54%) | ||
Recipe for river fish soup. Calorie, chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “river fish soup”.
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 26.7 kcal | 1684 kcal | 1.6% | 6% | 6307 g |
| Squirrels | 3.1 g | 76 g | 4.1% | 15.4% | 2452 g |
| Fats | 0.4 g | 56 g | 0.7% | 2.6% | 14000 g |
| Carbohydrates | 2.7 g | 219 g | 1.2% | 4.5% | 8111 g |
| Organic acids | 0.1 g | ~ | |||
| Alimentary fiber | 0.5 g | 20 g | 2.5% | 9.4% | 4000 g |
| Water | 91.2 g | 2273 g | 4% | 15% | 2492 g |
| Ash | 0.395 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 124.3 mcg | 900 mcg | 13.8% | 51.7% | 724 g |
| beta carotene | 0.745 mg | 5 mg | 14.9% | 55.8% | 671 g |
| beta Cryptoxanthin | 0.0446 µg | ~ | |||
| Lycopene | 0.0056 µg | ~ | |||
| Lutein + Zeaxanthin | 0.1905 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.019 mg | 1.5 mg | 1.3% | 4.9% | 7895 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.013 mg | 1.8 mg | 0.7% | 2.6% | 13846 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 0.15 mg | 500 mg | 333333 g | ||
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.054 mg | 5 mg | 1.1% | 4.1% | 9259 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.048 mg | 2 mg | 2.4% | 9% | 4167 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 1.942 mcg | 400 mcg | 0.5% | 1.9% | 20597 g |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 2.88 mg | 90 mg | 3.2% | 12% | 3125 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.049 mg | 15 mg | 0.3% | 1.1% | 30612 g |
| gamma tocopherol | 0.0042 mg | ~ | |||
| delta tocopherol | 0.0001 mg | ~ | |||
| Vitamin H, biotin | 0.102 mcg | 50 mcg | 0.2% | 0.7% | 49020 g |
| Vitamin K, phylloquinone | 1 mcg | 120 mcg | 0.8% | 3% | 12000 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 0.7352 mg | 20 mg | 3.7% | 13.9% | 2720 g |
| Niacin | 0.203 mg | ~ | |||
| Betaine | 0.0083 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 78.96 mg | 2500 mg | 3.2% | 12% | 3166 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 9.66 mg | 1000 mg | 1% | 3.7% | 10352 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 6.41 mg | 400 mg | 1.6% | 6% | 6240 g |
| Sodium, Na | 62.66 mg | 1300 mg | 4.8% | 18% | 2075 g |
| Sera, S | 35 mg | 1000 mg | 3.5% | 13.1% | 2857 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 13.3 mg | 800 mg | 1.7% | 6.4% | 6015 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 125.97 mg | 2300 mg | 5.5% | 20.6% | 1826 |
| Microelements | |||||
| Aluminium, Al | 124.7 mcg | ~ | |||
| Bor, B | 23.1 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vanadium, V | 13.84 mcg | ~ | |||
| Iron, Fe | 0.231 mg | 18 mg | 1.3% | 4.9% | 7792 g |
| Yod, I | 0.71 mcg | 150 mcg | 0.5% | 1.9% | 21127 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 0.853 mcg | 10 mcg | 8.5% | 31.8% | 1172 g |
| Lithium, Li | 7.526 mcg | ~ | |||
| Manganese, Mn | 0.0442 mg | 2 mg | 2.2% | 8.2% | 4525 g |
| Copper, Cu | 21.35 mcg | 1000 mcg | 2.1% | 7.9% | 4684 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 1.533 mcg | 70 mcg | 2.2% | 8.2% | 4566 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 1.579 mcg | ~ | |||
| Rubidium, Rb | 75.9 mcg | ~ | |||
| Selenium, Se | 0.126 mcg | 55 mcg | 0.2% | 0.7% | 43651 g |
| Fluorine, F | 133.26 mcg | 4000 mcg | 3.3% | 12.4% | 3002 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 9.57 mcg | 50 mcg | 19.1% | 71.5% | 522 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.2042 mg | 12 mg | 1.7% | 6.4% | 5877 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Starch and dextrins | 1.573 g | ~ | |||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 1.1 g | max 100 g | |||
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.2911 g | ~ | |||
| Sucrose | 0.6751 g | ~ | |||
| Fructose | 0.1456 g | ~ | |||
| Essential amino acids | 0.1039 g | ~ | |||
| Arginine* | 0.0217 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 0.0155 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 0.0045 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.0126 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 0.0177 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 0.0186 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.0036 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.0071 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.0135 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.0043 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 0.0136 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 0.0251 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | 0.1868 g | ~ | |||
| Alanin | 0.0156 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.0359 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.0136 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 0.0525 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 0.0123 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 0.0156 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 0.0113 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.0037 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Phytosterols | 0.0855 mg | ~ | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| 12:0 Lauric | 0.0002 g | ~ | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 0.0003 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 0.0078 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 0.0014 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.0169 g | min 16.8 g | 0.1% | 0.4% | |
| 16:1 Palmitoleic | 0.0005 g | ~ | |||
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 0.0163 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.0094 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 0.1% | 0.4% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.0087 g | ~ | |||
| 18:3 Linolenic | 0.0081 g | ~ |
The energy value of river fish ear is 26.7 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
Micro- and macroelements in Fish broth (ear) with meatballs
Fish broth (ear) with meatballs contains the following elements: Mono- and disaccharides, Cholesterol, Ash, Starch, Water, Organic acids, Dietary fiber, Unsaturated fatty acids, Sodium, Potassium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Calcium, Sulfur, Copper, Boron, Aluminum, Iodine, Manganese, Chromium, Fluorine, Molybdenum, Cobalt, Nickel, Rubidium, Zinc, Iron, Chlorine.
| Micro and macro element | Meaning |
| Mono- and disaccharides, g. | 0,3 |
| Cholesterol, mg | 26,9 |
| Zola, Mr. | 0,09 |
| Starch, Mr. | 0,04 |
| Water, city | 117,3 |
| Organic acids, g. | 0,007 |
| Dietary fiber, g. | 0,1 |
| Unsaturated fatty acids, g | 0,1 |
| Sodium, mg | 6,5 |
| Potassium, mg | 14,8 |
| Phosphorus, mg | 11,4 |
| Magnesium, mg | 1,2 |
| Calcium, mg | 4 |
| Sulfur, mg | 10,2 |
| Copper, µg | 6,4 |
| Boron, µg | 5,9 |
| Aluminum, µg | 11,8 |
| Iodine, mcg | 1 |
| Manganese, mg | 0,0081 |
| Chromium, µg | 10,4 |
| Fluorine, mcg | 82,7 |
| Molybdenum, mcg | 1 |
| Cobalt, µg | 0,6 |
| Nickel, µg | 1,2 |
| Rubidium, mcg | 14 |
| Zinc, mg | 0,2063 |
| Iron, mg | 0,1 |
| Chlorine, mg | 38,5 |
Why is ear useful?
Fish is initially a very healthy product. Content of minerals, fats
,
proteins and other equally important compounds depends on the type of fish, place of catch, and method of preparation
. Sea fish can become especially valuable, since in addition to easily digestible substances, it contains enough iodine and phosphorus. For example, cod fish soup, with a calorie content of 24.06 kcal, will be an excellent addition to any diet, just like a decoction of other types of fish products. The best option is hot soup.
Among the first courses, fish soup, better known as ukha, occupies a special place. Lovers of fish dishes constantly argue about which dish deserves the honorary title, and which is fish soup. There are so many people, so many opinions, but we will take it as an axiom that any first course made from fish is the favorite fish fish. There are simply a huge number of variations in its preparation; ukha can be prepared from crucian carp, carp and other representatives of the ichthyofauna - this is “black”, and if sturgeon or salmon were used for its preparation, then it is called “red”. For a long time, great attention was paid to the preparation of fish soup, and some types were cooked for several days, adding different varieties of waterfowl. In any case, it is tasty and healthy, and the question of how many calories are in the ear may not bother connoisseurs of healthy eating.
Wow, what kind of dish is this?
Several centuries ago, fish soup meant ordinary soup, made from anything, not just fish. Today, almost everyone knows that fish soup is very healthy and an essential component of the dish is fish. There are many recipes, of which the classic version of the decoction stands out. It involves the use of fish with such characteristics as a sweetish taste, freshness, and “stickiness.” Compliance with these requirements helps to obtain an exceptional taste and low energy
value of such a dish
. Therefore, eating fish soup during a diet is not only allowed, but also recommended.
The classic ear also has its own classification, according to which it stands out:
- Black ear, the calorie content of which is considered one of the lowest and varies around 31-40 kcal. The name itself is associated with the slight cloudiness of the broth, although in some recipes cucumber brine is added specifically for this purpose. Mostly river fish such as crucian carp, carp, rudd, as well as carp and asp are used for cooking. For comparison, the calorie content of carp fish soup is 31.57 kcal, but if the broth is prepared from crucian carp, the dish will become a little more nutritious. Calorie content of crucian fish soup is approximately 39.57 kcal
- White ear. For classic white fish soup, whitefish, pike perch, as well as ruff and perch are taken. For the best aroma and taste, other varieties are added, in particular, tench, catfish, and ide. Usually this is no more than 35% of all fish. This is especially important when observing the nutritional limits of a dish, since, for example, the calorie content of tench fish is 84.27 kcal, which will also affect the overall energy indicators;
- Triple ear. The methods for preparing the broth are different, as you can improvise with different types of fish. You can use one type of fish for cooking, and another for consumption. This option is especially good when you are on an ear diet and the kcal content is important;
- Red ear. From the name it is clear that this is red fish soup, the caloric content of which can also be regulated, the average is about 63.79 kcal. The dish is not exactly budget-friendly, but healthy and unusual in taste. Naturally, a lot depends on the cooking technology and type of seafood; for example, the calorie content of salmon fish soup can be only 38.87 kcal.
Beneficial features
Soup is often prepared from sea fish, it is perfectly complemented by the aromas of the sea, while sea fish gives the dish not only unforgettable flavor notes, it is very healthy and affects many vital processes occurring in the human body. The iodine it contains normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland, and phosphorus improves the nervous system and helps increase efficiency. Its main asset is the presence of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, which normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system and are capable of removing excess cholesterol from the body. Any fish also contains a large amount of valuable fat, while fish soup is considered dietary and is often included in the diet.
Vitamins in Fish broth (ear) with meatballs
Fish broth (ear) with meatballs contains the following vitamins: Mono- and disaccharides, Cholesterol, Ash, Starch, Water, Organic acids, Dietary fiber, Unsaturated fatty acids, Sodium, Potassium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Calcium, Sulfur, Copper, Boron, Aluminum, Iodine, Manganese, Chromium, Fluorine, Molybdenum, Cobalt, Nickel, Rubidium, Zinc, Iron, Chlorine.
| Vitamin | Meaning |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine), mg | 0,005 |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), mg | 0,02 |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), mg | 0,01 |
| Vitamin B9 (folic), mcg | 0,7 |
| Vitamin C, mg | 0,3 |
| Vitamin E (TE), mg | 0,1 |
| Vitamin PP (Niacin equivalent), mg | 0,9994 |
| Vitamin B12 (cobalamins), mcg | 0,02 |
| Vitamin D, mcg | 0,1 |
| Vitamin A, mg | 0,02 |
| Choline, mg | 11,8 |
| Vitamin A (VE), mcg | 20 |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic), mg | 0,06 |
| Vitamin PP, mg | 0,02 |
| Vitamin H (biotin), mcg | 1 |
Useful properties and composition of pig ears
No matter how skeptical people may be about pig ears, they are no less rich in a lot of vitamins and minerals necessary for humans, usually calculated per 100 g of product:
- Saturated fatty acids;
- Water (almost 62 g);
- A small amount of ash (up to 1 g);
- Vitamins PP, group B (thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, pantothenic acid, folate, cobalamin), niacin;
- Selenium, manganese, zinc, copper, phosphorus, iron, potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, iodine (or rather, their most important salts for the body).
The total calorie content of 100 g of pig ears (one ear weighs approximately 300 grams) varies from 210 to 240 calories.
Regarding the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, the situation here is ambiguous. Some claim that there is a carbohydrate component in pig ears, while others deny this fact. In any case, the standard used/w/w energy ratio is considered to be 38%/58%/1% (sometimes 0% is used for carbohydrates).