What is physical activity ratio?
Physical activity coefficient is a value equal to the ratio of a person’s energy expenditure during activity to expenditure at rest (the value of basal energy metabolism).
The value of the physical activity coefficient is always higher than one and can vary from 1.4 to 2.4. Values of 2.4-4.5 and higher can be observed in athletes during intense training or competitions and are temporary, periodic in nature.
Values below 1.4 (in the range of 1.2-1.3) occur when a person is bedridden due to age or illness, but even in this case, to determine the energy value of the diet, it is necessary to take into account the damage factor, temperature factor, the presence of protein-energy deficiency.
Physical activity coefficient is a value showing the ratio of a person’s energy expenditure during activity to energy expenditure at rest.
How to determine the physical activity ratio?
To determine the coefficient of physical activity, there are tables that show the coefficient of each type of physical activity per unit of time.
The problem is that throughout the day, different types of activities continuously replace each other. How can you find out your coefficient?
To do this, with varying degrees of error, you can use the data given below.
CFA value
The CFA value must always be above unity. The average person has a reading in the range of 1.4 to 2.4. Higher rates occur among professional athletes who train to the limit of their capabilities. For the body to recover, elevated levels should be temporary. Indicators below 1.4 appear in bedridden patients. In order to determine the physical activity coefficient, it is necessary to take into account temperature, metabolism and the effect of the disease on the body.
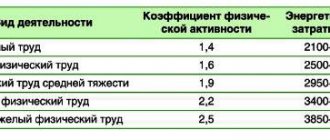
A coefficient of 1.4-1.6 indicates a sedentary lifestyle. Such people do not play sports and rarely walk. The work does not involve physical activity; the evening is spent in front of the TV or computer. This group includes office workers, housewives, and women on maternity leave with one child.
With indicators of 1.6-1.9, a person sometimes experiences physical activity. The work involves infrequent movements, the person takes walks and sometimes plays sports. This type also includes workers of light physical labor.
1.9-2.0 - coefficient of persons engaged in manual labor. These include production workers, as well as people who work out in the fitness room at least 3-4 hours a week.
A pronounced load of 2.0-2.2 is occupied by dancers, agricultural workers, and people who play sports 7 times a week.
Heavy physical activity starts at 2.2. It is typical for athletes and workers with difficult physical working conditions.
The benefits of active recreation
Active rest is the continuation of intense physical activity with a change in its type. This form of leisure is preferable for people whose work activities involve limited physical activity.
The stricter these restrictions are, the more a person needs active rest, which is, essentially, compensation for forced immobility during the working day.
On a note:
People whose work limits physical activity during the day need an active form of rest.
Of course, active recreation cannot always replace passive recreation (for example, reading books or doing creative work is a useful and necessary form of recreation). But you may well prefer walking or doing yoga to watching “endless” TV series or “deep immersion” in social networks.
On a note:
If you want to watch a movie, go to the cinema.
Just go, outline a walking route of 2-3 kilometers and walk them before and after the session. The ability to walk for a long time and quickly is determined not only by physical fitness, but also by appropriate equipment, and in order for your walk to be useful and enjoyable, you first need comfortable shoes.
If the weather is not conducive to walking, then you can start cleaning - this will increase energy costs by 60%. Working in the garden or playing outdoor games with children gives an even greater effect.
Basal metabolic rate (PPM): indicator for the formula for calculating physical activity ratio
The athlete's physical activity ratio is
Basic metabolic rate (PPM) - the lowest level of energy metabolism. This factor determines how much energy the body uses when performing basic physiological activities: heartbeat, breathing, digestion, tissue regeneration, etc.
- PPM allows you to determine what amount of calories is optimal for survival in a balanced living environment.
- It is worth noting that this factor does not include any activity.
- Therefore, it is calculated in the case of passive rest in a lying position and without mental stress.
When calculating PPM, the Harris-Benedict formula is usually used. The advantage is that this indicator can be calculated using a ready-made calculator, which significantly speeds up and facilitates the preparation of invoices. However, it is good to be able to calculate this parameter yourself so that you can understand what it consists of.
Women's PPM Formula:
- PPM [kcal] = 665.09 + (9.56 * weight in kg) + (1.85 * height in cm) - (4.67 * age)
Formula for PPM for men:
- PPM [kcal] = 66.47 + (13.75 * weight in kg) + (5 * height in cm) - (6.75 * age)
Using the above formulas, you can calculate the average basal metabolic rate. Of course, professionals individualize the formula so that the risk of violations is at the lowest level.
What is CFA
You will be interested in: Exercises for the arms: description, exercises with photos, step-by-step instructions, execution and working out the arm muscles
The ratio of calories burned per day to basal metabolic rate is called the physical activity coefficient (PFA). The value of the indicator depends on the professional activity that a person is engaged in during the day. Any activity increases the coefficient compared to a state of rest.
CFA is determined based on the following data:
- active actions throughout the day;
- gender;
- age.
The physical activity coefficient determines the relationship between activity and a person’s health and weight. Thanks to this, you can determine what needs to be increased or decreased during the day to bring your weight back to normal. Physical activity refers to all the actions that a person performs. This could be reading books, ice skating or watching TV. The state of a person’s health depends on the indicators of physical activity. More and more diseases occur due to a passive lifestyle.
Relationship between CFA and health
Chronic diseases are more common in people with a low level of physical activity factor than in people with an average level of physical activity factor. The fact is that to maintain good condition you need to move. Excess weight provokes diseases such as hypertension and diabetes. Obesity puts a strain on the cardiovascular system. With improper metabolism and lack of physical activity, the risk of increasing cholesterol levels increases several times. Constant fluctuations in weight affect your health, so it is important to maintain CFA at a sufficient level to avoid weight gain.
Source
What are the recommended levels of physical activity?
Children and adolescents aged 5-17 years:
- Must engage in at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity per day;
- Physical activity of more than 60 minutes per day will provide additional benefits to their health.
- Physical activity aimed at developing the musculoskeletal system should be done at least three times a week.
Adults aged 18-64 years:
- Must engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week, or at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week, or an equivalent combination of moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity physical activity.
- For exercise to provide additional health benefits, adults in this age group should increase their time of moderate-intensity physical activity to 300 minutes per week or otherwise achieve a similar level of activity.
- Strengthening exercises that work major muscle groups should be performed twice a week or more often.
Adults age 65 and older:
- Must engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week, or at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week, or an equivalent combination of moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity physical activity.
- For exercise to provide additional health benefits, adults in this age group should increase their amount of moderate-intensity physical activity to 300 minutes per week or otherwise achieve a similar level of activity.
- Adults in this age group with limited mobility should engage in physical activity to improve balance and prevent the risk of falls three times a week or more often.
- Strengthening exercises that work major muscle groups should be performed twice a week or more often.
The intensity of different forms of physical activity varies between people. In order for physical activity to help strengthen the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, the entire activity should be divided into time periods lasting at least 10 minutes.
Key Facts
- Insufficient physical activity is one of the leading risk factors for death worldwide.
- Insufficient physical activity is a major risk factor for noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes.
- Physical activity has important health benefits and contributes to the prevention of NCDs.
- One in four adults in the world are not active enough.
- More than 80% of adolescents worldwide lack physical activity.
- Policies on physical inactivity are in place in 56% of WHO Member States.
- WHO member states have agreed to reduce the prevalence of insufficient physical activity by 10% by 2025.
How to learn to count calories? Activity coefficient and calculation rules (formula)
Today we will learn how to learn to count calories
food products, as well as what
the activity coefficient
, why it is needed and what
formula
can be used
to calculate the calorie content
of a particular dish
HOW TO LEARN TO COUNT CALORIES? ACTIVITY COEFFICIENT AND CALCULATION RULES (FORMULA)
Good afternoon, today we will talk about how to learn to count calories
food products, as well as
what the activity coefficient is
, why it is needed and what
formula
can be used
to calculate the calorie content
of a particular dish.
Have you ever thought about how much
do our
bodies
actually
calories for
normal functioning
?
Contrary to popular belief
, using a very simple
method
, we can easily
determine
this
value
.
True, the figure will be approximate
, but still it is much
better
than the popular “
thousand
”.
HOW TO LOSE WEIGHT CORRECTLY AND QUICKLY? PERSONAL EXPERIENCE
On how many calories
Our body needs
to be influenced
by many
factors
.
Important factors are weight
,
height
,
gender
,
age
,
the nature of the work performed
,
physical activity
,
body constitution
,
medications taken
,
eating habits
and much, much more.
There is a very simple method
that
takes into account
only
gender
,
weight
and
activity level
.
So, for example, for reference, in cream cheese
contains about
216 kilocalories
,
a small natural yogurt
-
170 kilocalories
, and sunflower oil - as much as
560 kilocalories
.
Most products
, available on
store shelves
contain
information
that tells us about their
calorie content
, most often we diligently
ignore
or simply
do not notice them
.
Now let's pick up a calculator
and use
a simple formula
to
count calories
in a particular
food product
.
So, for women
,
the formula for calculating calories
will look
like this
:
WEIGHT x 24 HOURS x 0.9 x ACTIVITY RATIO
Formula for calculating calories
for
men
it will look
like this
:
WEIGHT x 24 HOURS x ACTIVITY RATIO
Now let's find out what the activity coefficient is
?
This indicator establishes the numerical value of
a person’s activity throughout the day.
Conventionally, the degree of activity
a person can be divided into
four main degrees of intensity
:
1. LOW (lack of physical exercise, sedentary work) – 1.3;
2. MEDIUM
(training 3 times a week, sedentary work) – 1.6;
3. HIGH
(daily intense exercise, leg work) – 1.8;
4. VERY HIGH (daily intense training, physical work for most of the day) – 2;
For example: