October 17, 2012
We tell you how to calculate your individual calorie needs and how many calories you need to burn to lose one kg of fat.
Science defines one calorie as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius. In practice, calories measure the amount of energy a person receives from food and spends on physical activity and metabolic processes, such as breathing. By the way, when it comes to caloric intake or energy expenditure, it is more correct to use the term “kilocalorie”. The calorie itself is too small, and the average diet when calculated in such units becomes millions. However, the abbreviated term “calorie” is used in everyday life.
Where do calories come from?
The only fuel that supplies calories to the human body is food. Drinks also contain calories
, for example, juices, milk, sweet soda.
Some drinks, particularly the aforementioned soda, contain empty calories
. They don't provide any nutritional value, but they still need to be considered. Calories are found in the three main components of food: fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Fat has about twice the calorie content of proteins and carbohydrates, but this is not a reason to give it up completely - the body needs fats.
Got enough sleep - burned calories
We calculated how many calories a person spends while performing daily activities. Simply enter keywords (such as "office work" and "sleep") to determine your body's energy expenditure.
Harris-Benedict formula
Physiologists F. G. Benedict and D. A. Harris created its original version empirically back in 1919. To do this, they studied more than 200 people of different genders, age and weight categories. In 1984, the original formula for calculating calorie intake per day was slightly modified in order to more correctly take into account a person’s age. Here's what the refined version looks like:
- women: 447.593+9.247×Weight [kg]+3.098×Height [cm]−4.33×Number of completed years;
- men: 88.362+13.397×Weight [kg]+4.799×Height [cm]−5.677×Number of complete years.
To determine the exact number of kilocalories that the body needs daily, you also need to multiply the resulting BMR value by the physical coefficient. human activity. It is this coefficient that lies the main problem with the accuracy of the results obtained, since its value can vary over a fairly wide range (from 1.2 to 1.9). This means that the final result may differ by several hundred kilocalories.
According to the Harris-Benedict method, there are five degrees of weekly activity of an individual:
- low (complete absence of any physical activity) - 1.2;
- low (light exercise every other day or two) – 1.375;
- average (more intense classes every other day) – 1.55;
- high (daily sports) – 1.725;
- maximum (intensive professional load) – 1.9.
As an example, let’s try to calculate the daily calorie intake for women using the formula developed by these scientists. Let's consider a girl, 30 years old, 1 meter 70 centimeters tall, weighing 55 kilograms, who trains in the gym every other day.
BMR = 447.593+9.247×55+3.098×170–4.33×30=1353 kcal. Multiplying the resulting figure of 1353 by 1.55 (activity coefficient) gives us the final result - 2097 kilocalories. This is her daily norm.
Calorie norms for men are calculated in the same way. For comparison, let’s take a 30-year-old young man with the following parameters: B - 70 kg, P - 180 cm, who also goes to the gym every other day. We substitute these parameters into the formula and get 1720 kcal. Multiply by the coefficient of active metabolism 1.55, the result is 2665 kcal.
Try doing the same calculations with your data.
How to gain and lose weight?
To form one kg of fat reserves, about 7700 kcal are needed. It follows that to lose a kilogram of fat you need to spend about 7700 kcal
.
True, refusing food does not bring the desired result. You need to lose weight wisely: by moderately reducing your caloric intake and burning excess calories through exercise. Reducing calories and/or spending about 500 kcal per day
leads to a loss of about 450 grams of excess weight per week.
Nutritionists consider losing weight at such a speed to be the healthiest
and emphasize that the weight lost in this way will not return quickly.
Starvation diets, on the contrary, not only harm the body, but are also ineffective
. The weight will drop quickly, but with a return to normal nutrition it will instantly return.
Daily calorie intake for women
Recently, more and more girls are striving for an ideal figure. Perhaps this is largely the influence of social networks - sometimes it begins to seem that you are the only one who doesn’t have pumped up buttocks and a flat stomach. In this regard, many girls began to wonder how to determine their calorie intake per day. Taking care of yourself is a great idea, the main thing is not to go to extremes and not sit on the water with apples, which many girls do.
The average daily caloric intake for women from 18 to 35 years old is 2350-2500 kcal, but for many girls, especially those of short stature and with a little excess weight, this norm is considered too high.
Calories for weight loss are calculated using the same formulas, but with numbers different from the formula for men.
Harris-Benedict formula
BMR = 655 + [9.6 x weight (kg)] + [1.8 x height (cm)] - [4.7 x age (years)].
Mifflin-Saint-Geort formula
BMR = [9.99 x weight (kg)] + [6.25 x height (cm)] - [4.92 x age (years)] -161.
We remind you that BMR is an indicator of basal metabolism, that is, the amount of energy consuming which you will not gain weight or lose weight.
The result obtained must be multiplied by the activity coefficient (see image above), but evaluate it objectively, since your result depends on it.
And again we remind you: in order to calculate the number of calories for weight loss per day, you need to subtract 10-15 percent from the resulting figure to create a calorie deficit, but no more if you want to lose weight efficiently and without health problems. To gain weight, add 15-20% to the result. If you are satisfied with your figure, then simply use the received norm.
Determining the basic need
There are many formulas for calculating individual calorie intake, but most often experts use the Harris-Benedict formula
.
It was created back in 1919 and adjusted in 1984, taking into account the fact that over 75 years people began to lead a much less energy-intensive lifestyle. First, we calculate the basic energy requirement necessary for the body to function normally. A person uses about 60 percent of the calories entering the body only to maintain the vital functions of the body. The main factors that influence basic energy requirements are height, weight, age and gender. Basic energy requirement for women = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kilograms) + (3.098 x height in centimeters) - (4.330 x age in years). Basic energy requirement for men = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kilograms) + (4.799 x height in centimeters) - (5.677 x age in years). Please note that this formula only works for adults
.
For example, for a 35-year-old woman weighing 65 kilograms and 165 centimeters tall, 1409 kcal is required daily to maintain the vital functions of the body. Attention:
even with minimal physical activity, the need for energy increases significantly!
The whole truth about metabolism
How do excess calories turn into fat? Why should you reduce your caloric intake as you age? What hormone helps men spend more energy? Read about what metabolism is and how it relates to body weight.
What does calorie counting in PP mean?
Proper nutrition comes down to the fact that a person should consume as many calories as his body and mind require to function effectively. The main advantages of tracking the energy value of your diet:
- Using calorie tables, you can create a harmonious menu for the day, decade, and even month in advance;
- when reading information about the number of kilocalories in another product, you are more likely to pay attention to its composition (presence of preservatives, GMOs, etc.);
- by building your diet in accordance with your daily energy expenditure, you will avoid the dangerous slowdown in metabolism that occurs when your diet is insufficient;
- By monitoring the calorie content of your daily diet, you minimize the possibility of junk food appearing on your regular table;
- By following the system, you significantly reduce the risk of overeating healthy foods, because even pure gluten-free foods can cause unwanted weight gain when a person consumes more than he really needs.
Determining daily needs
Now let's calculate the daily calorie requirement taking into account the level of physical activity. Be objective
and don’t overestimate her!
If you spend 8-12 hours a day at the computer and have long forgotten what the gym looks like, your physical activity can be assessed as very low or even classified as a sedentary lifestyle. Sedentary lifestyle:
daily calorie requirement = basal calorie requirement x 1.2.
Low physical activity
(half an hour of walking and light housework per day): Daily calorie requirement = base calorie requirement x 1.375.
Moderate physical activity
(daily 1-hour walk, 20-minute jog, or housework): Daily calorie requirement = basal calorie requirement x 1.55.
Daily Workout:
Daily Calorie Need = Base Calorie Need x 1.725.
Professional sports Thus, for the woman mentioned above with low physical activity, the daily energy requirement is 1937 kcal. This is enough to maintain your current weight. To lose weight, our hypothetical heroine would need to either increase her physical activity or reduce her calorie intake.
Daily calorie intake for men
The average daily calorie intake for men from 18 to 45 years old ranges from 2800 to 3050 kcal. After 45 years, the metabolic rate decreases and the body needs less energy to function. If the average is not enough for you, then you need to use special formulas and calculate your personal norm.
Harris-Benedict formula
BMR = 66 + [13.7 x weight (kg)] + [5 x height (cm)] - [6.76 x age (years)].
BMR is an indicator of basal metabolism, that is, the amount of energy consuming which you will not gain weight or lose weight.
You need to multiply the result obtained by the activity coefficient, but you need to evaluate it adequately.
How to calculate your daily calorie intake for weight loss: you need to subtract 10-15% from the result obtained to create a calorie deficit. If your goal is to gain weight, then you need to add 15-20% to this figure. And if your goal is to maintain your current shape, then consume the resulting number of calories.
Mifflin-San Geor Formula
BMR = [9.99 x weight (kg)] + [6.25 x height (cm)] - [4.92 x age (years)] + 5.
The principle is the same, only the numbers in the calculations are different. Don’t forget to multiply the result by the activity coefficient, then for weight loss subtract 10-15%, for weight gain add 15-20%, if you want to stay in your current shape, then use the basic norm.
General information about calories
A calorie is the amount of energy that heats 1 g of water by 1ºC.
1000 energy units equal 1 kcal. Daily caloric intake and calorie content of food products are calculated in laboratories. Biophysicists systematize information and create tables to determine the energy value of products. The daily diet includes dishes consisting of fats, carbohydrates, proteins, microelements, vitamins, and water. Energy is provided only by the first 3 components. The calorie content of dishes is their energy value, which is used for human life. If the body receives more energy than it can expend, the excess calories are converted into fat deposits.
Actions that cost money
Energy is spent on generating heat in the body and on movement (sports, walking, cleaning, etc.). At night, calories are also consumed: about 600 kcal are spent on 8 hours of healthy sleep. But for this you need to go to bed in a calm and relaxed state, ensure a comfortable temperature in the room, and do not eat fatty, sweet and high-calorie foods 3 hours before bedtime.
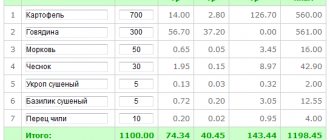
Calorie expenditure for various activities.
Consequences of lack of intake
Energy deficiency has an adverse effect on the body. If few nutrients come from food, then the missing energy is taken primarily from muscle tissue, rather than from fat reserves.
Against the background of a lack of carbohydrates and proteins, basal metabolism decreases, and glycogen reserves from the liver are actively consumed.
Glycogen, which is contained in the muscles, is gradually eliminated, so weight is reduced. But as soon as supplies run out, weight loss stops. During weight loss, fat deposits are consumed in minimal quantities, because they are not suitable for feeding the brain. Mainly bone and muscle tissue is lost. But if a dieter completely eliminates fat from the diet, muscle loss will increase. As a result, the risk of malnutrition will increase.
Daily activity rate
The daily activity coefficient directly depends on whether time is devoted to physical activity and how often the training takes place:
- 1.2 – minimal physical activity;
- 1.375 – training three times a week;
- 1.4625 – physical activity 5 times a week;
- 1.55 – intensive training 5 times a week;
- 1.6375 – daily training;
- 1.725 – classes several times a day;
- 1.9 – constant physical activity + mobile work activity.
How to calculate calorie intake
Calculating the daily calorie intake begins with identifying the characteristics of metabolism. You need to understand how many kcal the body needs to maintain vitality, in other words, to maintain “resting energy.” This indicator reflects the number of calories burned daily, while the energy released ensures metabolism, proper brain function, maintaining normal body temperature, etc.
The kcal norm is determined individually for each person based on the characteristics of his body. This indicator is influenced by gender, age, work activity and lifestyle (active/passive). On average, the daily norm is:
- 1800-2200 kcal for women;
- 2400-2800 kcal for men.
How many calories do men need per day?
The metabolic process occurs much faster in men, so a man’s daily diet is significantly different from a woman’s. An adult man of average build needs about 2500 kcal. in a day. But, if we take into account the level of physical activity, the picture looks like this:
Men leading a sedentary lifestyle need:
- from 18 to 30 years - about 2400 kcal;
- from 31 to 50 years - 2200 kcal;
- after 50 years - 2200-2400 kcal.
Article on the topic
Male strength and health. What foods should be in the diet of the stronger sex? For men leading a moderately active lifestyle, the following indicators are the norm:
- from 18 to 30 years - 2600-2800 kcal;
- from 31 to 50 years - 2400-2600 kcal;
- after 50 years - 1800 kcal.
During high activity, men need to consume the following amount of calories:
- from 18 to 35 years old - about 3000 kcal;
- from 31 to 50 years - 2800-3000 kcal;
- after 50 years - 2400-2800 kcal.
You can calculate the calorie intake for men using the Harris-Benedict formula :
66.5 + 13.75 x weight (kg) + 5.003 x height (cm) - 6.775 x age (years)
Article on the topic
Diet for the stronger sex: what to feed a man to lose weight? We multiply the result obtained by the coefficient of physical activity:
- 1.2 - minimum or absence;
- 1.375 - 3 times a week;
- 1.4625 - 5 times a week;
- 1.550 – intensively 5 times a week;
- 1.6375 - every day;
- 1.725 - every day intensively or 2 times a day;
- 1.9 - daily + physical work.
According to the Mifflin-San Jeor formula, the calorie intake per day for men is calculated as follows:
10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) - 5 x age (years) + 5
Here the result is also multiplied by the activity coefficient.
Article on the topic
On a dangerous solder. Seven mistakes of a losing weight teenager