Types of red spots
Red spots on the skin occur in people of different age groups, including infants.
There is a wide variety of rashes. They usually differ not only in size and shape, but also in shade. It all depends on the reason for their appearance. In any case, seemingly harmless spots cannot be ignored. Conventionally, red rashes on the body can be classified into the following types:
- flat and convex;
- wet and dry;
- swollen and inflamed;
- vague and having clear shapes;
- smooth and rough;
- itchy and not causing discomfort;
- purple or reddish.
The localization of red spots is also varied. Most often they appear on the arms and legs, back, neck, chest and face, less often on the genitals. By the location of the spots and their appearance, a specialist can understand what kind of disease they are a symptom of.
How to remove acne marks
Inflammatory erythema, the red marks left by acne, is treated with creams and serums containing anti-inflammatory ingredients. Therapeutic masks that soothe the skin have a good effect. It is undesirable to be in the sun without sunscreen, since hyperpigmentation in the form of dark areas may appear in place of the red spots.
Hyperpigmentation - dark marks are removed using whitening masks or creams. If there is no effect, they resort to prescription drugs - hydroquinone, azeleic acid and tazarotene, which improve the appearance of the skin. The laser gives a good effect. Two to three procedures are usually sufficient to significantly lighten age spots.
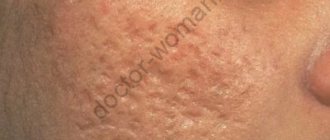
Atrophic acne scars, which appear as depressions or pits in the skin, usually do not go away without treatment. In this case, carbon dioxide and erbium lasers will help, which stimulate the production of collagen, the protein that fills such traces. The effect of microneedles helps, breaking up scars and stimulating the restoration of skin structures.
Hypertrophic scars also do not disappear over time. To eliminate them, laser and mechanical resurfacing – dermabrasion – is prescribed. Peels help well - procedures during which the top layer of skin along with scars is removed with the help of chemicals. Such treatment can be combined with the prescription of absorbable drugs.
Removing acne marks
Causes of red rashes
The appearance of red spots on the skin makes many people panic. And for good reason, because they are a symptom of many diseases. Some of them do not pose a threat, while others can cause serious problems in the body if treatment is delayed. Most often, red spots indicate the development of skin or infectious diseases, less often – a pathology of a mental nature.
There are several factors that can trigger the occurrence of skin rashes:
- allergic reactions;
- infectious diseases;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- dermatological diseases;
- autoimmune disorders;
- parasitic and bacterial infections;
- frequent stress;
- excitement;
- insect bites.
In some cases, red spots are the result of poor nutrition.
When to go to the doctor
If you have severe rashes, it is not recommended to delay your visit to a specialist. Ignoring them can aggravate the disease or lead to the spread of the process if there is a serious pathology.
If single small spots appear, you can postpone a visit to the doctor. Dermatologists recommend observing such rashes first. If there is no tendency to disappear within two to three days, especially if their appearance changes, consultation with a specialist is required.
You should immediately visit a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- severe itching in the affected area;
- peeling on the surface of the spots;
- getting wet;
- rapid increase in size;
- pain when pressing and palpating;
- swelling;
- inflammatory process.
What is nevus of the sebaceous glands?
Nevus of the sebaceous glands of Jadassohn is a congenital malformation, a benign tumor represented by altered sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
Localized on the scalp and face. Externally, it looks like a hairless yellow-pink oval or irregular plaque with a warty surface.
In 10% of patients, cancer develops at the site of the nevus. The high risk of malignant degeneration of a sebaceous nevus is an indication for its removal.
Surgical excision during puberty, observation by a dermatologist, and surgical excision if changes are present are recommended.
CO2 laser, electrocoagulation and cryodestruction are used to remove small areas of lesions without signs of malignancy.
Diagnostics
It is best to entrust the precise determination of the cause of red spots to doctors - a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist. The specialist conducts a visual examination to determine the nature and location of the spots, and during the conversation, finds out the general medical history. To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of tests are prescribed: a general analysis of urine and blood, scraping from the affected skin, a test for the presence of allergens and STDs, and an ultrasound of internal organs. In some cases, additional diagnostic methods are resorted to, which depend on the specific clinical picture and the suspected cause of the appearance of red spots.
Which vitamins have a protective effect?
Vitamins that have a protective effect against sun damage include the following:
- nicotinamide (or niacinamide, vitamin B3, vitamin PP) – improves DNA repair and prevents UV-induced suppression of skin immunity;
- retinol (or vitamin A) – regulates the process of skin cell renewal, an effective antioxidant, prevents malignancy of normal cells;
- tocopherol (or vitamin E) is a powerful antioxidant that neutralizes DNA-damaging free radicals formed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
What diseases cause red spots most often?
Allergy
Most often, red spots act as an external manifestation of an allergy. The rashes come in different sizes and shapes. They are often accompanied by swelling and itching. General malaise may occur in the form of weakness and chills. Allergic rashes are often observed in young children. Spots appear after consuming certain foods or medications, or using cosmetics. Sometimes rashes can be triggered by low temperatures. In this case we are talking about the so-called cold allergy.
Erythema
Erythema is characterized by redness of areas of the skin, which appears after the expansion of the capillary network and activation of blood circulation. Often this is a peculiar response of the skin to emotional excitement or physical overload. Erythema is observed after some cosmetic procedures, such as masks and massage. In this case, the red spots are relatively large, but they disappear quickly and do not require treatment.
However, the appearance of persistent facial erythema should alert you. It is characterized by spots that resemble bruises or bruises. Persistent erythema can lead to complications such as rosacea, so it is recommended to consult a dermatologist.
Measles rubella
One of its first symptoms is a red, small-spotted rash all over the body with maximum localization on the back, buttocks, neck and face. On the second day, the number of spots usually decreases. After three days they completely disappear, leaving no traces.
Scarlet fever
This infectious pathology is accompanied by small red spots measuring 1-2 mm. They appear after a sore throat occurs and are usually localized in the groin area and lower abdomen. Due to densely located spots, the skin appears reddened and inflamed.
Chicken pox
Chickenpox also has an infectious origin. It begins with red spots, in place of which bubbles up to 5 mm in size later form. After three days they become covered with dry crusts. With chickenpox, both spots and pimples are present on the skin at the same time. If you comb them, they will leave behind small pits, so-called pockmarks, which are difficult to get rid of.
Ringworm
In dermatology it is known as microsporia. This is a contagious disease of fungal origin. Its causative agent is a mold fungus of the genus Microsporum, which parasitizes the keratinized layer of the epidermis. With this pathology, the red spots have a round shape with a lighter center. Most often appear on the head and limbs.
Pink lichen of Zhiber
The disease is also known as roseola scaly. It occurs more often in spring and autumn, when the body is usually weakened. The pathology is characterized by pink, crimson and red spots about 3–5 cm in diameter. Outwardly, they resemble plaques. Usually within a week, other smaller spots appear near the first spot. The causes of Zhiber's deprivation are associated with decreased immunity and activity of the herpesvirus family in the body.
Eczema
People call it weeping lichen. At the initial stage, it is characterized by the appearance of light red rashes that may itch. Later, weeping bubbles similar to dew drops form. They quickly open with the formation of point erosions, giving way to severe peeling and crusts.
Helminthiasis
Parasites, during their life activity in the human body, release toxic substances to which the skin reacts in the form of red spots. Their appearance may vary depending on the degree of intoxication. At the initial stage of helminthic infestation, small rashes are observed, accompanied by severe itching. Later, the spots turn into purulent boils.
Photodermatitis
Photodermatitis is caused by increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays. It manifests itself as persistent redness, variegated spots all over the body, itching, and in some cases, burning and even blisters. It can be either an independent disease or a symptom of a pathology, such as systemic lupus erythematosus. In the first case, photodermatitis usually develops a day after exposure to the sun.
Psoriasis
It is considered one of the most common dermatological diseases. Psoriasis is of autoimmune origin. Against its background, small pale red nodular spots with a smooth glossy surface appear. After a few days, the rashes become covered with silvery-white scales. Soon they grow and merge into plaques of various sizes.
What is Dubreuil's melanosis?
Dubreuil's melanosis or lentigo maligna is most often observed on exposed skin in mature and elderly people. It starts with a small brown spot that slowly spreads around the periphery. Characterized by uneven pigmentation and increased pigmentation along the periphery of the lesion. It is a local malignant process that does not extend beyond the skin (cancer in situ) and is characterized by the proliferation of atypical melanocytes in the epidermis. It is characterized by slow growth and gradually transforms into lentigo-melanoma.
Diagnosis is carried out by dermatological and oncological doctors. Treatment is carried out by an oncologist surgeon. Surgical excision, CO2 laser removal are recommended, close-focus X-ray therapy, and photodynamic therapy are used.