Published: 03/09/2021 11:40:00 Updated: 05/06/2021
Hypothyroidism is a common disease of the endocrine system, in which the concentration of thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) decreases. The disease manifests itself in approximately 0.2-3% of people, and in another 10-12% of the world's population the condition is unnoticeable. In mature and old age it occurs 10 times more often than in young people.
A small butterfly-shaped gland located in the lower part of the neck secretes hormones that are essential for all metabolism. The thyroid gland affects the functioning of every organ in the human body. Its hormones are involved in energy metabolism and are important for immunity and the production of other hormones. We can say that the thyroid gland is a hormonal metabolism. Without the required level of its hormones, natural processes in the body begin to slow down. Low levels of thyroid hormones are called hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism. With this pathology, the thyroid gland, on the contrary, secretes an excessive amount of hormones.
Forms and causes of hypothyroidism
There are two forms of the disease:
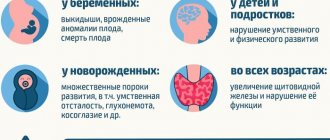
- Congenital hypothyroidism. Develops as a result of a pathologically enlarged thyroid gland, hereditary defects in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, and iodine deficiency in the diet of a pregnant woman. Congenital hypothyroidism is dangerous due to disturbances in skeletal development and mental retardation. If the problem is detected in time, some consequences can be avoided by maintaining normal hormone levels artificially.
- Acquired. A more common form of the disease.
Among its reasons:
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland, which produces thyroid-stimulating hormone, which, in turn, controls the production of thyroid hormones.
- Iodine deficiency in foods is an unbalanced diet, addiction to fast food and fast carbohydrates.
- Complete or partial removal of the thyroid gland.
- Reactive iodine therapy.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland.
Diet for hypothyroidism for weight loss menu. Basic principles of nutrition
During treatment, the diet solves several problems at once:
- Normalizes metabolic processes;
- allows you to maintain normal weight;
- prevents atherosclerosis;
- restores blood circulation in tissues.
The calorie content of the therapeutic diet should be about 2300 kcal. A diet for hypothyroidism involves reducing the amount of hard-to-digest foods and cholesterol, as well as saturated fats. The menu should contain about 70 g of fat per day, about 20 g of which is vegetable. Carbohydrates should be consumed from 350 to 400 g, with sugar accounting for a maximum of 50 g. Proteins need about 80 g, of which more than half should be vegetable.
There are also several important rules. So, it is better to replace meat with fish or seafood, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, and eat dried fruits instead of sweets. It will also be useful to arrange a fasting day once every seven days.
It is better to cook by baking in a sealed container or boiling in a double boiler. Use only iodized salt, and use oils and fats to a minimum. Food should be warm and chewed well. We eat 5-6 times a day, but the portions are small. Dishes should be light, well prepared and varied.
Hypothyroidism and excess weight
Many people are interested in how exactly hypothyroidism and excess weight are related. The fact is that when the level of thyroid hormones (T4, T3) drops, the production of digestive tract enzymes is disrupted and energy consumption decreases, plus tissue hypoxia is observed. All this has a negative impact on body weight, and not only on it. Hypofunction of the thyroid gland also means swelling, fatigue, atherosclerosis and hypotension.
Therefore, a diet for losing weight with hypothyroidism should not only solve the problem of excess weight, but also maintain the overall tone of the body, as well as the heart. Usually, people with a diseased thyroid gland are recommended to follow diet No. 8 or the diet of writer Mary Chaumont. We will look at them a little later, but now we will focus on products that are beneficial for the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of thyroid dysfunction. In the early stages, the disease may proceed completely unnoticed. Often the first symptoms are weakness, fatigue and weight gain. As the pathology progresses, it manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- muscle weakness, chronic fatigue;
- weight gain, obesity;
- swelling, especially on the face;
- depressed mood, in advanced cases – depression;
- constipation;
- feeling of cold, chilliness;
- decreased sweating;
- slow heart rate;
- dry skin, thinning hair;
- memory impairment;
- fertility problems, irregular cycles;
- pain and stiffness in the joints.
Most symptoms of hypothyroidism are nonspecific, meaning they occur with many other diseases.
This is the main difficulty in early diagnosis of thyroid problems. The only way to detect the disease at an early stage is preventive laboratory diagnostics. Over time, patients with hypothyroidism without proper treatment develop characteristic external signs: slowness in movements, excess weight, swelling, the face becomes rounded, puffy, the skin becomes dry, cold and pale, hair becomes brittle, patients are cold even in summer, atherosclerosis progresses and vascular damage. In order not to start the disease, you need to check the function of the thyroid gland for preventive purposes and at the first suspicious symptoms.
Treatment of hypothyroidism without hormones
Can hypothyroidism be treated without hormones? In some cases (especially in the case of iodine deficiency, diagnosis at an early stage of the disease, etc.) the answer is affirmative.
You cannot do without replacement therapy if the thyroid gland is absent or its production cells are destroyed. This happens due to strong radiation or total surgical intervention.
But even if the cells are destroyed (given the presence of the organ itself), they can be restored from progenitor cells (provided a healthy microenvironment) and resume production of the necessary hormones. The question is whether the body has enough resources for this.
Is it possible to help him? Yes . And this help lies not so much in medicinal compensation of missing functions, but in creating and maintaining a healthy balance - a necessary condition for renewal. This entire “set of measures” has long been called a “healthy lifestyle,” which includes not only improving the body (nutrition, conditioning, daily routine, etc.), but also mental care and work.
Non-hormonal treatment of hypothyroidism is possible within the framework of traditional medicine.
Who is at risk?
Hypothyroidism can develop in both women and men of any age. Even children are affected by the disease. However, an increased risk of developing the disease is observed in the following groups:
- Women of middle and older age.
- Age over 60 years.
- There is a family history of thyroid disease.
- An autoimmune disease (eg, type 1 diabetes) is present.
- Has been treated with radioactive iodine or antithyroid drugs.
- We received a large dose of radiation.
- There was surgery on the thyroid gland (partial thyroidectomy).
- Residents of areas with increased background radiation.
- People living in regions of iodine deficiency.
What should you not eat if you have hypothyroidism?
What should you not eat if you have hypothyroidism? Endocrinologists recommend limiting the consumption of foods containing sulfurocyanins and goitrogens. These substances inhibit the absorption of iodine and contribute to the development of goiter, that is, hypertrophy of the thyroid gland. Foods that cause goiter include:
- vegetables from the cabbage family - mainly cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, turnips, rutabaga;
- legumes (soybeans);
- peanut;
- mustard;
- milk from silage-fed cows.
Hypothyroidism in infants
Although hypothyroidism most often affects middle-aged and older women, anyone can develop the disease, including newborns. In children, hypothyroidism is usually congenital. There are pathologies in which a child is born with a dysfunctional thyroid gland; in rare and complex cases, the gland can be greatly reduced in size, and the production of hormones can be minimized.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism in newborns include:
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes);
- slow intestinal motility, frequent constipation and abdominal pain;
- lack of appetite;
- decreased activity of the child;
- labored breathing;
- hoarse crying;
- large fontanelles;
- decreased heart rate;
- umbilical hernia;
- cardiac pathologies (in 40-80% of cases).
Hypothyroidism causes serious physical and mental retardation in infants if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism in newborns is based on clinical symptoms and laboratory blood tests, which are performed on the third day of life. The first test to diagnose hypothyroidism is TSH thyrotropin, a pituitary hormone that stimulates the production of thyroid hormones. The standard indicator for newborns is 0.73-4.75 mU/l. Until the fourth day of life, TSH levels are normally significantly elevated.
How does the thyroid gland affect body weight?
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones, in particular triiodothyronine and thyroxine. And they, in turn, affect various systems of the body, including hormonal. Dysfunction of this gland leads to an imbalance of female sex hormones and causes the development of various diseases of the reproductive system, for example, polycystic disease, lack of ovulation and infertility.
At the same time, the nervous system begins to suffer, irritability, tremors, and insomnia appear. Changes are also observed in the gastrointestinal tract - there is a tendency to constipation, food is not completely digested.
In addition, under the influence of thyroid hormones, metabolism accelerates and subcutaneous fat is broken down (lipolysis). The lack of these hormones, leading to hypothyroidism, causes a slowdown in metabolism and lipolysis, as a result of which a person begins to gain excess weight even without visible disturbances in diet and lifestyle.
With a sharp deficiency of thyroid hormones, the metabolism becomes so slow that even with a low-calorie diet, an increase in body weight occurs - the body stores everything in reserve. Correction of nutrition alone will not solve the problem - you will need hormone replacement therapy, which is selected by an endocrinologist based on tests, examinations, symptoms and course of the disease.
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism
As we have already described, the symptoms of the pathology are nonspecific and often occur among the general population. Therefore, the diagnosis is suspected in many people, but fortunately, it is not confirmed so often. Consequently, thyroid function tests are one of the most requested laboratory tests. The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is confirmed, the level of thyrotropin (TSH) in the serum is higher than normal, and the hormones T3 and T4, on the contrary, are insufficient. The first and main way to detect thyroid dysfunction is through laboratory tests. Hypothyroidism can be detected through the following tests:
- TSH. An abnormally high TSH level may indicate decreased thyroid function and, as a result, hypothyroidism. The first test that must be taken if a pathology is suspected is a study of the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood.
- Total T4 and free T4 (thyroxine).
- Total T3 and free T3 (triiodothyronine). T3 and T4 are thyroid hormones. Their reduced values are a signal of hypothyroidism.
The doctor may also prescribe:
- General blood analysis. Impaired iron absorption is a nonspecific sign of hypothyroidism.
- Blood chemistry. The study will tell about water-salt metabolism in the body, which suffers from diseases of the endocrine system. If T3 and T4 levels are low, sodium levels may be low and creatinine levels may be high.
In addition to laboratory tests, ultrasound is required to fully diagnose the condition of the thyroid gland.
An ultrasound examination will evaluate the size of the gland and its structure. It is important to understand that only an experienced doctor will be able to correctly interpret the research results and make the correct diagnosis. At CITILAB you can take all the necessary tests and get advice from a specialist on interpreting their results.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Treatment of hypothyroidism with herbs
Herbs for hypothyroidism can also act as an independent or auxiliary therapeutic agent.
With their help, you can target the cause of damage to the thyroid gland, eliminate painful consequences (edema, for example), and create a “healthy environment” that accelerates its recovery (for example, help the body get rid of toxins in the most optimal way).
There is only one condition. Both diagnosis and treatment must be carried out by a doctor. Only an individual approach can ensure the effectiveness and harmlessness of the phytotherapeutic method, because herbs are potent agents.
The combination of herbal medicine and iridology gives very good results, allowing one to identify organs and systems that need priority support.
Main manifestations of hypothyroidism
Speaking about problems with the thyroid gland, we should name the main manifestations of hypothyroidism. So, patients with a lack of the hormone T4 experience the following symptoms:
- decreased performance;
- slowing down energy processes;
- decreased attention and hearing;
- weight gain;
- slow heartbeat;
- manifestation of dry skin;
- constant feeling of cold;
- brittle nails are observed;
- hair loss;
- disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract have been noticed;
- liver enlargement;
- metabolic disease.
In addition, frequent companions of this disease: swelling of the limbs and face, muscle weakness, headaches.
Hypothyroidism also harms a person’s psychological state. Interest in the environment disappears, passivity and a constant desire for rest arise. In the female half, the reproductive functions of the body are disrupted, the cycle is disrupted, and problems arise with conception. Puffiness of the face and bulging of the eyeballs appear.
A few words about where the thyroid gland is located. Thyroid functions
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland that is responsible for the normal functioning of the entire body. The thyroid gland is located in the neck, under the larynx, covering the trachea. It looks like a butterfly or a shield. This important organ weighs only 12-25 grams, but is of great importance for humans. So, let's look at the functions of the thyroid gland.
The most important task of our small but very important gland is to fill the body with thyroid hormones T3 - triiodothyronine and T4 - thyroxine. These hormones are responsible for filling cells with oxygen, for the functioning of muscles, the musculoskeletal system, the heart, and the brain. The production of these hormones affects: human growth, psychological state, metabolism, puberty, childbirth, formation and gestation of the fetus, digestive system, circulatory system, immune system, weight, energy metabolism, body temperature.
The drug "Thireo-Vit" helps patients with hypothyroidism lose weight
A good helper for obesity due to hypothyroidism is the drug “Thyreo-Vit”. This dietary supplement is created on the basis of medicinal plants, such as white cinquefoil, kelp, and Echinacea purpurea. "Tireo-Vit" is produced in Penza, and its main components are grown in the ecologically clean region of the Sursky region. The dietary supplement contains plants that are beneficial for the thyroid gland, which means it helps you lose weight.
Not everyone knows that such a valuable herb as white cinquefoil grows in our country. It has many names: cinquefoil, quinquefoil, interdigital, quinquefoil, Potentillaalba. One of the first to study cinquefoil was scientists of the former USSR G.K. Smyk and V.V. Krivenko. When treating patients with hypothyroidism with white cinquefoil, an improvement in the condition of the thyroid gland or a complete restoration of its functions was revealed. An important consequence of using the plant was the reduction in weight of obese patients. Due to its properties, cinquefoil stimulates the thyroid gland, ultimately helping to lose weight.