Basic types of isometrics in sports
These trainings are divided into several types, depending on the technique of execution.
- Static-isometric - imply the greatest muscle tension, without body movement, while resisting an insurmountable obstacle, for example, an attempt to move a wall.
- Weight training, in which you need to freeze in one position. For example, half squats with dumbbells.
- Exercises with the greatest burden.
- Isotonic exercises - during muscle contraction, their length also changes. Such exercises need to be done dynamically.
There are also three groups of similar training: deadlifts, bench presses and half squats.
General rules for performing isometric exercises
With complexes, in principle, everything is extremely clear. It is enough to follow the technique of performing isometric exercises to achieve success. However, there are a number of tips that would be worth following to make your classes as effective as possible.
- Concentrate on the muscle group or specific muscle being trained. Don’t get distracted, try to think only about this, abandoning everything else.
- It is advisable to do all exercises in front of a mirror without baggy clothes (ideally shorts and a T-shirt or top for women). The fact that you will see how the muscles work will help pump them up better.
- All movements of static exercises should be performed with the maximum tension of which you are capable.
- There is no need to focus on the number of approaches or repetitions. In fact, “quality” plays a role here, that is, technique and effort.
- Be sure to pay attention to your breathing. It should be smooth, as slow as your exercises.
- It is recommended to exercise twice a day, morning and evening. Ten minutes for each workout is enough.
- Do not forget that any physical education will be effective only with an integrated approach. First of all, this concerns diet. If you consume tons of fast food, sweets and cakes, you will not get good results. Therefore, make your diet balanced, then everything will be as it should be.
After completing your workout, professional athletes recommend taking a shower and then very thoroughly rubbing your body with a hard towel. This will “disperse” the blood after static efforts, ensuring the supply of oxygen to all organs and tissues of the body.
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of isometrics
So, let's start with the disadvantages of these workouts:
- Such training, like static exercises, is extremely contraindicated for people with problems with blood pressure and the cardiovascular system in general. And if you don’t have such problems yet, then there is a risk of getting them. But this is not a fact, but simply a probability.
- If you are a bodybuilder and your goal is to gain more muscle, then isometric muscle training is definitely not for you. It is aimed more at increasing strength and developing tendons rather than muscle mass. Such exercises, of course, partially help with this, but still they cannot replace dynamic training.
Well, that's probably where the shortcomings end. There are many more benefits.
- Ease of implementation and the need for special training equipment.
- Increased muscle strength.
- If done regularly and correctly, you can count on losing weight.
- Development and strengthening of various muscle groups, including deep ones.
- You can do isometric exercises at home.
- You don't need much time to rest.
Isometric exercises for developing strength: what is the essence
Modern novice athletes often don’t even realize that even in the ancient Shaolin monasteries, static loading was practiced, training strength and endurance. This is how warriors learned to stand or sit in one place for hours without moving, without giving away anything, and then quickly attack when necessary, without creaking their joints, as if the door hinges were not greased. However, isometric exercises gained particular popularity in the second half of the twentieth century, after the media widely spread reports of the athletic successes of those who practiced them. Today, this kind of complexes is used in training by light and weightlifters, cyclists, rowers, skiers and other athletes.
Isometric exercises are those that provide physical stress to the muscles, while completely immobilizing the joint, as well as maintaining the length of the muscle itself. It is because of this that isometric techniques have a second name - static.
What is it and how does it work
These types of exercises are used for specific purposes. They help to quickly overcome the so-called dead spots, while significantly training strength. The deep essence of this gymnastics can be outlined as follows: over a short period of time (5-12 seconds), you need to make maximum effort in order to hold in place or resist any object.
In fact, unlike dynamic type training, which is fundamentally important to repeat a certain number of times, the priorities are completely different. What plays a role here is not the number of repetitions or approaches, but the duration of holding your body in a certain position (position). Conscious awareness of your body also plays a fundamental role in isometric training. More details about what muscles are trained during such gymnastics and how it works can be found in the article on health training from Dr. Borshchevsky.
Benefits of doing isometric exercises
Each sport has different benefits that suit different groups of athletes. That is why some people do jogging, others do weightlifting or Pilates, and still others choose isometric exercises at home or in the gym. What advantages do static loads have specifically?
- The first thing that all fans of isometrics highly appreciate is the significant savings in personal time. It only takes a couple of minutes to put your muscles to work.
- During static exercises, muscles do not get tired as much as during dynamic loads. Therefore, after an hour-long workout, they do not need a day or more to recover. At the same time, if you do not give them the necessary rest, then increasing strength or endurance, as well as increasing volume, remains a big question.
- For the above reason, you can train much more often.
- A positive quality can also be called the ability to pump up in isolation exactly those muscles that currently need it, without affecting others.
- Conventional dynamic exercises actually provide momentary tension on the muscles. That is, in a couple of hours you will receive no more than 2-5 minutes of payloads. Isometric training allows you to exercise over a longer period of time.
Many people believe that dynamic exercise is more beneficial, since muscle tissue, skin and other parts of the body and tissues are better supplied with oxygen and nutrients. Indeed, when performing isometric exercises, the vessels contract, preventing a sufficient amount of oxygen from reaching its “destination”. Tissue cells have to work with double effort, but they do not need to spend the generated energy on movement. Therefore, the entire unspent energy wave is directed to tension, and the muscles grow many times faster.
How to do the exercises correctly
There is a small number of rules, following which you can achieve maximum efficiency from your training and minimize all the risks associated with them, for example, injuries.
- In most cases, the duration of one approach is 6-12 seconds.
- The break between trips should be from 30 seconds to a minute.
- The full training cycle is about 20 minutes.
- You should strain your muscles to the maximum (not for beginners), but smoothly and gradually, and not abruptly.
- For the best results, it would be a good idea to combine isometrics with dynamic exercises.
- Be sure to do a light warm-up before your workout.
Methodology of Alexander Zass
It is impossible not to pay attention to the technique of such an outstanding person, with amazing strength and endurance, who literally broke chains, lifted horses and lay down under a truck with coal. Let us consider here the isometric exercises of Alexander Zass and several examples of practical training by Iron Samson, aimed at strengthening the tendons. After all, according to Zass, it is thanks to tendons, and not bulky muscles, that your strength increases.
For gymnastics equipment, you will need an ordinary, thin chain and loop handles for them, which you can make yourself from improvised means. If there are none, then at worst you can simply twist it around your hand, or you can take a rope or belt instead of a chain.
- Hold one end of the chain tightly with your outstretched left hand, and bend your right hand at the elbow and grasp the other end. Try to break or stretch it in this way. Switch hands and repeat the approach.
- Extend your arms above your head and hold the chain approximately shoulder-width apart. Stretch it in this position, while tensing not only the muscles of your arms, but also the muscles of your chest and back.
- Take two chains with loops at the ends. Place your feet into the loops and begin to stretch the chain with your hands.
- Place the chain behind your back, at the level of your shoulder blades, and stretch.
- Do a lying position and put your hands through the loops, and bring the middle of the chain behind your neck and try to break it.
Technique
First of all, it’s worth talking about the technique of performing such exercises. For those who don’t know, isometric abdominal exercises are strength exercises in which the load on certain groups is carried out not through movement, but by keeping the body stationary in a certain position. A striking example of this is the plank exercise for the abdominal muscles. Any dynamic movements aimed at strengthening the press can be easily made static.
Speaking about static exercises for the press, it is worth noting that the main work should be concentrated in the abdominal area. While tensing the abdominal muscles, you should exhale deeply and hold your breath for a few seconds. What is the recommended duration of isometric abdominal exercises? The duration of the workout largely depends on the degree of physical fitness and muscle tension. The maximum effort lasts on average 2-3 seconds, after which it is necessary to relax the muscles and let them rest. Subsequently, it is possible to increase this indicator to 7-8 seconds. The average duration of a workout that includes isometric abdominal exercises is 10-15 minutes. If this is too much for you and you feel unwell during the session, it is recommended to stop training, subsequently reducing its duration to 5-7 minutes per day.
Bruce Lee Method
Let's not neglect Bruce Lee's famous isometric exercises here. Despite the fact that for this outstanding martial arts master in the past, isometrics was only a small part of his entire range of activities, but he valued its role very highly. Let's look at a few specific examples of his training. However, such isometric gymnastics will require additional sports equipment in the form of a fixed crossbar.
- Secure the bar approximately 10 cm below the level of your outstretched arms. Grasp it with your hands shoulder-width apart and with maximum effort push the bar up for 6-12 seconds. The same execution time will be required for the examples below in this section.
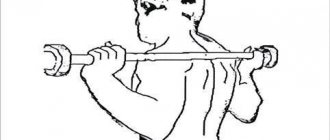
- Place the bar at chin level and press it forward in the same way.
- Place the bar approximately 10 cm below the groin. With your elbows slightly bent, pull it up. The back should remain straight.
- Place the bar just below your knees and take a shoulder-width grip. With your head slightly tilted back and your back straight, pull up with maximum effort.
- The bar is placed at shoulder level when you are in a squat position. Grasp it with your arms and try to rise.
- Install the horizontal bar slightly below (10-15 cm) shoulder level. Sitting under it, push up without lifting your heels from the floor and keeping your back straight.
Training complex for various parts of the body
The above examples are mainly suitable for the muscles and tendons of the arms. We will describe below a set of isometric exercises for other parts of the body and give a few more examples that can be performed at home or in the office, without any special sports equipment.
To strengthen the buttocks and legs
- While sitting at a table, cross your legs. Use your upper knee to push the table upward.
- Standing on one leg, bend the other at the knee and hold your foot with your hand. Press your foot down as hard as you can.
- Sitting on a chair, straighten your legs, place them one on top of the other and lift them up. Press your lower leg up and your upper leg down.
To strengthen the press
- Sitting on a chair, clasp your hands behind its back. Try to lean forward like this.
- Lying on your back, place your hands on the floor. Raise your outstretched legs and hold for 6-12 seconds. Then lower your legs and raise your back to 45 degrees and hold in this position.
For the back
- While sitting on a chair, bend over and squeeze the legs of the chair with your hands. Try to pull them up.
- Sitting on a chair, tuck your legs and clasp your hands around your hips. Without bending your arms, try to lift your shoulders up.
For the chest
- Sit down and clasp your bent arms in your palms at chest level. Squeeze them vigorously for 6-12 seconds.
- With your arms extended in front of you, clasp your hands together. Try to break this lock.
- Clench one palm into a fist, and with the other palm press firmly on the fist, extending your arms at chest level.
For neck muscles
- Place your hands behind your neck and clasp them there. With maximum effort, try to pull your neck forward, while your neck should resist the pressure on it.
- Sitting on a chair, throw your head back and rest your elbows on the table. Place your chin in your palms and try to lower your head.
- Do the same, only rest your forehead on your palms instead of your chin.
Well, we looked at many different trainings. We hope that this information was useful to you and these classes will be a good help for you in developing the strength of your muscles and tendons. Good luck in the gym and beyond!