What is basal metabolism?
Such physiological processes support the vital functions of the body.
A significant portion of the energy released as a result of metabolic reactions of the basal type is spent on:
- heartbeat;
- respiratory activity;
- functioning of the endocrine glands;
- thermoregulation;
- digestion;
- work of the hepatobiliary mechanism;
- renal activity.
Basal metabolism is the main material metabolism determined during the period of wakefulness, with muscular and emotional rest, a comfortable ambient temperature within the range of +18...+22°C.
The transformation of endogenous compounds and nutrients is a constantly occurring biochemical change in a living organism, affecting tissue structures, cells, and biological fluids.
The key goal of basal metabolism is to process food into the energy necessary to maintain life.
During basal metabolism:
- protein and other proteins are synthesized;
- fats are broken down;
- carbohydrates are released;
- some amino acids are produced;
- Nitrogen waste, which is a by-product of such physiological reactions, is removed.
Basal type metabolism can be primary or secondary. Each has its own complex purpose. Primary metabolic reactions are aimed at carrying out basic biochemical reactions.
They determine the development, vital activity and growth of the body.
Basal Metabolism
As a result of such processes, the following are produced:
- saccharides are the main source of energy;
- lipid substances that form the basis of subcutaneous tissue, the protective capsule of some vital internal organs;
- amino acids;
- nucleic substances that store, transmit and implement genetic information.
Secondary basal metabolism - biochemical reactions in individual structural groups.
They are aimed at the production and breakdown of specific substances of non-protein nature:
- immunocompetent compounds;
- hormones;
- pigments;
- building molecules that form the skeletal frame, hair, nail plates.
The rate at which food is converted into energy is called the metabolic rate. This indicator is individual. It depends on the functioning of the nervous system and the endocrine mechanism, the current state of the internal organs.
Why is it necessary to calculate the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
Such calculations are important for determining the number of calories burned daily at rest, emotional stress, and physical activity. The calculation is used by athletes and representatives of various sports. Determination of UMR is necessary for the treatment of metabolic disorders.
The technique is used for figure correction in cases of morbid obesity. Knowing your own basal metabolic rate is important for creating a diet, increasing muscle mass, and acquiring the desired anthropometric parameters.
To maintain optimal body weight based on the BMR calculation, consume the same amount of calories as burned.
Basal metabolism provides:
- hormonal synthesis;
- secretion of enzymes;
- cognitive functions;
- falling asleep;
- immune support;
- the correct proportion of anabolic reactions and catabolic processes.
In case of such violations, the UMR indicator is used to draw up effective therapeutic tactics and determine a treatment plan. Basal metabolism is regulated by the hypothalamus.
Calculation of the rate of metabolic reactions is performed when diagnosing functional disorders of this part of the cerebral zone. The indicator is distinguished by phenotypic flexibility.
The function can be reversibly regulated with medications and physiotherapeutic methods. The rate of metabolic reactions is influenced by endogenous and exogenous factors.
Basal metabolic processes are accelerated in certain pathological conditions:
- elevated body temperature;
- burn injuries;
- bone fractures;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- fever.
BMR changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, at different periods of pregnancy. Calculation with the necessary adjustments is used to determine the cause of sudden weight loss or, conversely, abnormally rapid weight gain.
How to speed up your metabolism?
People with normal metabolism look slim. Slow metabolism leads to obesity. This has become a problem for many of our contemporaries. To speed up the process of burning calories in your body, follow the simple rules outlined below.
Drink more clean water
Dehydration gradually leads to a significant slowdown in metabolism. And, as you know, tea, coffee and carbonated drinks dehydrate the body rather than saturate it with moisture. Avoid drinking sugary and carbonated drinks. Drink only clean water. Its daily consumption should not be less than 1.5 - 2 liters.
Reduce the time between meals
Try to have snacks between main meals, the amount of which can be significantly reduced. Consuming small amounts at regular intervals helps speed up metabolism. Train yourself to have breakfast half an hour after waking up. Then you can eat every 1.5 - 2 hours.
Consume protein foods
Protein is found in white meat chicken, fish, nuts, legumes, eggs, buckwheat and low-fat dairy products. Protein, once in the stomach, is digested much more slowly than carbohydrates or fatty foods. At the same time, the metabolic process is significantly accelerated. It is very important that a protein diet allows you to maintain muscle mass. And muscle mass, in turn, even at rest, burns more calories than fat layers. That is why the greater the muscle mass, the faster metabolic processes occur in the body.
Eat citrus fruits
Citric acid, which is found in citrus fruits, ensures the “breathing” of all cells in the body. Oxygen helps speed up metabolism. Tangerines, oranges, grapefruits and limes are ideal foods to speed up your metabolism and are best eaten on a full stomach. By eating a few slices after your main meal, you improve intracellular oxygen exchange.
Don't neglect foods containing omega-3 acids
These acids are responsible for burning fat in the human body. Train yourself to take fish oil daily. If its taste seems disgusting to you, eat fatty fish, walnuts and season salads with flaxseed oil. This will help significantly speed up metabolic processes.
Sports and metabolism: try to build muscle mass
Lead an active lifestyle. Try to do simple exercises every day. Walk more. It has been found that 1 kilogram of muscle burns 13 calories even at rest. At the same time, the same amount of fat in the human body burns only 5 calories per hour. During physical activity, muscles become more active and significantly increase calorie expenditure, thereby speeding up your body's metabolism.
Maintain a sleep schedule
Healthy sleep promotes the production of the “satiety hormone” leptin. The longer you sleep at night, the more active your metabolism is during the daytime. Doctors advise sleeping in a cool, well-ventilated area. This promotes oxygen exchange of cells. It is better not to consume carbohydrates at night so that metabolic processes do not slow down.
Norm depending on age group and gender
Basal metabolism is an indicator of the rate of basic material metabolism, which is considered a constant value for each organism under conditions of complete rest and comfortable temperature.
UMR serves as an integral value of the intensity of redox reactions in tissue and cellular structures. The norm depends on the type and nature of the external influence on the body.
The level of basal metabolism changes with excessive or excessive saturation of the body with food products and physiologically active substances. The speed of such processes is influenced by physical activity and climatic factors.
BMR depends on gender, age, and functional state of the body. The approximate daily calorie consumption for an adult is estimated at 1600-1700 kcal.
Approximate basal metabolic rate indicators for adults of different ages and gender are presented in the table.
| Age, years | Standard basal metabolic rate, kcal per 1 m2 of body area per hour | |
| Men | Women | |
| 16-18 | 43,0 | 40,0 |
| 18-20 | 41,0 | 38,0 |
| 20-30 | 39,5 | 37,0 |
| 30-40 | 39,5 | 36,5 |
| 40-50 | 37,0 | 35,5 |
| 50-60 | 35,3 | 32,7 |
In children under 16 years of age, the basal metabolic rate is unstable and subject to significant fluctuations under the influence of numerous factors. The daily calorie requirement of infants, according to various research data, is 46-54 kcal/kg body weight.
In the first months of life, the mechanism of thermoregulation is actively formed, requiring an increased amount of energy. Heat production constantly increases, reaching its maximum value at the beginning of the second year after birth.
During this period, the child’s thermoformation exceeds that of adults by 1.5-2 times. In different life phases, basal metabolism either accelerates or slows down. As the body develops, the basal metabolism stabilizes and at the age of 16 years it reaches standard values characteristic of adults.
The increased rate of metabolic processes in children is due to a large volume of protoplasmic mass, significant reaction activity, and rapid growth of skeletal structures and tissue structures.
Is the BSM indicator reliable?
Yes, when it comes to specifying the minimum calorie requirement that will keep us maintaining our basic life functions, and that is his job. However, it is worth remembering that when calculating BMR, physical activity is completely ignored, which increases the calorie requirement for active people by up to 50 percent, and for lazier people by about 15%.
The so-called thermal effect, that is, the fact that when we eat, digest and store food, an increase in energy also occurs. Thus, our daily calorie requirement (DCR) is greater than that indicated in the BMR. Here's how to calculate them.
How to measure BMR?
Minimal neural activity is required to obtain a reliable and objective laboratory value. The subject is immersed in a state of complete rest. For the calculation, a specially developed Harris-Benedict, Mifflin-San Jeor or Kutch-McArdle formula is used.
The first one was developed in 1984 by an American physiologist and nutritionist, after whom it is named. In 1990, a more accurate and up-to-date formula for calculating basal metabolic rate was introduced. Its authorship belongs to a group of American nutritionists, led by Doctors Mifflin and Saint-Jeor. This formula is considered the most accurate.
The Kacha-McArdle scheme appeared relatively recently. Its difference from other used formulas lies in the possibility of calculating the body’s energy expenditure during sleep. It takes into account the volume of muscle mass and the activity of muscle structures in an unconscious state. The technique is suitable for professional athletes. Basal metabolism slows with age and as lean body mass decreases.
Strength and aerobic exercises significantly increase the body's energy consumption. The Kutch-McArdle formula allows you to accurately calculate this indicator. Graphically it is written as follows: BMR=370+21.6 (1-F) x W.
The letter F means the percentage of body fat from the total body weight, W – weight in kg. The updated Harris-Benedict equation for calculating basal metabolic rate in men is as follows: BMR=13.397xW+4.799xH-5.667xA+88.362.
The letter H is height in cm, A is age. The formula for women differs in the coefficients entered, but not in the calculation principle. It looks like this: BMR=9.247xW+3.098xH-4.330xA+447.593.
Basal metabolic rate can be calculated using the Mifflin-St. Jeor formula. This equation is used to determine daily calorie needs. The formula for men is as follows: BMR=10xW+6.25xH-5xA+5. The equation for women differs only in the last numerical factor. It has a value of -161.
Basal metabolic rate - formulas and calculators
The BSM calculator actually covers a variety of formulas for calculating calorie needs, which can be easily verified by any Internet user trying to use one of the many BSM converters available on the Internet.
Three US scientists even decided to take a closer look at BMR calculators, and in 2013, 248 basal metabolic rate calculations were made. They took into account various factors: age, gender, height, weight, race, body fat level and body mass index ( BMI) .
It is worth noting that BMR measures are assumed to inform the caloric needs of a person who is awake, has not eaten for at least 12 hours and has been on a protein-free diet for 3 days, has slept 8 hours and has remained in a comfortable thermal environment, physical and peace of mind. So, to bring your BMR closer to our actual calorie needs, you need to multiply it by your physical activity ratio (you'll learn how to do this later in this article).
BSM and other meanings
Basal metabolic rate calculator based on gender, age and weight
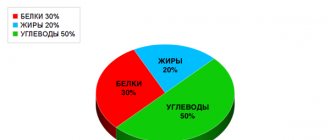
About 70% of the energy obtained from food is consumed by vital physiological processes. About 20% comes from nervous activity and physical activity.
The remaining 10% consume postprandial thermogenesis reactions associated with the digestion, breakdown and absorption of food. All of these metabolic reactions require oxygen and coenzymes.
In relation to the level of basal metabolism, a significant share of energy resources is spent on enzymatic processes, regulation of osmotic pressure in tissues and bloodstreams.
An energy resource is needed to evacuate carbon dioxide released as a result of the Krebs cycle.
The UBM calculation calculator takes into account the following factors:
- The initial rate of metabolic reactions. The indicator is unchanged for an individual organism. It is determined by the ratio of mobility to the excess amount of energy released.
- Saturation of blood with hormonal substances. With diabetic pathology or dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, the basal metabolism proceeds more slowly than the established norm.
- Gender. In men, metabolic reactions occur faster than in women, due to a larger volume of muscle tissue and less fat. Testosterone gives a 10% increase in speed. In women during the menopausal phase, the activity of the thyroid gland decreases, which causes weight gain. There is a hormonal imbalance that impairs the regulation of glucose, insulin, gucagon - catalysts of metabolic reactions.
- Body weight. A slender constitution speeds up the basic metabolism. Excess weight indicates slow metabolic reactions.
- Age. The natural slowdown in basal metabolism begins after age 40. At the age of 25, bone tissue growth stops. From this point on, the basal metabolic rate slows down by approximately 2% every 10 years.
In the formula for calculating the BMR, a coefficient of physical activity is introduced from 1.2 for a passive lifestyle to 1.9 for professional athletes.
Calculations are approximate and relative
Basic metabolism depends on a bunch of factors:
- age;
- weight;
- gender;
- features of the constitution;
- concomitant diseases;
- genetic characteristics;
- ambient temperature;
- ratio of muscle and fat mass;
- work of the thyroid gland and other internal secretion organs;
- other external and internal differences.
In order to find out your BM level, that is, how much your body needs for its own needs, you can use different methods. The most accurate: place yourself in a chamber with a moderate temperature and calculate how much heat you generate over a certain period of time.
Since not everyone has access to such an experience, various scientists and semi-scientific men have developed special formulas for calculating basal metabolic rate:
- by weight, height and age;
- by weight minus body fat;
- by gender - 1 kcal per hour per kg for men, 0.9 for women;
- per square meter of body surface (approximately 915 for men and 854 for women);
- and also calculators based on the formulas of Muffin Jeor, Ketch-McArdle and other smart researchers.
And here is the online basal metabolic rate calculator:
And yet we must understand that all formulas are very approximate, not a single calculation gives the true picture. The results can only be used to give yourself a starting point . And we should not forget: the calorie consumption calculator shows only the needs of the body itself, without taking into account how much you spend on everyday activities and physical activity.
How to calculate your basal metabolic rate?
To obtain objective and reliable results, it is necessary to accurately know many anatomical and physiological parameters. You can approximately calculate your own basal metabolic rate using a simple formula.
Basal metabolism is a physiological characteristic of the body that is subject to changes depending on:
- gender;
- age;
- body constitution;
- type of physical activity;
- presence of pathologies.
The formula for approximate calculation of the basal metabolic rate for an average 25-year-old girl weighing 50 kg and height 165 cm is as follows: 10.4x50+615x1.65-282.
According to the result, she needs to consume 1253 kcal daily to maintain normal functioning of the body. The above formula does not take into account the type of physical activity, individual endocrine activity, and hormonal levels.
A constant and personal parameter is food thermogenesis. About 10% of consumed energy resources are spent on its maintenance. Another important factor influencing BMR is the rate of breakdown of proteins, fats, and carbohydrate compounds.
The first ones are the most energy-consuming. Approximately 20-30% of their calorie content is spent on processing protein substances. For the absorption of carbohydrates, 6-8% is required, fats - 2-3%.
What matters is the type of food, which is taken into account in special formulas for calculating the UMR by assigning the appropriate coefficient. High-protein diets are used for figure correction due to the high energy costs of such substances.
In addition to high calorie consumption, such compounds instill a false sense of satiety, which makes it easier to adhere to the diet.
Lipid nutrients are divided into:
- saturated;
- polyunsaturated;
- monounsaturated;
- dietary cholesterol;
- trans fats.
Each variety requires its own amount of energy to process, which affects the basal metabolic rate. The accuracy of the calculation ensures an individual and multifactorial approach. Below are the current UBM calculation options.
Larne formulas
The calculation method takes into account the age category, which affects the rate of basal metabolic reactions. For men 18-29 years old, use the following Larne formula: 15.3 x weight in kg + 679. For women of the same age, only the coefficients change.
The calculation is made by multiplying body weight by 14.7. A coefficient of 496 is added to the result obtained. To calculate the level of basal metabolism in men aged 30-59 years, the body weight in kg is multiplied by 11.6 and added to the resulting numerical value of 879.
For women of the same age, the coefficients are 8.7 and 829, respectively. Such formulas are characterized by relative accuracy, since individual physiological and pathological factors that can change the rate of metabolic reactions within a significant range are not taken into account.
In clinical medicine, determining UBM has diagnostic value when choosing treatment tactics for numerous gastroenterological diseases, endocrine pathologies, and digestive disorders.
Nutritionists and doctors of other profiles use updated tables, which take into account the maximum number of factors, and correction factors apply. Additionally, calometric methods are used based on recorded gas exchange rates.
They make it possible to calculate and characterize energy losses with thermal effects characteristic of individual metabolic reactions reflecting the activity of organs, cytological units, and intracellular organelles.
Harris and Benedict formulas
Basal metabolism is a physiological characteristic, when calculating which it is necessary to take into account the type of physical activity. For such calculations, the Harris and Benedict formulas are used.
Each type of physical activity is assigned an individual coefficient by which the resulting BMR result is multiplied. For men, the following formula is used: 66.5 + (13.5 x weight in kg) + (5 x height in cm) – (6.75 x age).
When calculating the female level of basal metabolism, the first correction factor remains unchanged, the rest acquire values of 9.55, 1.8 and 4.7, respectively.
The result obtained reflects the approximate daily consumption of energy resources in calories. To clarify the BMR parameters, the calculated value is multiplied by an additional and independently determined coefficient of physical activity.
With a sedentary lifestyle, this figure is 1.2. For the average person, a coefficient of 1.375 is used. For those who go to the gym, go for daily morning jogs, or engage in heavy physical labor, it is recommended to multiply the result by 1.725.
What does it all depend on?
First, we need to define the concept of basal metabolism (basal metabolism) - this is the amount of energy that the body spends at rest on the processes of blood circulation, heartbeat and, in general, on maintaining normal functioning in a state of complete inactivity of the digestive system (about 12 hours fasting), without taking into account motor and mental activity.
- The liver consumes 27% of basal metabolic energy;
- Brain – 19%;
- Muscles – 18%;
- Kidneys – 10%;
- Heart – 7%;
- Other organs and tissues – 19%.
The release of energy in this state is sufficient only to maintain the functioning of vital organs: heart, lungs, nervous system, kidneys, liver, intestines, genitals, muscles and skin. And this figure is different for everyone, it can vary from 1000 to 3000, and 70% of this value is genetically determined. What exactly does this variation in energy costs depend on?
1. Genetic differences in the functioning of “useless” cycles. In the body of slender people, a large number of reactions function, consisting of two metabolites, which at the same speed turn into each other alternately, which wastes energy. The process occurs without any physical activity, this increases the value of basal metabolism. There are still some factors that have not been fully studied, but probably affect the level of basal metabolism; this item is the least interesting for fitness, since the athlete can no longer do anything with genetically determined factors.
2. The rate of basal metabolism falls with age and with loss of body weight, and that is why an athlete during the “drying” period gets rid of excess fat in the first stages much easier than in the last. That is why you should not sharply reduce your caloric intake.
3. Stress is a factor that greatly increases basal metabolism; stress turns on the sympathetic nervous system, producing hormones from all layers of the adrenal glands, all of which directly and indirectly increase the level of basal metabolism, activating the heartbeat and more.
4. Heat - high body temperature increases the level of basal metabolism, which is why people lose weight during illnesses, as they are accompanied by an increase in body temperature, which is why so-called thermogenic supplements for weight loss were invented. Therefore, in winter, during cold weather, the accumulation of fat in subcutaneous depots is slightly better than in summer, for this reason many athletes, perhaps risking their heart health, do aerobic training in warm sweatshirts.
5. But with age, this figure steadily decreases.
6. Muscle mass, as already mentioned, consumes up to 18% of the total amount of energy, and this is at rest, without taking into account weight training; even at rest, muscles require blood supply, nutrition, and metabolic processes occur in muscle tissue. This figure is for a person with an average body weight, therefore, the more muscle mass you have in your body, the higher your basal metabolic rate, the less likely you become to gain fat. So one way for people prone to obesity to stay in shape and not gain weight is to build muscle mass.
7. The digestive system also requires energy, and the more often you start the digestive process, the more your basal metabolic rate will increase. That is why nutritionists advise dividing the diet into a large number of servings. Digesting protein foods is also the most energy-consuming.
8. The level of basal metabolism is directly and indirectly increased by thyroid hormones, catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine) and androgens.
Factors influencing UBM
In addition to the age, gender, and physiological reasons described above, the rate of basal metabolism is affected by a large number of behavioral, pathological, and genetic factors.
Meaning:
- Specific dynamic absorption of nutrients. Substances contained in food are usually broken down within 5-6 hours, but for each person this process has a different speed, which is reflected in the BMR indicator.
- Ambient temperature. Prolonged exposure to cold speeds up metabolic processes. When the temperature drops 10° below the established comfort level, the basal metabolic rate increases by 2.5%.
- Circadian rhythms. Basal metabolism changes depending on the time of day, days of the week, and seasons. During sleep, basal metabolism slows down by 13% compared to the waking period due to relaxation of skeletal muscles.
- Taking medications. The natural course of metabolic processes changes the consumption of diuretic medications, oral contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids, venotonic and many other drugs.
The tone of the autonomic and sympathetic parts of the nervous system has a significant influence on the rate of basal metabolism. The neurotransmitters they produce play an important role in thermogenesis. A pronounced change in the basal metabolism is observed with damage to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland of the brain.
Pathological influence factors include tumor processes in chromaffin tissues. Such neoplasias secrete adrenaline and norepinephrine, which sharply accelerate the basal metabolism. A change in the UBM causes traumatic injury or tumor damage to the autonomic centers of the diencephalic zone.
Surgical amputation of the sympathetic plexuses and degeneration of the adrenal medulla lead to a decrease in the rate of basal metabolism. The hormones they secrete can affect not only the functions of internal organs, but also primary thermogenesis.
The biochemical mechanism of this effect is not fully understood. A change in the rate of basal metabolism leads to a violation of the production of thyroid hormone. This physiologically active compound performs specific regulation of tissue respiration and energy metabolism.
Rubner's surface law
Another interesting factor that affects the rate and expense of basal metabolism during the day is Rubner's surface law. According to this law, people with more surface area waste more surface area. What follows from this? Two main conclusions can be drawn from this:
- Tall people need twice as many calories to maintain basic metabolic processes in the body.
- Overweight people lose weight faster because they very often incorrectly calculate the level of their own basal energy metabolism, therefore they spend more calories than expected.
- People with smaller volumes find it much easier to gain weight since they can add fewer calories to their daily diet.
How it works?
The thing is that our body spends a certain amount of energy to maintain heat levels. When we are sick and the temperature rises, the body spends more energy. When we are tired, our body temperature drops. The body needs to warm up about 75 kilograms of weight in proportions 1.7 * 0.8. Based on this, we can calculate the heat capacity of the body, which is about 2000 joules per kilogram of body per hour. Or, in terms of calorie content, it is 0.5 kcal per kilogram of body and liter of volume. Those. The average person spends about 300 kcal per day just on heating themselves. The error for tall and overweight people is actually not as big as it seems - only +- 100 kcal per day. However, when following extreme mono-diets, this factor must be taken into account.
Another important feature of the Rubner surface is that heating is carried out depending on the external temperature. Therefore, in winter we need 200-300 kcal more per day than in summer, and this is due solely to the ambient temperature.