The structure of the simulators, as well as their functional features, were discussed by us in the previous article, which gave rise to a series about the purpose of very specific stations, or more precisely about what work they are intended to do. This article, according to the previously proposed classification, will cover the topic of the purpose of strength training equipment in the broadest sense of the word. We will also find out what muscles they load, what they are intended for, and what characteristic features all these structures have.
Introduction
Each simulator, which is quite logical, has its own purpose. It is based on these considerations, for the convenience of presenting the material, that we have divided them into categories, or more precisely, into muscle groups that they are intended to develop. The main aspects to which we will draw your attention will be: the muscles that it loads and its purpose. In this article, we have combined load-bearing and load-bearing structures into one list, since often both categories have their own duplicate analogues, and of course for the main reason that both categories of simulators belong to strength ones.
Exercise machines for gluteal muscles
Reduction, spread of legs
Smith machine lunges
Leg abduction in crossover
Romanian deadlift on the Smith machine
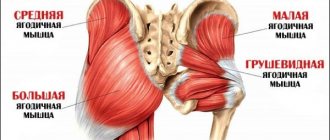
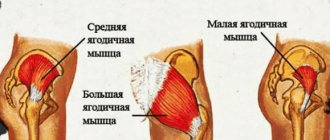
So, finally, let's look at what exercise machines pump up the buttocks. Let me remind you that the gluteal muscles are divided into large, small and medium. One lies under the other. In order to get good shape, you need to pay attention to each of them.
- Lower block row (we secure the cable of the block with a cuff on the leg, and perform back swings).
- Romanian deadlift in the Smith machine (a must for those who really want to pump up beautiful buttocks).
- Lunges with a barbell in a Smith machine (we try to squat on one leg, leaning slightly on the other).
- Lowering and spreading the legs in the simulator (we train the gluteus minimus muscles, add volume to the butt).
- Squats in a Smith machine (simpler than regular squats due to the reduced effort required to maintain balance).
In every exercise that you perform for the first time, it is important to follow the technique. If you doubt the correctness, it is better to ask a coach, a friend, or the Internet. Your health is more important than embarrassment, and besides, most athletes are kind and sympathetic people, and many will be happy to help with advice.
This concludes today’s review of the main simulators for muscle groups. We've looked at a decent list of exercises and equipment. Now you understand the purpose of most of the equipment in the gym, and you definitely won’t be bored at your next lesson in the gym.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the best home exercise machines for weight loss
Exercise equipment for chest muscles
The following simulators are designed to train the pectoralis major and minor muscles at different angles:
Press at an upward angle. Muscles worked: pectorals, triceps, anterior deltoid. The emphasis in the exercise is on working the upper part of the pectoral muscles. Description: both block and loaded exercise machines can be used as a replacement for bench presses with barbells or dumbbells lying at an upward angle, or as an additional exercise to them, since working on these machines with large weights does not require the presence of a spotter.
Horizontal press. Muscles worked: pectorals, triceps, anterior deltoid. The emphasis in the exercise is on working the entire volume of the pectoral muscles. Despite the different design, both machines can be used as a replacement for barbell or dumbbell bench presses lying on a horizontal bench, or as an additional exercise to them, since working with them with large weights does not require the presence of a spotter.
Butterfly (chest machine). Muscles involved: pectoralis major and minor. The emphasis in the exercise is on training the separation of the chest in the center. The differences are that the first has a handle feed lever and involves working with your arms bent at the elbows. The second involves bringing together outstretched arms, and having a combined design, it is adapted to perform exercises on the rear delts. More on this below.
Pullover. Muscles involved: the main load goes to the pectoral and serratus muscles, additional load is taken by the latissimus dorsi and abs. Working in the simulator is safer and does not require a spotter, which allows beginners to perform the exercise to master the technique. Has a handle feed lever.
Main conclusions
The purpose of sports equipment is to facilitate exercise and ensure the safety of the athlete:
- Any work on simulators implies familiarity with the instructions for their use.
- It is better to start working with the minimum weight or the most gentle setting.
- The effectiveness of training also depends on the correct technique for performing the element.
Most simulators are simple and easy to use, but to avoid injuries, it is better to conduct the first classes under the supervision of a trainer or instructor.
Back muscle trainers
The following simulators are designed to train back muscles such as the teres major, infraspinatus, rhomboid, trapezius and latissimus muscles at various angles:
Vertical traction. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, rhomboid. The emphasis depends on the grip: the wider it is, the greater the load on the latissimus muscles; the narrower the grip, the more load the middle part of the back receives. The grip can be not only narrow, medium and wide, but also straight (palms facing away), reverse (palms facing you), parallel, and the pull can be done to the chest or behind the head. A simulator combined with horizontal traction has the same functions.
Horizontal thrust. Muscles involved: lats, trapezius, back extensors. The rear delta takes on additional load. The emphasis of the exercise is on the lower part of the lats, increasing their thickness. Also, the use of different handles allows you to shift the emphasis of the load with a wide, narrow, parallel, forward and reverse grip.
Vertical traction. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, biceps receive additional load. The manufacturer places emphasis on the possibility of alternating traction with one hand. Rows facing the machine and facing away from the machine, as well as the design features of attaching the handles, allow you to work the back muscles at different angles.
Gravitron (for doing pull-ups). Muscles involved: latissimus, rhomboid, teres major. The biceps receive additional load. Imitating a pull-up bar, the design has a platform and a counterweight that help people with insufficient training to perform pull-ups on their own.
Lever rod. Muscles involved: latissimus, trapezius, teres major. The rear deltoids and biceps receive additional load. The emphasis of the load is focused on the latissimus dorsi muscles and disabling the back extensors. Both designs allow for identical work and have a handle feed lever.
Back extensor. Muscles involved: rectus spinalis (extensors). The simulator can be used as a replacement for the hyperextension exercise. It is also often used in sports medicine for rehabilitation purposes to prevent spinal diseases. The block frame allows you to vary the load level.
T-bar row at an angle. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, trapezius, rhomboid. The rear deltoids and biceps also receive a load. The simulator allows you to isolate the latissimus muscles and turn off the back extensors from work. Footrests and a chest support fix the body in a stable position, thanks to which you can effectively work out your entire back.
Bent-over T-bar row. Muscles involved: latissimus, teres major, trapezius, rhomboid. The rear deltoids and biceps also receive a load. By and large, the simulator allows you to work out the same muscles, but the lack of fixation of the body connects the stabilizer muscles and allows you to independently choose the angle of inclination of the body in relation to the horizontal floor.
Exercise machines for leg muscles
The following machines are used to train lower body muscles such as quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles:
Leg press. Muscles worked: entire front thigh, entire back thigh, and buttocks. The simulator can be used as an alternative to squats with a barbell, or as an additional exercise to them, since it does not require the presence of a belayer due to the presence of locking levers. The tilt level of the lounger and platform is adjustable.
Hack machine. Muscles worked: entire front thigh, entire back thigh, and buttocks. The emphasis in the exercise is on the front of the thigh and its outer side. The simulator can be used as an alternative to squats with a barbell, or as an additional exercise to them, since it does not require the presence of a belayer due to the presence of locking levers.
Smith's car. Muscles involved: the specific design of the machine allows you to work out almost all muscle groups, but is often used specifically for squats, which allows you to load the front and back of the thigh, as well as the buttocks. The counterbalanced design increases the smoothness of the rails and reduces the weight of the bar.
Hip extensor. Muscles involved: front of thigh. The emphasis in the exercise is on the medial (teardrop-shaped) muscle located above the knee. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes, as well as for the prevention of possible diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Hip flexor. Muscles involved: back (biceps) of the thigh. The calf muscles receive additional stress. The exercise allows you to focus the load on the lower part of the thigh biceps. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes, as well as for the prevention of possible diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Leg information. Muscles involved: hip adductors. The emphasis in the exercise is on the inner part of the thigh, which allows you to form its correct and beautiful shape. In sports medicine, it is often used to increase or restore the elasticity of muscle fibers in a given area.
Leg spreads. Muscles involved: hip abductors. The emphasis in the exercise is on the outer part of the thigh, which allows you to form its correct and beautiful shape. In sports medicine, it is often used to increase or restore the elasticity of muscle fibers in a given area.
Swing to the side. Muscles involved: adductor, abductor muscles of the thigh and buttocks. The machine is designed to train the inner and outer thighs. It is successfully used for figure correction, as well as for the formation of expressive and beautiful legs, making it popular among women.
Backward leg press. Muscles involved: gluteal muscle. The exercise machine is successfully used for figure correction, as well as for the formation of expressive and beautiful legs, which makes it popular among women. In sports medicine, the simulator is often used for rehabilitation purposes to prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Shin machine (standing). Muscles involved: calf muscle. The machine is very effective for training the lower legs and for developing strong and beautiful calves.
Shin machine (inclined). Muscles involved: calf muscle. The difference from the previous design allows you to remove the axial load from the spine.
Shin machine (sitting). Muscles involved: calves, gastrocnemius.
The emphasis in the exercise is on focusing the load on the soleus muscles.
Exercise machines in the gym: names with descriptions, purposes and pictures
Each workout should begin with a warm-up and is most effectively done with the help of cardio equipment, so these will be the first on the list.
Cardio equipment
Exercise bike
This exercise machine is aimed at strengthening the cardiovascular system and can tone the calf muscles and thighs. Structurally, it is very similar to a traditional bicycle, as it has a seat, handlebars and pedals. Modern exercise bikes have a display that displays information about speed, load level, heart rate, and calorie consumption. Such exercise machines also include a bicycle ergometer and a spin bike. There is a separate type of fitness training using only an exercise bike - cycling.
Treadmill
A very effective exercise machine that provides excellent aerobic exercise. While running, all muscle groups are involved, so using a treadmill for a full cardio workout or warming up before strength training will be a great way to speed up your metabolism and burn extra calories. The exercise machine allows you to adjust the load level, heart rate, calorie consumption, as well as running speed, time of use and other indicators.
Orbitrek (elliptical trainers)
An effective cardio machine that simulates skiing. This simulator can strengthen ligaments and tone muscles. During the load, all muscle groups are involved. This exercise machine minimizes the load on the knee joints. Like an exercise bike and a treadmill, the Orbitrack is equipped with an information display.
Stepper
Exercise machine for training the cardiovascular system, leg muscles and buttocks. The athlete chooses the pace of the load himself. It is possible to change the load on each pedal (in some models). The stepper simulates climbing stairs. More about the stepper →
Climber
Reminiscent of climbing a sheer cliff and similar to an escalator. In terms of efficiency and principle of operation, it resembles a stepper, however, the design of this simulator is more monumental. This machine is more suitable for more advanced athletes rather than beginners. Read more about the cardio machine staircase →
Rowing machine
This simulator allows you to form a powerful shoulder girdle and arms. In addition to developing strength, the device helps strengthen the cardiovascular system and increase endurance. While working on the machine, the athlete also uses his legs. Read more about the rowing machine →
Strength training equipment
Upper and lower block traction
These are the same type of simulators, the action of which is to pull the load towards you, however, the pull of the upper block is carried out vertically using a crossbar behind the head, and the pull of the lower block is carried out with handles horizontally to the lower back. These block exercise machines are designed to develop the back muscles.
Thrust of the upper and lower (horizontal) block
Read more about horizontal block traction → Vertical block traction →
Butterfly trainer
It is an excellent additional exercise machine for working out the pectoral muscles. This is a block exercise machine equipped with a horizontal (90 degree) backrest that serves as a back support. The moving parts are hand levers that move along the same path. Thanks to them, the athlete smoothly brings his hands together. This connection provides excellent concentration at the peak of the reduction and excellently works the central part of the pectoral muscles. Read more about bringing your arms together in the butterfly simulator →
Hammer trainer
This is a lever trainer aimed at developing the muscles of the chest and anterior deltoid. Read more about the bench press in the Hammer simulator →
Hummer Bench Press
Smith machine
With this multifunctional exercise machine you can develop any muscle group - from the trapezius to the calf. Its design is a bar in a power frame, moving vertically along guides. The machine is also equipped with safety hooks, which you can use by turning the bar with your hands. More about the Smith machine →
One of the Smith simulator options
Crossover
This multifunctional trainer, just like the hummer, was discussed a little earlier. The block simulator is a whole training complex with which you can train the whole body.
Gravitron
Designed for those who cannot do pull-ups or do dips on their own. Due to the load and the block system, the athlete, having taken a position on the platform, receives compensation (pushing out the weight) with the help of a counterweight. That is, the platform is pushed upward under the weight of the load. The higher the weight chosen, the easier it is for a person to do pull-ups or push-ups. Read more about the gravitron simulator →
Linkage
The simulator is a device for training the back muscles. It has a bench, the back of which serves as a chest support. You can perform deadlifts with a horizontal or vertical grip. Read more about linkage →
T-neck design
Another simulator for training your back. Working on it is reminiscent of training on a lever pull. The athlete performs the same movement - pulling the weight towards himself. Read more about the T-bar row →
Leg extension machine and leg curl machine
These are two separate simulators that have the same type of operation. Their main advantage is the unloading of the knees, which makes it a safe tool in achieving results. These machines are perfect for working the quadriceps (extension) and biceps femoris muscles (flexion). Read more about bending and extending legs in the simulator →
Leg extension in the simulator
Leg curls in the simulator
Simulator for mixing or breeding
Often found in one design of a simulator for both muscle groups, they are also found as separate simulators in the line of some manufacturers. Purpose – training of the abductor and adductor muscles of the thigh. Read more about bringing your legs together in the simulator and spreading your legs.
bringing the legs together
Leg spread
Hackenschmidt simulator
The hack machine is a highly effective simulator for training leg muscles. Unlike a pressing platform, a hack machine works the quadriceps and buttocks muscles more effectively. If you exclude squats with a barbell, then training in this machine can be considered the most effective compared to other leg machines. In addition to the quadriceps, the gluteal, semitendinosus, and adductor muscles are also used when working on the simulator. Read more about squatting in the Hack Machine →
Platform trainer
This machine allows you to train all the muscles in your legs. To do this, you should place your feet on the platform in different ways, for example, a narrow position of the feet will effectively work the outer part of the thigh, and a wide one (plie) will focus on the adductor surface of the thigh. The platform moves along guides and is weighted by weighting disks. The exercise machine allows you to exercise with heavy weights. The advantage of training with a platform is that the load on the spine is reduced. Read more about the leg press in the simulator →
Calf trainers
– there are several varieties of them, however, both block and lever exercise machines work by raising the toes. Read more about sitting calf raises →
Body weight machines
In addition to block, lever and cardio machines, there are also machines for working with your own weight, such as the Roman chair, parallel bars or hyperextension. Such exercise machines are aimed at strengthening muscles using body weight. With their help you can strengthen your abdominal and back muscles.
Arm muscle trainers
The following machines are designed to train biceps, triceps and forearms:
Biceps machine. Muscles involved: biceps. The simulator is designed to train the muscles of the arms, namely the biceps, which is achieved through a design that ensures their isolation. The seated design allows you to unload the spine, and the angle of the handles and their rotation provide the most comfortable conditions for training.
Triceps machine. Muscles involved: triceps. The machine is designed to train the muscles of the arms, namely the triceps, which is achieved through a design that ensures their isolation. The seated design allows you to unload the spine, and the angle of the handles and their rotation provide the most comfortable conditions for training.
Triceps block. Muscles involved: triceps. The anterior delta band receives additional load. The emphasis in the exercise is on fixing the spine, which prevents loosening of the body and allows you to focus on the triceps brachii muscle. This simulator is quite rare, since a crossover is often used instead. More on him later.
Bars sitting. Muscles involved: triceps, pectoral, anterior deltoids. The simulator simulates push-ups on uneven bars. The block design, or rather the adjustable weight, allows the exercise to be performed by people with an initial level of training who do not have enough strength to lift their own weight on the uneven bars.
Gravitron (for performing push-ups on uneven bars). Muscles involved: triceps, pectoral, anterior deltoids. Simulating push-ups on uneven bars, the design has a platform and counterweight that help people with insufficient training to perform push-ups on their own.
Seated French press. Muscles involved: triceps. This simulator allows you to significantly isolate the triceps and put a significant load on its inner and middle bundle. The seated design allows you to relieve the spine, and the grip angle of the handle provides the most comfortable conditions for training.
Roller block. Muscles involved: forearms. The simulator is effective for building and developing forearm muscles.
Shoulder exercises
To train the front, middle and rear deltas, the following equipment is used:
Seated press. Muscles involved: anterior and middle deltoids. The simulator is effective for developing a strong and beautiful upper shoulder girdle. The seated design allows you to relieve the spine as much as possible. The handle feed lever and adjustable seat height and backrest angles make exercising on it as comfortable as possible.
Seated fly-through. Muscles involved: middle and anterior deltoids. The emphasis in the exercise is on the middle delta beams. The seated design allows you to isolate the deltoid muscles as much as possible and relieve the load on the spine. The machine can be used as an alternative or addition to dumbbell raises while standing or sitting.
Reverse fly while sitting. Muscles involved: posterior deltoids. The simulator involves raising outstretched arms, and having a combined design, it is adapted to perform chest exercises, which is implemented by changing the position of the handle levers. This was mentioned at the beginning.
Main types of simulators
Each fitness club may have a different arrangement of equipment. There is equipment for basic exercises and designs for isolated training of specific muscles. All devices are divided into 4 main types and differ from each other by the type of load creation:
- Weight block simulators. The basis of block devices is a cable mechanism with a built-in set of fixed weights. It can be adjusted depending on the athlete’s training level and goals.
- Free weight designs. Classes in the area with free weights provide the greatest opportunities in forming the load and its variations. The intensity can be set by selecting dumbbells and plates for the barbell of the desired weight.
- Cardio equipment. Bodyweight training equipment is used for active calorie burning, warming up and warming up.
- Racks, benches, hyperextensions. Racks are necessary for placing equipment, and a bench and hyperextension will be indispensable assistants for performing exercises.
It is quite problematic for a beginner to remember the operating mechanism of each simulator, and for now there is no need for this. But it is very useful to get acquainted with the list and description of the main types of equipment.
Exercise machines for abdominal muscles
The rectus and oblique abdominal muscles can be trained using the following machines:
Seated crunches. Muscles involved: rectus abdominis. Additional load is received by: serratus and intercostal muscles. The simulator allows you to specifically work the upper and middle parts of the rectus abdominis muscle. In sports medicine it is often used to prevent spinal diseases.
Twister. Muscles worked: external, internal and transverse obliques. The machine is designed to perform oblique turns and train the oblique abdominal muscles. Effective for building an athletic physique. In sports medicine it is often used to prevent spinal diseases.
Multifunctional trainers
Crossover. Muscles involved: biceps, triceps, deltoids (front, middle, rear), chest, back, abs, hip abductors and adductors, hamstrings, buttocks. The design has four traction blocks: two upper and two lower, which allows, by connecting various handles, to perform a large set of exercises on all parts of the body.
Block frame. Muscles involved: biceps, triceps, deltoids (front, middle, rear), chest, back, abs, hip abductors and adductors, hamstrings, buttocks. Both designs have two traction blocks, which, by connecting various handles, allow you to perform a large range of exercises on all parts of the body.