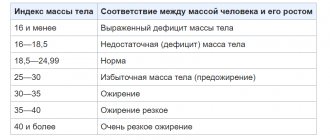
Muscle Growth Factors
Effective formation of new tissues to replace damaged ones is a complex process that depends on several “parameters.” Let's list them:
We recommend reading: Collagen: what is it and how does it slow down aging
- Genetic features of muscle structure (thickness of thread-like structures, ratio of fast and slow fibers, number of capillaries and nerve endings).
- Athlete body type. It is believed that a person with any body type can achieve success in bodybuilding, but mesomorphs are most adapted to mass-gaining training.
- Complete rest. In order for a muscle damaged during strength training to recover, you need to give it at least a day of rest and quality eight-hour sleep.
- Calorie diet. To form new fibers, the body requires proteins, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins. All this should be contained in abundance in a bodybuilder’s diet.
- Proper strength training. Muscles quickly adapt to loads. Therefore, each lesson should be a little harder than the previous one. In addition, you should change the program frequently.
Age also affects the body's ability to build muscle size. This is due to the amount of hormones produced. After 30 years, testosterone secretion gradually decreases every year. Therefore, athletes under 30 progress much faster than their older colleagues.
Bad habits and muscle growth
Smoking has a negative effect on muscle fiber hypertrophy:
- Tar and nicotine interfere with normal protein synthesis.
- Tobacco smoke constricts blood vessels, which impairs the delivery of nutrients to damaged muscles.
- Smoking impairs the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which not only threatens serious health problems, but also interferes with performing strength training exercises with weights.
Alcohol causes no less harm to the body than smoking tobacco:
- Ethyl alcohol inhibits muscle synthesis.
- Frequent use reduces the production of male sex hormones.
- Alcohol has a toxic effect on all body systems. Because of this, there is a decrease in the athlete’s strength capabilities, a slowdown in recovery processes in the muscles, a deterioration in overall well-being, and a decrease in energy and motivation.
How do muscles grow?
Skeletal muscle consists of bundles of muscle fibers - the structural elements of muscle. Muscle fibers, in turn, consist of hundreds to thousands of myofibrils, depending on the specific muscle. Each myofibril consists of contractile proteins - 1500 myosin threads and 3000 actin. The area between the end of the myosin filaments on one side and the end of the actin filaments on the other is called a sarcomere - the smallest
It turns out that muscles are not lumps or lumps. And the threads, which, when contracting, come closer to each other, and diverge accordingly when relaxing.
Muscle tissue consists of water and proteins. There is also glycogen, lipids, nitrogen-containing substances, salts of organic and inorganic acids, and so on. But to a greater extent, muscle is protein .
And now closer to the point: what causes muscles to grow? Protein is a building material for thickening muscle fibers. If you eat enough protein, your hormones will cause the protein to thicken your muscle fibers during exercise. That is, muscles grow not from microtraumas, but from thickening of muscle fibers.
With a microtear, the muscle swells, becomes inflamed, and becomes filled with water. Accordingly, it increases. But this cannot be called growth. As a result, the rupture site is overgrown with fibrous connective tissue that is unable to contract. This is trauma. Growth occurs due to the presence of anabolic hormones, amino acids - building elements, hydrogen ions, free nucleotides, as well as vitamins involved in most biochemical processes.
We recommend reading: Circular training program for men and women in the gym with iron and your own weight
How hormones affect muscle growth
Hormones are the next element responsible for muscle growth and recovery and are of great importance in regulating the activity of satellite cells. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), mechanical growth factor (MGF) and testosterone are the most important hormones directly related to muscle gain.
The goal of many athletes when working out in the gym is to produce testosterone. Everyone knows that it increases protein synthesis and reduces protein breakdown, activates satellite cells and stimulates the production of other anabolic hormones. Despite the fact that we cannot use up the overwhelming (up to 98%) part of the testosterone secreted by the body, strength training not only stimulates its production, but also makes the receptors of our muscle cells more sensitive to free testosterone. It can also increase the production of growth hormone by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in damaged fibers.
Insulin-like growth factor regulates muscle mass by increasing protein synthesis, improving the uptake of glucose and amino acids (constituents of protein) by skeletal muscles, and also activates satellite cells for greater muscle growth.
How fast do muscles grow?
With regular exercise, muscle growth is noticeable almost immediately. Over time, the growth rate decreases. A month of working with a barbell or dumbbells gives a good visible effect. The increase in chest volume can reach 5 cm, muscle mass increases by 2-2.5 kg.
After three months of serious training, muscle mass can increase by 5 kg, the girth of the biceps increases by 3 cm, and the chest by 6 cm. Over the course of a year of training, the biceps “grows” by another 5 cm, and the muscle mass becomes heavier by 10 kg.
The results of training largely depend on your body type and individual characteristics. Genetic factors are no less important. It is also important to provide the muscles with proper rest. Research shows that after exercise, your arms, shoulders and abs need 48 hours to recover. Legs, chest and back require 72 hours. During this time, muscle protein synthesis will be completely completed. How to train to grow muscles? Experts advise sticking to the “schedule”:
- Option 1: lower body - Monday or Friday, upper body - Wednesday;
- Option 2: shoulders, arms, abs - Monday, back and chest - Wednesday, legs - Friday;
- Option 3: top + bottom - Monday and Friday.
To pump up muscles, you need to “drive” the body into a stressful state. This is achieved by changing the load and intensity of the exercises. At the end of the training, it is important to provide the body with the good rest necessary for muscle recovery and growth.
Triggers of Muscle Growth
Natural muscle growth is based on its ability to constantly overcome increasing tension/load. This stress is a major factor involved in muscle development and it disrupts homeostasis in the body. Stress and subsequent disruption of homeostasis trigger three primary mechanisms that stimulate muscle growth.
No. 1. Muscle tension
To increase muscle growth, you must apply a load greater than what your body has adapted to. How to do it? The main way is to lift heavier weights. This additional stress causes changes in muscle chemistry that allow for growth factors that include activation of mTOR and satellite cells. Muscle tension has the greatest effect on the connection of motor units to muscle cells.
No. 2. Muscle damage
Muscle pain after training is damage from the load, another trigger for muscle growth. Local muscle damage causes the release of inflammatory molecules and immune system cells, which activate satellite cells so they can go into action. It is not at all necessary that you should experience muscle pain (pain) after training. It is more important that the damage from training is present in your muscle cells (is inside).
Muscle soreness dulls over time and is weakened by other mechanisms, so often athletes with experience (more than one year) do not experience virtually any pain after lifting weights.
No. 3. Metabolic stress
Stress at work will in no way affect the growth of your muscles, but the “burn” of the muscle from exercise (burning/pumping effect) is precisely the effect of metabolic stress. Metabolic stress causes the cells around the muscle to swell, which helps contribute to muscle growth without necessarily increasing the size of the muscle cells themselves. From the addition of muscle glycogen, the muscles begin to swell along with the proliferation of connective tissue. This type of growth is known as sarcoplasmic hypertrophy. It is one of the ways in which you can achieve increased muscle size without increasing strength.
We recommend reading: When is it better to do cardio before or after strength training?
These three mechanisms are the basis of muscle growth, but they are not the only ones that contribute to hypertrophy.
The best exercises for muscle growth: basic training
There is a basic set of exercises that will help you achieve results much faster than any other workout. First of all, this is the golden three: squats, deadlifts and bench presses. But this is not all that needs to be done. Let's figure out exactly what exercises you need to include in your program to build muscle.
Squats
There are many “unloved” exercises among athletes, and squats can be called the first of them. It is very difficult and exhausting, but for developing your body as a whole it is almost the most effective.
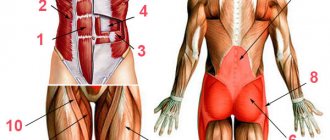
- The load during squats mainly falls on the quadriceps and buttocks.
- The higher the weight (squats with dumbbells, barbell), the more muscles you can use.
- The back extensors, abdominal muscles, stabilizer muscles, and calf muscles are loaded.
You need to understand that despite all their effectiveness, squats are quite dangerous in terms of injury. Therefore, the technique must be studied thoroughly, and additional weights must be introduced gradually and very slowly, otherwise you can not only damage ligaments and joints, but even break your back, which will subsequently require long-term treatment.
Deadlift
This exercise works well on the back of the buttocks and thighs, and also trains the back extensors. Moreover, the technique of this exercise allows you to manipulate fairly large weights without much risk of injury. Therefore, muscle mass grows quite intensively. However, technique will not be superfluous here, as well as preliminary warm-up to warm up the muscles.
Pull-ups
The most popular among non-professional athletes and home-taught people is pull-ups on the bar. The peculiarity of this exercise is that it engages the biceps, forearms, back, and indirectly even the rear deltoids. The abs also work if you do exercises with variations. Moreover, the wider the grip of the hands on the horizontal bar, the load covers the back more, and, on the contrary, falls on the biceps.
Bench press
This exercise alone can find hundreds and even thousands of materials on the Internet and paper sports literature. This is a true powerlifting classic that works well on the chest, triceps and deltoids. The emphasis of the loads varies significantly, depending on the inclination of the bench on which the athlete lies, the width of his grip, the presence and magnitude of the deflection.
Standing press
This exercise is one of the most effective additional ones, with which you can effectively work out the muscles of the shoulder girdle. The entire load is focused on the deltoids and triceps, as well as on the upper back (in the negative part of the press). This way you can pump up many muscles.
The basis of sports nutrition is protein
Muscle is protein. To gain muscle mass, an athletic person needs to consume approximately 2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This is 100–160 grams of protein per day. Where can I get it?
Animal protein
Sources of animal protein (per 100 grams):
- tuna, 30 grams
- cottage cheese, 25 grams
- cheese, 25 grams
- beef, 25 grams
- duck, 20 grams
- eggs, 15 grams
Products of animal origin are easier to digest, since their structure is similar to human cells and tissues.
Vegetable protein
Vegetable protein sources (per 100 grams):
- spirulina, 70 grams
- legumes, 25 grams
- soy, 25 grams
- seitan, 25 grams
- nuts, 25 grams
- seeds, 20 grams
Vegetable protein is digested worse than animal protein, so you need to eat about 20% more of it. More examples of plant-based protein foods were given in the article about sports nutrition for vegetarians.
Calculate your ideal sports weight!
The Role of Protein Synthesis in Muscle Gain
Each cell in the human body contains only one nucleus, while muscles have a large number, which allows them to synthesize new, high-quality proteins that consist of a certain amount of amino acids. The nuclei of muscle cells signal the ribosomes to synthesize the required type of protein.
If you don't supply your muscles with the necessary building material, they simply won't be able to grow. Once again, as you can see, it all comes down to nutrition.
Muscle tension and its effect on muscles
The tension created by the muscle during exercise is another critical element. It is responsible for launching the protein synthesis mechanism, signaling the muscle cells to feed the “affected” fibers.
Thanks to this, new tissue appears, muscle mass and volume increase. Receptors in cells are very sensitive to maximum loads and high voltage. This is why all professional bodybuilders advise exercising as long as your strength allows.
It is necessary to cross the pain threshold to start the process of protein synthesis and supercompensation.
The role of hormones in the training process
Muscle growth is built on 3 “pillars”:
- Testosterone
- Insulin
- A growth hormone
Each of these hormones has a powerful effect on muscle cells. Insulin speeds up the process of delivering protein to the muscles. The potassium-sodium pump carries out the process of transferring amino acids to muscle tissue. The other two hormones, on the contrary, act on muscle fibers and cause them to disintegrate. This whole process is only possible under powerful loads.
The role of amino acids
An amino acid is a protein particle. The necessary protein is built from them. 1 type of protein contains several types of amino acids. Your weight gain results depend entirely on how much protein you consume in your diet.
The required amount of protein is determined by the intensity level of the training process. Also, in addition to protein, calories play an important role, which supply the necessary energy for complex physical exercises.
How to make muscles grow?
In order for muscles to grow, it is necessary to increase the number of myofibrils in muscle fibers. Muscle growth is impossible without special amino acids that affect the formation of myofibrils. Amino acids, in turn, are obtained from proteins of animal origin. It is a building material for muscles. This means that the first condition for their growth is a diet rich in proteins. Proteins are what makes muscles grow.
This doesn't mean you need to eat more than usual or increase your calories. You need to eat in the same usual amount. The ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be optimal: 30\10\60.
The rate of muscle growth is largely determined genetically. However, it is possible to interfere with nature. Factors that influence muscle growth potential include:
- thickness of transverse muscle fibers;
- fiber type (slow or fast twitch);
- number of muscle fibers;
- the amount of fluid that is in the muscles;
- the amount of sarcoplasm present;
- the number of blood vessels in the muscles.
You cannot influence what a person is already born with. But it is quite possible to correct the potential inherent in nature. In this case, you need to take into account the type of body structure.
There are types such as:
- endomorph (short limbs and wide body);
- mesomorph (body parameters are relatively harmonious);
- ectomorph (thin people with problems building muscle).
Individual nutrition and training are selected for each body type.
Rest time between workouts and its role
Merely eating meat and other proteins is not enough without a proper exercise and relaxation routine. Periods of work and rest should be alternated correctly. Training is the determining factor for muscle growth and hypertrophy. When the body feels that it lacks the physical potential to complete a given task, it resorts to hypertrophy.
Training solves several problems at once - not only promotes the growth of muscle tissue, but also helps to grow up if a person is not yet 25 years old. A person can grow 5-6 centimeters in a year. And training also helps launch the mechanism for the formation of amino acids - important components of proteins.
Without going into complex medical terms, you just need to understand that after training it is extremely important to get proper rest . And even during the workout itself, you need to take 3-5 minute breaks. The optimal pause between active training is a day. Or even better – 48 hours. That is, you need to study in a day or two.
Note! Of course, you need to follow expert advice, but you shouldn’t ignore your own feelings: the body itself will tell you when to add rest and when to add exercise.
The fact is that for muscle growth the body needs to overcome physical fatigue. If there is not enough recovery time between workouts, fatigue will accumulate and muscle growth will stop. The body will spend energy on maintaining vital functions, and not on increasing muscle volume.
Important! Muscles grow when the rate of recovery exceeds the rate of muscle protein breakdown.
The effect of muscle tension on muscle growth
Muscle tension is one of the factors for muscle growth. Therefore, weight lifting is often used in classes. When muscles tense, chemical processes in muscle tissue are activated, affecting cell growth. In order for muscles to increase in volume, it is necessary to give the body such a load to which it has not yet had time to get used.
Interesting! Painful sensations after exercise almost completely disappear after a year of training. The pain dulls over time, the person no longer feels it.
The role of hormones in the process
Do muscles grow due to additional hormone production? Certainly. During training, testosterone levels increase, and it stimulates the response to growth hormone. This process begins at the moment when a person is unable to lift a projectile or do push-ups. This is called muscle failure. This condition causes a shock to the body, which is why an additional portion of hormones is produced.
Athletes additionally take artificial hormones to speed up results. But according to many doctors, it is better not to get carried away with this. In order for growth hormones to reach the muscles and not be destroyed by the liver, hydrogen ions are needed. Hydrogen ions should be no more and no less than necessary. With a deficiency or excess, muscle growth will be inhibited. Hormonal balance is maintained by the correct regime of exercise and rest.
The role of amino acids
Amino acids are part of protein compounds, and without them muscle growth cannot be achieved. There are 22 types of amino acids in the body. Our body produces 4 of them itself, and another 8 come to us with food.
To the list of essential amino acids you can add:
- leucine – protects muscles from destruction;
- isoleucine – increases muscle endurance and promotes their rapid recovery after microtrauma;
- valine – affects the speed of muscle tissue construction;
- methionine is an important amino acid for muscle growth and the synthesis of creatine and adrenaline.
Most essential amino acids are found in plant and animal products, namely in proteins.