What is it and why is it needed?
BJU is a generally accepted abbreviation for the combination of “proteins, fats, carbohydrates.” Collectively, these substances are called nutrients. Nutrients are the main components of our body. Both the appearance and health of a person largely depend on them. Each of the nutrients has its own properties and role in our life. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Squirrels
. They form muscles, support immunity, and also promote cell growth. Proteins are found in eggs, meat, cheese, fish, legumes and other foods. However, in each case they are accompanied by different excipients, so it is not recommended to obtain proteins, for example, only from chicken meat. In addition, you need to ensure that your diet contains both animal and plant proteins. Although the latter contain fewer essential amino acids, they have an anti-sclerotic effect, that is, they normalize the functioning of blood vessels. - Fats
. They are secondary, but no less important sources of energy; they increase the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, as a result of which the tissues receive more nutrients from the blood. Their deficiency in the body leads to liver and kidney diseases, fluid retention and skin problems. It is fats that affect the level of cholesterol in our blood, so their excess often causes atherosclerosis. Fats are contained in vegetable (sunflower, corn and other oils) and animal (meat, fish, butter) foods. The recommended ratio of vegetable and animal fats in the diet is 3:7. - Carbohydrates
. This is the primary source of energy. Nutritionists usually divide carbohydrates into simple (fast) and complex (slow). The first group includes monosaccharides and disaccharides. The most common example is table sugar, but simple carbohydrates are also found in fruits and sweets. They are called fast because of the speed of breakdown and absorption in the body. Their functions are regulation of blood sugar levels, nutrition of muscles and brain. And now about complex carbohydrates: they are found in pasta, cereals, vegetables and white bread; they take a long time to break down, thanks to which they saturate the body with energy and have virtually no effect on sugar levels. Excess carbohydrates can turn into fats, which again causes cholesterol levels to rise and atherosclerosis to develop. Excluding carbohydrates from the diet is one of the most popular diets: if they are lacking, the body will begin to use fat reserves as an energy source.
In order for nutrients to properly perform all of the above functions, they must be supplied in the right quantities and proportions. This is the purpose of calculating BZHU - to find out how many nutrients of each type need to be consumed to achieve a particular goal.
What are calories?
If you're wondering how many calories you burn per hour when running, first tell us your weight, age, and type of running activity.
In simple terms, a calorie is a unit of measurement of heat that produces energy. For example, you ate a banana; in the process of assimilation, energy was released, which gave you strength and a cheerful state of mind. If you spend a lot of energy without providing the body with enough calories, it begins to turn to its fat reserves - this is how they are burned. In other words, to lose weight, you need to burn more calories than you consume.
The calorie content of food is the amount of energy that the body will receive if it completely absorbs what it eats. By the way, complete digestibility occurs extremely rarely. Unfortunately, the more harmful a product is, from the point of view of proper nutrition, the better it is absorbed. And vice versa, the more useful it is, the more problems there are in its absorption.
All products today are labeled with their calorie content - we recommend that you read the labels carefully and keep a biased count. This way you will know exactly how many kcal you consumed per day and will not exceed the daily limit. For normal life, a person needs 2.5 thousand kcal per day, provided that he has an average build and average weight.
Daily norm
Nutritionists have long calculated nutrient consumption standards. They allow you to find out what limits it is better not to go beyond when creating a diet, because serious deviations from the norm (which is often found in pseudo-effective diets) lead to the development of diseases and exhaustion of the body. So, every day a person needs to consume approximately:
- 1.5-2 g of protein per 1 kg of weight, the exact figure depends on the level of activity;
- 0.8-1.5 g of fat per 1 kg of weight;
- 2 g of carbohydrates per 1 kg of weight (athletes can increase this norm by 2 or more times).
However, these values are approximate. The exact norms depend not only on activity, but also on a person’s physical data and his goals (losing weight, staying in shape, gaining muscle mass).
Calorie calculator
Unfortunately, losing weight is not as easy as gaining weight. In order to lose excess weight, you need to make an effort in the form of daily physical activity. Walking, running, swimming, dancing will help you with this.
But you should also monitor your diet, excluding your favorite but harmful foods from the daily menu, as many contribute to weight gain and slower metabolism.
We will tell everyone who has undergone such a test about the correctness of calculating calories using modern technology and willpower.
Ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
In addition to daily norms, the proportions of nutrients also help control the diet. Let's divide them into three types:
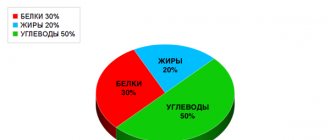
- For a healthy diet. The standard ratio is 3/3/4, that is, 30% of the diet consists of proteins and fats, and 40% of carbohydrates.
- For weight loss. To lose weight, you need to reduce the amount of fat you consume in favor of carbohydrates. So the latter should make up half of the diet, proteins - from 25 to 35%, and fats - no more than 30%.
- For gaining weight. In this case, you again need carbohydrates (workouts require a lot of energy) and proteins (muscles are made up of them). We get a proportion of 35/30/55. It is also noted that before gaining weight you need to make sure there is no excess fat. In other words, first we lose weight and burn fat, and then we build muscle.
Calories Burnt While Walking
Walking is great fun and a great way to burn calories and help with weight loss. As you walk you exercise and raise your heart rate, which will increase calories burned.
The key to any weight loss program: Everyone must find an activity that they can maintain that gets their heart rate up and burns calories.
Walking to lose weight is a great way to see your surroundings and lose weight for free.
Calculation formulas
Above, we determined what portion of our diet (in calories) should be made up of one or another nutrient.
The next step is to determine the total number of calories we should consume per day. You can find out your caloric intake using special calculators on the Internet. You just need to enter gender, weight, height, age and lifestyle in the appropriate lines and get an answer. However, you can do the calculations yourself. There are special formulas for this.
Mifflin-St. Geora counting formula
Developed in 2005 by a group of American nutritionists and has the following form:
- (10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) – 5 x age (g) + 5) x A - for men;
- (10 x weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) – 5 x age (g) – 161) x A – for women.
For greater clarity, let’s take a closer look at the calculation process using this formula:
- Multiply the weight in kilograms by 10;
- Multiply height in centimeters by 6.25;
- Multiply the age in years by 5;
- We add the results of steps 1 and 2 and subtract the result of step 3 from the resulting amount;
- For men, we add 5 to the resulting number, for women, we subtract 161 from it;
- We multiply the result by coefficient A.
A is a coefficient expressing the level of human activity. It has 5 meanings:
- 1.2 - almost complete lack of activity. This includes people with a sedentary lifestyle who do not exercise.
- 1.375 – weak activity. This is either a sedentary lifestyle coupled with small workouts 1-3 times a week, or activities that require regular long walking.
- 1.55 – average activity. This coefficient is chosen by those who play sports 3-4 times a week for 30-60 minutes.
- 1.7 - high activity. This includes daily or almost daily training, or employment in construction, agriculture, etc.
- 1.9 - extreme activity. This includes athletes with repeated daily training sessions and people with long working hours, such as in coal mines.
Using this scheme, calculating the calorie level is recommended only for persons from 14 to 80 years old.
Harris-Benedict formula
Its first version appeared already in 1919, but 65 years later an adjustment took place and now the formula looks like this:
- (88.362 + (13.397 x weight (kg)) + (4.799 x height (cm)) - (5.677 x age (g))) * A - for men;
- (447.593 + (9.247 x weight (kg)) + (3.098 x height (cm)) - (4.330 x age (g))) * A - for women
The activity coefficient in this case is determined in exactly the same way.
How to correctly calculate BZHU
The last step on the path to results is to convert calories into grams of individual nutrients. To do this we need to know the following:
- One gram of protein or carbohydrate contains 4 calories;
- One gram of fat contains 9 calories.
Thus, to find out your daily requirement of a particular nutrient in grams, you need to multiply the percentage of this nutrient in the diet by the caloric intake calculated above, and then divide this by the number of calories in one gram of the nutrient.
Now let's look at two examples of a full-fledged calculation of BZHU. Let a 30-year-old man, 180 cm tall and weighing 80 kg, spend about an hour every day to get to the office, and the same amount on the way back. He wants to switch to a healthy diet. Let's calculate the BZHU norms for his case. We have:
- Height - 180 cm;
- Weight - 80 kg;
- Age - 30 years;
- Activity - weak;
- The goal is to stay fit and switch to a healthy diet.
Based on the goal, we get a proportion of 3/3/4, that is, proteins and fats in the diet - 30% each, carbohydrates - 40%.
Activity corresponds to a coefficient of 1.375. Let's find out the caloric intake using the Mifflin-San Geor formula: (10 * 80 + 6.25 * 180 - 5 * 30 + 5) * 1.375 = 2447.5 kcal. Now we find out the amount of each of the nutrients: 2447.5 * 0.3 / 4 = 183.5 g - proteins; 2447.5 * 0.3 / 9 = 81.6 g - fat; 2447.5 * 0.4 / 4 = 244.8 g - carbohydrates. Let's consider another case. A 25-year-old girl, 165 cm tall and weighing 70 kg, wants to lose weight. Due to her employment in the mental sphere, her activity is as limited as possible. So we have:
- Height - 165 cm;
- Weight - 70 kg;
- Age - 25 years;
- Activity - absent;
- The goal is to lose weight.
She will consume 50% carbohydrates, 30% proteins and 20% fat.
The activity level gives a coefficient of 1.2. Let's calculate the caloric intake using the Harris-Benedict formula: (447.593 + 9.247 * 70 + 3.098 * 165 - 4.33 * 25) * 1.2 = 1797.3 kcal. Then the girl needs to consume: 1797.3 * 0.3 / 4 = 134.8 g - protein; 1797.3 * 0.2 / 9 = 40 g - fat; 1797.3 * 0.5 / 4 = 224.7 g - carbohydrates. Our calculator (new version) uses this formula:
The result of a 1200 calorie average consumption for gaining weight or maintaining weight:
- 1200 * 0.3 / 4 - proteins;
- 1200 * 0.3 / 9 - fat;
- 1200 * 0.4 / 4 - carbohydrates.
And for weight loss
- B: (1200*0.3)/4;
- F: (1200*0.2)/9;
- U: (1200*0.5)/4.
Calories burned per step
So how many calories are lost in one step?
The average person will take 2000 steps to walk 1.6 km, (based on a stride length of about 0.6-0.7 meters).
This works out to be 0.04-0.06 calories per step, depending on your weight and pace.
BY TAKING 10,000 STEPS, YOU WILL BURN 400 TO 600 CALORIES , DEPENDING ON YOUR WEIGHT AND SPEED, AND IT WILL TAKE YOU FROM 1 HOUR 15 MINUTES TO 1 HOUR 40 MINUTES .
Consequences of incorrect calculation of BZHU
Diet compilers most often neglect calculating BJU and take into account only the number of calories. As a result, the balance of substances in the human body is disrupted, which leads to:
- Constant hunger. A person has just eaten and is already dreaming about the next meal. This clearly indicates a lack of fats and carbohydrates.
- Slow weight loss. The body receives too few nutrients, so it adapts to save resources, so that fat is burned slowly.
- Constant volume. Weight decreases due to the removal of fluid from the body and a reduction in muscle mass. But the fat layers remain in place, so there are no visual changes.
- Disturbances in the functioning of hormones. This leads to mood swings, decreased performance, and sore skin, hair and nails.
- Health problems. Nausea, dizziness, tinnitus and even fainting - all this signals an unbalanced diet.
Thus, calculating BJU is an important procedure not only for losing weight or gaining muscle mass, but also for maintaining good physical shape and improving the health of the body. Nutrition in accordance with the calculations provides all the substances necessary for the body, which entails a lot of positive consequences.
So how many calories do we actually burn?
Overall, it depends on your weight, health and fitness, and how fast you walk. Assuming you weigh 200 pounds, the information shown on the kbju calorie burn calculator page shows, for example, that walking for 1 hour at a reasonable level speed will burn about 360 calories. 2 miles can take over 30 minutes, so we can calculate maybe 100 burned per mile.
This compares to about 580 burned by running over the same distance, according to the calculator, but of course you can continue to walk for much longer than you can run.