Author: Timko Ilya - the ruler of the entire site and fitness trainer | more details >> Rod. 1984 Trained since 1999 Trained since 2007. Author and creator of the site tvoytrener.com. CCM in powerlifting. Champion of Russia and South Russia according to AWPC. Champion of the Krasnodar region according to IPF. 1st category in weightlifting. 2-time winner of the Krasnodar Territory championship in t/a. Author of more than 700 articles on fitness and amateur athletics. Author and co-author of 5 books.
Place in the author rating:
out of competition
(become an author) Date: 2012-05-29 Views: 652,898 Rating: 5.0
| All articles by the author >> | Medals articles >> |
Articles are loading...
| Article medals: | article in TOP 100 | more than 500 thousand views |
Why medals are given to articles:
| Bronze medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 100 2. The article has more than 3. The article has more than 100 | |
| Silver medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 50 2. The article has more than 3. The article has more than 500 | |
| Gold medal: | |
| 1. The article is in the TOP 10 2. The article has more than 1 3. The article has more than 1,000 | |
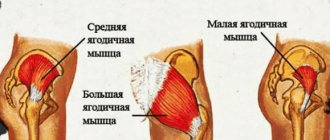
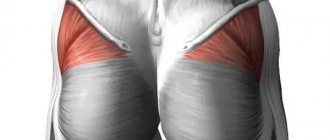
Primary muscles - gluteus maximus and quadriceps femoris Additional - posterior thigh Difficulty - medium
What are the benefits of walking uphill?
This is a functional movement that occurs all the time in everyday life, such as when you walk up the stairs or climb onto a stool to get something from the top shelf.
The Lifehacker Telegram channel contains only the best texts about technology, relationships, sports, cinema and much more. Subscribe!
Our Pinterest contains only the best texts about relationships, sports, cinema, health and much more. Subscribe!
Stepping up to the high ground
Despite their simplicity, step-ups effectively train several muscle groups at once, and in some cases even have an advantage over such icons of strength training as squats and lunges.
Pumps up the buttocks better than many other movements
The main function of the gluteus maximus muscles is to extend the hip joint, so exercises that include this action are used to pump them up. For example, glute bridges, bench-supported hip raises, squats and deadlifts.
In stepping, the gluteal muscles not only have to extend the pelvis, but also participate in stabilizing the hips and knees, keeping them from excessive adduction and rotation. Due to this, the muscles receive more load.
In Gluteus Maximus Activation during Common Strength and Hypertrophy Exercises: A Systematic Review, 16 scientific studies using electromyography (EMG) data found that stepping outperformed many other movements.
While the hip extension activates the gluteus maximus at only 75% of maximum voluntary contraction (MVIC), the deadlift at 61%, and the back squat at 53%, the step-up variations deliver 125%.
But here it is important to note that by performing the same pelvic extensions or squats, in which both feet are firmly on the floor, you can take a lot of weight and fully load the buttocks.
At the same time, it is not safe for even experienced athletes to step up onto a hill with significant weights, and beginners should not even think about it: the risk of injury is too great.
Stepping is one of the best movements for pumping up the buttocks in conditions where working with weights is impossible.
Works many muscle groups
In addition to the gluteus maximus, step-ups also work the gluteus medius, quadriceps, and hamstrings. Moreover, you can Electromyographical analysis of lower extremity muscle activation during variations of the loaded step‑up exercise shift the load on any muscle groups by changing the execution option.
The work also includes the core muscles, which are responsible for the sense of balance and keep your body in a straight position.
Corrects imbalances in muscle development
If the muscles on one side of the body are stronger than the other, in bilateral movements like squats, the stronger side will take away the load. Over time, using heavy weights can result in injury.
Stepping equally Gluteus Maximus Activation during Common Strength and Hypertrophy Exercises: A Systematic Review loads the muscles on the left and right sides, helping to get rid of misalignment.
Develop a sense of balance and reduce the risk of falls and injuries
Unlike squats, which are performed in place, step-ups teach the body to move forward and backward effectively while maintaining balance on one leg.
Because of its functionality, the movement is recommended to be performed by Step up your fitness and safety - Harvard Health for older people to strengthen muscles, rely less on hand support, and eliminate the habit of shuffling when walking.
Stability of the hip and knee joints, a good sense of balance and the habit of proper technique can ultimately reduce the risk of injury in people of any age.
Allows you to practice without equipment or special training
In the gym, steps are done on a step platform, boxing or weightlifting bars. But, in fact, for the exercise you can use any stable elevation - a chair, a step, a park bench or a high curb.
If you don't have dumbbells, you can use a backpack filled with heavy things as weight, or pick up bottles of water or sand.
In addition, the exercise can be easily scaled to suit any level of training. Elderly, poorly prepared and very overweight people can step Step up your fitness and safety - Harvard Health on a platform 10–20 cm high, trained athletes on a 45–50 cm box, while holding dumbbells in their hands or with a barbell on their shoulders.
How to perform steps correctly
Make sure the support is stable and solid. Wobbly structures made from step platforms and chairs with soft upholstery or insufficiently large seats will not work.
Stand in front of a support, you can put your hands on your belt or keep them loose at your sides. Straighten your shoulders and straighten your back, tighten your abs.
Place your right (working) foot on a raised platform so that your entire foot is pressed against the surface and your heel is near the edge of the platform.
Keeping your back straight, transfer your body weight to your working leg, and then climb onto the platform and straighten your leg at the hip and knee joints. After this, you can place the second leg side by side on a full foot, on the toe, or even leave it suspended.
Smoothly and under control lower your left leg to the floor as you step down from the platform. It is allowed to either place the working leg close to the supporting leg or leave it on the platform for the next step.
Perform a full set with your right leg and then repeat with your left.
What mistakes should you avoid?
There are several common mistakes that can make your steps less than effective and even dangerous.
Slouched back
Make sure that when lifting, the body does not bend towards the knee: this spoils the shape and takes the load away from the legs.
Pushing off the floor with the supporting leg
This movement takes the load away from the working leg, which means it makes the exercise less effective. Make sure that all the effort when lifting is made only by the leg that is standing on the hill.
The second one simply rises with the body and is substituted only at the end of the phase.
Turning the knee inward
By rolling your knee inward as you lift, you put it at a biomechanical disadvantage and increase stress on the ACL.
Make sure your knee is always pointing in the same direction as your toe to help avoid injury. You can even turn it outward a little to prevent it from rotating inward.
Substituting the leg until fully straightened
By shortening the lifting phase, you reduce the load on the muscles. Straighten your knee completely, and if that doesn’t work, choose a lower platform.
What muscles work
When jumping onto a stand, all leg muscles work, although the main load falls on:
- Calf.
- Biceps femoris.
- Quadriceps.
- Gluteal.
Also, when jumping, the muscles of the shoulder girdle, back, and core muscles are partially loaded. The latter are responsible for dampening the inertia from the jump in the body area.
When to use weights and how to do it
If you can do 10 steps on each leg without any problems, try adding weights. Take light dumbbells of 2-4 kg or bottles filled with water or sand.
If you don't lose your balance and the exercise's form doesn't deteriorate after 10 repetitions, you can increase the weight further. If you access dumbbells with different weights, increase the load until you reach a pair that you can only do 10-12 times.
If you feel confident, you can try step-ups with a barbell on your back. To start, take an empty bar weighing 15–20 kg, or even better, a bodybar weighing 7–8 kg.
As you get used to it, add weights until you reach a weight that you can perform 8-12 times without turning your knees inward or leaning your body too much forward.
Squats with dumbbells
Squats with weights pump up the lower back and quadriceps.
Instructions:
- Stand straight, place your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Take dumbbells and lower your arms along your body.
- Now do a squat, your back should remain straight. The depth of the squat should be maximum.
- Return to the starting position. Do 2-3 sets of 10 repetitions.
How to do step-ups to shift the load on different muscle groups
In one study, Electromyographical analysis of lower extremity muscle activation during variations of the loaded step‑up exercise, they checked how different variants of step-up execution—classical, sideways (lateral), diagonal, and cross—change the load on the muscles.
15 trained women performed an exercise on a 45 cm high box with additional weights (6RM), and the scientists tracked the activity of different muscle groups using EMG. Here's what they found.
Sideways (lateral)
According to the results of the study, lateral steps are recommended to shift the load on the rectus femoris muscle - one of the heads of the quadriceps, which is responsible for hip flexion.
Stand to the left of the box with your right side facing it. Place your right foot on an elevation, transfer your body weight to the bent leg and rise up until fully straightened.
As with classic steps, you can place your other leg next to your working leg or leave it suspended. In the first case, place the foot of your working leg 10–12 cm from the edge of the support, in the second you can place it right on the edge, as in the video.
Diagonally
Such steps load both the rectus and medial heads of the quadriceps better than the classic ones. In addition, it is recommended for good pumping of the muscles of the back of the thigh.
If you are stepping onto a box or chair, stand to the left of the support one step further from the edge. If you are climbing onto a stable bench, you can stand in front of it, as in the video.
Place your foot on the support so that the thigh is located diagonally from the body and take steps, observing all technical aspects.
Crosswise
This is the last option that was tested in the experiment. Scientists have concluded that such steps pump up the gluteus medius muscles better than others.
Stand to the left of the box, turning your right side towards it. Place your left foot on the box close to the edge. Then straighten your knee and hip as you step up and place your right foot next to your left. You can also not put your leg up, but leave it suspended.
Step down from the elevated position with your right leg and repeat the movement.
Rules for working with the step platform
In order for exercises on the steppe to benefit the body, you must follow the following rules for working with equipment:
Read also: What is CrossFit?
- Your back should be straight while doing the exercises.
- Climbing onto the apparatus is carried out using the leg muscles.
- The entire foot is placed on the surface of the board; there should be no sagging of the heel or toes.
- You only need to exercise in comfortable non-slip shoes.
- You are allowed to stick your butt out when doing squats.
- You cannot jump or lower yourself to the floor with straight, tense legs.
- Movements should be fast, but not intermittent.
This type of sports activity is beneficial for the cardiovascular system, for improving coordination, balance, stability, endurance and elevating mood.
To practice step aerobics, you do not need to have special physical training, because every person can move up and down the steps. During training, walking on the “step” will alternate with jumping and squats. Even those who didn’t like these standards at school are happy to stomp and jump to the music. And losing 4 kg of excess weight from the body in a month will please any athlete.
Moreover, you don’t need to go to the gym specifically to practice the step; you can buy this equipment and practice sports on it at home. The projectile does not take up much space.
How else can you do steps?
The following types of stepping have not been tested experimentally, but since they involve additional movements, it can be expected that they will increase the load on the muscles.
With hip flexion at the top
Do a classic step-up with your right foot, but instead of just stepping up with your left, bend your hip and bring your knee forward. Step back down with your left leg and repeat the movement.
With hip extension at the top point
Take a step with your right foot, and at the top point, straighten your left thigh, simultaneously straining your buttocks. Step back down with your left leg and repeat the exercise.
With a lunge
Step up with your right foot and bring your left knee forward, then step down with your left foot and lunge back with your right. Rise up from the lunge and repeat the exercise.