Beef is one of the most common types of meat. In cooking, different parts of the carcasses of bulls, cows and calves are equally valued (the flat part of the brisket, the upper part of the shoulder, the middle part of the rump, the rib, neck, sirloin, shoulder, hip or shoulder parts). To prepare main courses, soups, and minced meat, tenderloin, shoulder, flank, front and back shanks are used.
Sausage and cutlet meat usually consists of two types: beef and pork. For steaks, the marbled variety with small layers of fat is preferred, which makes the meat juicy and tender (for example, for T-bone steak), or false fillet. It is cooked steamed, grilled, in the oven, baked in foil and in whole pieces. But what are the calorie content, composition, benefits and harms of this product?
Raw beef calories
What is the energy value of raw beef? Per 100g of lean pulp there are 187 kcal. The nutritional value of the product is represented by the following figures:
- proteins - 18.9 g;
- fats - 12.4 g;
- carbohydrates - 0 gr.
If for some categories (varietal, sirloin and rump) these indicators are the norm, then in the fatty variety, which is usually removed from the lower outer part of the thigh, the calorie content can reach up to 230 kcal. There are also a lot of layers in the flank. The prime cut from the back, the point of the shoulder and the inside of the shoulder are the leanest parts.
If earlier cutlets were prepared from homemade minced meat, now they usually take purchased ones (for example, from Miratorg). Its calorie content should be looked at on the packaging.
Calorie content of boiled beef
When planning the menu for the day, many include boiled meat rather than fried thick sirloin. But how many calories are in boiled beef?
Photo source: shutterstock.com
100 grams contain 232.4 kcalories, and BZHU has the following indicators:
- proteins - 24.3 g;
- fats - 15 g;
- carbohydrates - 0.22 gr.
But the figures given are valid for lean meat. If it has layers of fat, which sometimes occurs, or is smoked and boiled, then the energy and nutritional value will be higher.
Calorie content of beef stew
An even lower calorie dish is beef stew, which goes well with steamed vegetables.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
How many calories are in 1 serving of this dish? Per hundred grams comes out to 220 kcal. In this case, the BZHU is represented by the following ratio:
- proteins - 18.3 g;
- fats - 13 g;
- carbohydrates - 0.07 g.
This stewed variety is ideal for a diet.
Beef for weight loss and sports nutrition
Introducing beef into your diet for the purpose of losing weight or as an element of sports nutrition is a great solution, because the product has a lot of useful properties. Red meat from cattle is one of the least high-calorie meats, which is why it is recommended for people who want to lose a few extra pounds.
Beef is healthier in this regard than chicken. For this reason, red meat is an ideal protein base for lunch or dinner. You just need to supplement the product with vegetables - and your meal will be healthy, balanced and rich in nutrients. Such food will give you a feeling of satiety, normalize metabolism and become a faithful assistant in the fight against excess weight.
Why is beef recommended for dietary nutrition? The answer is simple: this type of meat has little fat and no carbohydrates at all. At the same time, the product is rich in vitamins and minerals, which improve metabolic processes in the body, which leads to getting rid of excess weight. Fat burning occurs faster by consuming natural protein, which is easily digestible.
The main thing is to cook the meat correctly. It is better to boil, bake or stew it, since in this case the beneficial substances are retained in the composition. Moreover, after such heat treatment, the number of calories in the product remains low.
Advice! If you are hoping to lose weight with beef, do not fry it under any circumstances, especially in oil. Firstly, it is harmful, and secondly, meat prepared in this way contains many more calories than boiled, stewed or baked meat. The calorie content of fried beef is almost twice as high as the listed heat treatment options.
Beef is prized by athletes and bodybuilders. This is due to the composition of the meat. Vitamins and amino acids are needed to restore strength after heavy physical activity and grow muscle mass. Vitamin B12, protein, iron, zinc, folic acid, calcium - these substances contribute to the rapid gain of muscle weight. Red meat is also rich in creatine, the positive properties of which are known to all athletes. For this reason, nutritionists recommend that people who want to build muscle eat 1-2 grams of beef for every kilogram of body weight.
Athletes and bodybuilders are better off focusing on the following parts of the carcass: fillet, back, tenderloin. It is better to stew the first one or bake it in the oven, since this meat is tougher, and the second and third ones should be boiled or grilled, since the tenderloin and back are the softest pieces.
Calorie content of lean beef
Parts of carcasses that are sold in pieces without layers of fat are considered lean. At its core, it is a fillet that is recommended to be cooked without the use of oil. The product is considered dietary and even after cooking is able to retain most of its beneficial properties.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
So how many calories are in lean beef? 100 grams of this product contain only 158 kilocalories, and BJU is considered ideal for weight loss. This is 7.1 g of fat and 22.2 g of protein. There are no carbohydrates here at all.
How many calories are in baked beef?
Here's how much:
The calorie content of baked beef is 170 kcal per 100 grams.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates (BJU) in gr. per 100 grams:
Proteins - 12.0
Fats – 11.0
Carbohydrates – 0.0
A:
The calorie content of baked beef in foil is 203 kcal per 100 grams.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates (BJU) in gr. per 100 grams:
Proteins - 31.7
Fats – 7.6
Carbohydrates – 0.2
Composition and nutritional value of beef
What is the main advantage and biological value of this type of meat? This variety has a balanced chemical composition. Thanks to it, beef meat products provide quick satiety. What substances are included in the chemical composition of this type of meat?
Photo source: shutterstock.com
It is represented by the following substances:
- iron;
- zinc;
- B vitamins;
- calcium;
- potassium;
- vitamin E;
- magnesium;
- fluorine;
- manganese;
- molybdenum;
- phosphorus.
Also, the rich mineral and vitamin complex contains copper, vitamin PP and other substances beneficial to the body of an adult and a child. At the same time, beef meat does not provoke allergies. That is why it is often introduced into baby food.
Useful properties of beef
- Beef contains complete, easily digestible proteins that are of great importance in the human diet. The highest amount of protein is found in beef tenderloin (the softest part of the carcass).
- Beef also contains many trace elements (magnesium, zinc, calcium, potassium, iron, phosphorus, sodium), which strengthen the musculoskeletal system and vitamins: group (good for the visual organs), PP (part of the enzymes), C (strengthens the walls of blood vessels ), B6 and B12 (actively involved in the absorption of iron).
- After cooking, meat promotes recovery from injuries, infectious diseases and burns.
- It contains a small amount of fat and is considered lean. This quality makes it ideal for dieters and athletes.
Daily intake of beef
What piece can you eat a day so that it is healthy and does not harm the body? The daily intake is 150 grams for an adult.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
For children, this figure is less and is only 80 grams. However, doctors strictly do not recommend including beef in your daily diet. But you should not use it more than 3-4 times a week.
The benefits and harms of beef
What are the beneficial properties of the product? How is it good for the body of a man, woman or child? The benefit of beef lies in its high protein content. Due to this, it is able to satiate a person as quickly as possible without harming the figure. At the same time, the meat contains very little fat, which reduces the load on the kidneys, heart, liver and blood vessels.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
Beef can be safely included in the diet during weight loss and for pregnant women. The amino acid composition of the product is absolutely safe. There are other positive properties of tenderloin, which provide:
- improvement of metabolism;
- removing harmful cholesterol from the blood;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels;
- increase in muscle mass.
Another product allows you to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, effectively restores blood flow, and provides high-quality prevention of anemia. Beef stimulates active brain activity, strengthens hair, bones, nails and teeth, and normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system.
It is recommended to include beef in the menu of people who actively train or whose work involves heavy daily loads. It will prevent the body from becoming exhausted. It is also worth introducing it during the recovery process after injuries, operations, loss of large amounts of blood and serious illnesses.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
But beef is not always healthy for everyone. For some, it can only bring harm. It is important to consume meat in moderation, otherwise excessive intake of protein into the body can impair the optimal functioning of the stomach, liver and kidneys. You may also encounter other problems:
- formation of stones;
- decreased immunity;
- increased risk of esophageal cancer;
- failure in the functioning of the myocardium;
- inflammation of the pancreas, kidneys and other organs.
Also, excessive consumption of meat can provoke the formation of cholesterol plaques, which lead to blockage of blood vessels.
ABC RECOMMENDS
Fried potatoes: calorie content, benefits, nutritional value
Benefits of beef
Due to the content of a large number of useful elements in its composition, beef has many positive properties that have a beneficial effect on the human body. Meat is especially useful for a growing body, for people leading an active lifestyle, athletes, as well as those who have suffered injuries, burns and serious illnesses.
Beef is useful in the treatment of urolithiasis, helps to recover from infectious diseases, injuries and burns. The collagen contained in beef helps restore healthy joints.
The benefits of beef, when consumed on a regular basis, are as follows:
- strengthens the immune system and increases the body's protective properties;
- helps speed up metabolism;
- improves vision;
- normalizes the functioning of blood vessels;
- gradually reduces the level of “bad” cholesterol;
- prevents the appearance of atherosclerosis;
- increases blood clotting;
- normalizes stomach acidity;
- cleanses the body of toxins and waste;
- helps in the fight against insomnia.
Beef meat helps the male body well in the synthesis of testosterone (male hormone) and increases potency. It also increases physical endurance, mental activity, and also prevents early baldness by strengthening the hair follicles.
Beef is also beneficial for women:
- relieves chronic fatigue;
- supports the endocrine system;
- helps in restoring the body after heavy menstrual bleeding;
- regulates the functioning of the reproductive organs;
- gives strength to nails and hair.
Beef is especially beneficial for pregnant women, as it provides essential vitamins and minerals not only to the mother, but also to the child.
Beef calorie table
To make it easier to calculate the energy value of your menu for the day, use the ready-made data presented in the table:
| Name of the dish | Calorie content per 100 g (kcal) |
| Beef broth | 4 |
| Entrecote | 220 |
| Shchi with beef | 42 |
| Beef Stroganoff | 193 |
| Beef pilaf | 219 |
| With onions and other vegetables | 116 |
| Smoked-boiled | 113 |
| Boiled in water without salt | 217 |
| Dried | 235 |
| With gravy | 117 |
| Dry-cured | 272 |
| Baked in the oven | 168 |
This video recipe will help you prepare a dietary beef dish:
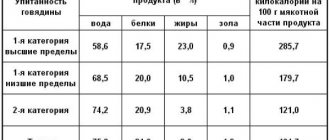
What is useful for Beef 1 cat.
You can see a complete guide to the healthiest foods in the “My Healthy Diet” app.
Energy value, or calorie content
- this is the amount of energy released in the human body from food during the digestion process. The energy value of the product is measured in kilocalories (kcal) or kilojoules (kJ) per 100 grams. product. The kilocalorie used to measure the energy value of food is also called a food calorie, so when caloric content is reported in (kilo)calories, the prefix kilo is often omitted. You can see detailed energy value tables for Russian products here.
The nutritional value
— content of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the product.
Nutritional value of food product
- a set of properties of a food product, in the presence of which the physiological needs of a person for the necessary substances and energy are satisfied.
Vitamins
, organic substances required in small quantities in the diet of both humans and most vertebrates. Vitamin synthesis is usually carried out by plants, not animals. A person's daily requirement for vitamins is only a few milligrams or micrograms. Unlike inorganic substances, vitamins are destroyed by strong heat. Many vitamins are unstable and are “lost” during cooking or food processing.
Source
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Beef, shoulder on bone.”
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 130 kcal | 1684 kcal | 7.7% | 5.9% | 1295 g |
| Squirrels | 17 g | 76 g | 22.4% | 17.2% | 447 g |
| Fats | 7 g | 56 g | 12.5% | 9.6% | 800 g |
| Water | 75.9 g | 2273 g | 3.3% | 2.5% | 2995 g |
| Ash | 1 g | ||||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.11 mg | 1.5 mg | 7.3% | 5.6% | 1364 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.21 mg | 1.8 mg | 11.7% | 9% | 857 g |
| Vitamin B4, choline | 70 mg | 500 mg | 14% | 10.8% | 714 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.6 mg | 5 mg | 12% | 9.2% | 833 g |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.42 mg | 2 mg | 21% | 16.2% | 476 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 9.6 mcg | 400 mcg | 2.4% | 1.8% | 4167 g |
| Vitamin B12, cobalamin | 3 mcg | 3 mcg | 100% | 76.9% | 100 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.57 mg | 15 mg | 3.8% | 2.9% | 2632 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 3.5 mcg | 50 mcg | 7% | 5.4% | 1429 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 4.54 mg | 20 mg | 22.7% | 17.5% | 441 g |
| Niacin | 4.7 mg | ||||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 324 mg | 2500 mg | 13% | 10% | 772 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 8 mg | 1000 mg | 0.8% | 0.6% | 12500 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 25 mg | 400 mg | 6.3% | 4.8% | 1600 g |
| Sodium, Na | 60 mg | 1300 mg | 4.6% | 3.5% | 2167 g |
| Sera, S | 230 mg | 1000 mg | 23% | 17.7% | 435 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 183 mg | 800 mg | 22.9% | 17.6% | 437 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 59 mg | 2300 mg | 2.6% | 2% | 3898 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Iron, Fe | 2.8 mg | 18 mg | 15.6% | 12% | 643 g |
| Yod, I | 7.2 mcg | 150 mcg | 4.8% | 3.7% | 2083 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 7 mcg | 10 mcg | 70% | 53.8% | 143 g |
| Manganese, Mn | 0.035 mg | 2 mg | 1.8% | 1.4% | 5714 g |
| Copper, Cu | 182 mcg | 1000 mcg | 18.2% | 14% | 549 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 11.6 mcg | 70 mcg | 16.6% | 12.8% | 603 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 8.6 mcg | ||||
| Fluorine, F | 63 mcg | 4000 mcg | 1.6% | 1.2% | 6349 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 8.2 mcg | 50 mcg | 16.4% | 12.6% | 610 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 3.24 mg | 12 mg | 27% | 20.8% | 370 g |
The energy value of beef, shoulder blade on bone is 130 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.