HOW TO EFFECTIVELY TIGHTEN YOUR FACIAL SKIN AFTER 30, 40, 50 YEARS WITHOUT SURGERY: PROCEDURES AND METHODS
Modern cosmetology offers many ways to tighten facial skin without a surgeon’s scalpel.
Depending on the nature of the patient’s problem, the GMTClinic cosmetologist will create an individual rejuvenation and lifting program, using only proven and effective hardware or injection procedures, as well as using thread lifting techniques. The first signs of sagging skin can appear at any age. Depending on hereditary factors, environmental conditions, nutrition, lifestyle, busy work schedule and the amount of stress, age-related changes can appear at 25 and 45 years. Depending on the age group of the patient, his skin reacts differently to the same procedures. Therefore, the transformation program needs to be adjusted regularly.
As practice shows, many patients do not know how to tighten their facial skin after 30 years. To maintain normal skin tone at this age, it is often enough to use the capabilities of hardware cosmetology. But in some cases, injection procedures and thread lifting may also be required. Micro-needle RF lifting will help restore an even facial contour, and laser resurfacing will restore the firmness and elasticity of the skin.
Usually, cosmetologists offer several procedures at once to achieve a comprehensive rejuvenation effect. Procedures that tighten the skin on the face after 40 are prescribed by a cosmetologist depending on the severity of age-related changes and the presence of contraindications. To restore soft tissues and skin to their original elasticity, SMAS lifting, Thermage and infrared thermolifting are used.
Many patients are concerned about the question of how to effectively tighten their facial skin after 50 years. And we have a solution. The treatment program will include a complex of different types of effects aimed at: reducing wrinkles, tightening the contours of the face, and evening out skin color. We will describe below what types of procedures a doctor can include in the program.
Types of obesity
Types of obesity vary depending on the causes of its occurrence.
Alimentary (exogenous): appears with overeating and a sedentary lifestyle. Pathological (endogenous): is the result of various diseases. A large amount of fat is considered a chronic pathology of a progressive nature, and if left untreated, serious complications can occur. With excess weight, the body begins to work at “full capacity”, because of this the internal organs are “produced” much faster. Consequently, the quality of life and its duration decreases.
Content:
- Types of obesity
- Causes of excess weight
- Full face
- Fullness of shoulders, arms and chest
- How to remove fat from shoulders and arms?
- Adipose tissue in the armpits
- Possible complications and preventive measures?
According to the treatment method, obesity is divided into the following types: adjustable and irreversible. Controlled: Can be eliminated with special diet and exercise. Irreversible is diagnosed very rarely.
It can also be divided into types according to dynamics. Stable is characterized by the patient’s constant weight, that is, kilograms do not increase or decrease. Dynamic: the patient’s weight increases every day. Constitutional fat deposition: a chronic pathology that appears as a result of physical, biochemical and metabolic processes. Constitutional fat deposition causes various complications and makes a person disabled. In addition, among patients with this disease, many deaths occur due to cardiovascular diseases.
To reduce risks, the patient must adhere to a special diet (most often a diabetic diet) and increase physical activity every day.
Constitutional obesity, in turn, is also divided into types. Female type (gynoid): considered the most harmless because it poses virtually no threat to human health. In this case, the figure becomes like a pear. Fat deposition occurs on the hips, buttocks, and lower abdomen. This type is often found in women whose endocrine system works correctly (most of the fat is formed under the skin).
Male type (android): appears when the body has high levels of androgens. In this case, a person’s figure becomes like an apple - fat is deposited on the stomach, chest and shoulders. If this condition is not given attention and pathology develops, then metabolic syndrome and abdominal obesity will occur (carrying serious complications). In addition, fat begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity and internal organs, which makes it unfavorable and dangerous.
The mixed type is the most common phenomenon that can be diagnosed even in a child. In this case, fat deposition occurs throughout the body. In addition, depending on the location, several types of adipose tissue are distinguished, these are:
- subcutaneous fatty tissue;
- deep layer;
- internal fat (located around the abdomen).
The ratio of species and the severity of the tissue will depend on age, genetic predisposition, metabolism and other equally important factors. Subcutaneous fat is present in varying quantities in all areas of the body. Thanks to it, the human body has smooth outlines, but it can be easily removed with the help of exercise and proper nutrition.
Based on the prevalence of fat, local and general forms can be distinguished. Local is divided into three types:
- delimited (adipose tissue has clear boundaries and an increase in the surface layer of adipose tissue);
- diffuse-local (characterized by the growth of subcutaneous fat in a certain anatomical area, this area loses its boundaries and smoothly passes into the neighboring area where adipose tissue is normal);
- finely lumpy contour disturbances (manifests as an increase in subcutaneous adipose tissue and the formation of an uneven contour of the skin (small tubercles and pits).
The local form of deposits can be quite stable, so it can persist even with severe weight loss.
INDICATIONS
If your skin is rapidly losing tone, certain areas of your face are sagging, and its oval has become unclear, you should consult a cosmetologist as soon as possible. Our specialists will tell you how to tighten sagging skin around the eyes, and how to treat gravitational ptosis of the face without surgery. They will also advise you on how to get rid of sagging skin on the chin and jowls. A network of wrinkles around the eyes and bags under the eyes, facial folds near the lips, hollows on the cheeks and the appearance of jowls are the most common types of changes that betray age. All these changes can be easily removed using hardware and injection techniques, as well as thread lifting.
How is a male facial massage beneficial and what stages does it consist of?
As we have already said, men, just like women, want to enjoy the reflection in the mirror. Facial massage is primarily beneficial from an aesthetic point of view, as it eliminates visual problems. But the advantages don't end there.
Natalia:
Massage helps smooth out wrinkles, lift the nasolabial and eyebrows, get rid of a double chin, remove bags and dark circles under the eyes, tone the skin and achieve a lifting effect. Naturally, this is necessary for all people. Secondly, massage relaxes, empties your head, and removes negative energy. After the procedure, the person feels rested and energized.
Don’t forget that a massage is also a full-fledged hour-long workout for the facial muscles. In the studio, like any activity in the gym, it is divided into several stages:
- cleansing the skin and preparing for massage;
- warm-up - warming up the muscles;
- deep muscle work (includes both the face and décolleté, neck, head);
- working out the oval of the face using Guasha combs;
- sculpting;
- cool down - relaxation and hydration.
It is not surprising that after such an extensive training program you will feel pleasantly tired.
On February 14, the fourth Face Fit studio opens in the Legend of Tsvetnoy business center on Tsvetnoy Boulevard. On the opening day, everyone can try a massage for free. In addition, passes on this day will be discounted up to 40 percent.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The list of all possible contraindications depends on the type of procedure. Here are the most common of them:
- oncological diseases,
- acute inflammatory and infectious diseases in the acute stage;
- systemic skin diseases;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding,
- installed permanent fillers and threads.
At the preliminary consultation, your cosmetologist will take a medical history to identify any contraindications to the procedure in order to minimize the risk of side effects. Do not forget to mention the presence of chronic diseases, surgical interventions performed, and whether you have ever experienced side effects after undergoing cosmetic procedures.
DEVICES AND PREPARATIONS FOR SOLVING THE PROBLEM
Hardware rejuvenation methods are very popular among our patients. At GMTClinic you can undergo the following hardware procedures:
Altera (SMAS-lifting) is an ultrasonic lifting technology that allows you to achieve a rejuvenation effect comparable to surgery. Alterotherapy ranks first among hardware techniques that work to lift soft tissues. The technique restores skin tone, strengthens and tightens the soft tissues of the face.
Thermage (RF-lifting) is a safe way to correct gravitational ptosis based on radiofrequency radiation, which provides long-term tightening results. Local tissue heating during the procedure is up to 60%. The skin flap is reduced and rebuilt, lifting occurs.
Sciton SkinTyte is an infrared thermolifting treatment based on the use of the infrared spectrum. During the session, the skin warms up, the production of collagen and elastane is stimulated, and its structure improves.
Microneedle RF lifting Infini is a face lifting technique based on the use of a device with an attachment made of many nanoneedles. They direct heat energy and radiofrequency pulses into the deep layers of the skin. During the session, the skin is slightly injured, which also stimulates its accelerated regeneration.
To rejuvenate the skin of patients, our experts recommend using laser correction techniques that give quick, lasting results and do not require trauma to the skin.
Types of laser resurfacing used:
- Dermablate
- CO2 Multipulse
- Fraxel re store Dual
- Sciton Halo – hybrid laser
- Quanta System Duetto is a soft neodymium and alexandrite laser.
Injection techniques have proven to be highly effective in combating gravitational ptosis of any severity. They either slow down this process by blocking the facial muscles, or restore normal skin tone by activating metabolic processes and the production of collagen and elastane. Injections will help make the skin elastic, even and smooth, and restore its radiant appearance. The following types of injection therapy are used at GMTClinic:
- biorevitalization,
- botulinum therapy,
- bioreparation,
- plasma therapy,
- contour plastic,
- bioreinforcement.
Thread lifting techniques (3D mesothreads and Aptos) help quickly restore the clarity of the face and cope with the problem of sagging soft tissues in various areas.
Preparation:
- 7 days before the procedure date, do not take blood thinners;
- It is advisable to avoid visiting the pool or bathhouse a week before the procedures.
Rehabilitation:
- swelling and redness subside within 1-5 days depending on the procedures;
- sunbathing should be taken only half a month to a month after the procedure;
- It is not advisable to visit the pool or sauna within 7 days after the session;
- You cannot use scrubs or massage for 7 days after the procedure.
The result of facelift procedures is: getting rid of the sagging of the upper eyelid, returning the clarity of the oval of the face, getting rid of wrinkles, returning normal skin tone, its firmness, smoothness and elasticity.
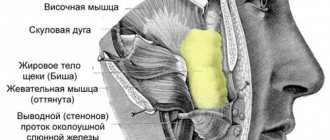
Age aspects of the structure of human facial skin
The skin covers the surface of the body and makes up about 16% of the total body mass, the surface area is 1.2-2.3 m². The skin performs a number of functions: 1. protective – protects from the effects of physical, chemical, mechanical factors, ultraviolet radiation, microorganisms; 2. homeostatic – maintains the constancy of the internal environment by regulating body temperature and preventing fluid loss; 3. excretory (excretory) - due to the activity of the sweat glands, nitrogen metabolism products, medications, lactic acid and other substances are released; 4. secretory – formation of vitamin D; 5. sensory – receiving information from the external environment using pain, tactile and temperature sensitivity receptors; 6. participation in water-salt metabolism; 7. immune; 8. blood deposition – about 1 liter of blood is deposited in the vessels of the skin; 9. diagnostic - reflects the condition of organs and the presence of certain diseases in the body. Human skin consists of three layers: • outer – epidermis (stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium); • middle connective tissue – dermis; • internal – hypodermis, consisting mainly of fat cells. The epidermis, the outer layer of the skin, is firmly connected to the underlying dermis through a basement membrane, which serves as a support for cells, regulates the supply of nutrients and the removal of cellular metabolic products. The structure of the basement membrane is determined by the interaction of keratinocyte epidermal cells and fibroblast dermal cells. The dermis, the middle layer of the skin, provides the skin with a structural basis and consists of cells and an intercellular matrix. It is located under the epidermis, provides its nutrition, gives the skin strength and contains its derivatives. Includes two layers: • papillary; • mesh. The papillary layer is represented by loose fibrous connective tissue and performs a trophic function. The mesh layer is formed by dense, unformed tissue and contains collagen fibers, which provide strength to the skin and prevent its excessive stretching. The hypodermis, the inner layer of the skin, consists of lobules of mature adipocytes, which are separated from each other by thin layers of connective tissue with blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves. Features of the structure of the skin at different age periods Skin of a newborn (0-2 years) In newborns, the skin is covered with a cheesy lubricant consisting of fat, glycogen, extractives, cholesterol, odorous and volatile acids and vitamins. Thanks to this, the skin is soft and elastic. After a few days the lubricant disappears. There are yellowish-white dots on the skin of the nose - the result of intrauterine excess secretion of the sebaceous glands, which disappear after 1-2 weeks. Due to the first irritation in their lives from environmental actions, physiological skin catarrh develops. It becomes hyperemic - bright red, sometimes with a bluish tint. After two or three days, the hyperemia gives way to peeling, especially pronounced on the palms and soles. The epidermis is thin - from 0.5 to 0.25 mm, it is loosely connected to the underlying layers of the skin. Collagen fibers are not yet complete (they mature by 4 months), so the skin of newborns is very vulnerable and prone to redness and inflammation. The dermis is 1.5-3 times thinner than that of adults. Subcutaneous fatty tissue is well developed. Sweat glands are not yet formed and do not function, so babies easily overheat. Miliaria occurs due to easy penetration of infection through the wide ducts of the sweat glands. The sebaceous glands in newborns are large and produce sebum more intensively than in adults. At 1 year of life, the number of fat cells increases. Complete renewal of skin cells in a newborn occurs within 72 hours. Children's skin (2-12 years old) Children's skin is finally formed by the age of 7 and gradually acquires the properties and structure of adult skin, and its protective functions become more advanced. There are differences between a child's skin and an adult's skin. The epidermis is thinner, the cells are much smaller in size. The density of sweat glands is 5-7 times higher than in adults. The thickness of subcutaneous fat is less. Children's skin is characterized by the presence of a significant number of sebaceous glands, so the skin is oilier. The ability to form melanin in children is lower than in adults, so they are less protected from ultraviolet rays. Their skin is highly hydrophilic (contains 80-90% water) and is characterized by high absorption capacity. In the skin of children under 7 years of age, signs of immaturity of the dermal-epidermal contact zone were revealed. Children's skin has high regenerative abilities. Skin of girls and boys (puberty) The final formation of the skin occurs. The skin of teenagers is excessively shiny due to increased oil content. It has clogged pores, which cause the formation of juvenile acne. Despite the fact that as the process of hormonal changes is completed, acne gradually disappears (by the age of 25), facial skin care should begin in adolescence. From the onset of puberty to adulthood, under the influence of female sex hormones, there is a gradual change in the percentage of different types of ceramides, which play an important role in the formation of the skin barrier that controls transepidermal water loss. During adolescence, the skin has the ability to quickly regenerate and is very elastic. Skin of a girl 25-30 years old At this time, the skin is smooth and elastic. There are no longer problems with acne, but by the age of 25, facial wrinkles appear in the corners of the mouth, eyes and forehead. Laughter lines become noticeable. Facial skin care at this age stage is extremely necessary, despite the fact that the skin still retains the ability to recover. Skin of a woman over 30 years old The rate of division of the basal cells of the epidermis decreases, the thickness of the basal layer becomes thinner, and the thickness of the stratum corneum increases. The number and functional activity of dermal cells (fibroblasts, macrophages, tissue basophils) decreases, therefore the volume of the ground substance, collagen and elastic fibers decreases. Starting from the age of 25, the synthesis of collagen and elastin decreases by 1% annually. Elastic and collagen fibers thicken, their structure is disrupted, and their arrangement becomes less ordered. A decrease in the level of hyaluronic acid in the skin leads to disruption of its hydration, turgor and elasticity, contributing to the appearance of dry skin and the formation of wrinkles. These factors are a direct signal implying comprehensive facial skin care. External signs of skin aging in people are expressed in thinning, dryness, deepening of facial folds, the formation of a network of fine wrinkles, and the appearance of pigmentation. The skin loses its elasticity. A gradual disruption of microcirculation leads to a decrease in trophism, which leads to an acceleration of the aging process and leads to a deterioration in complexion. The muscles of the forehead and chin shrink, forming deep transverse and longitudinal wrinkles. The muscles of the cheek area sag, causing drooping of the corners of the mouth and deformation of the oval of the face. Long before the onset of menopause, the process of hormonal transformation begins in a woman’s body. After 30 years, the level of the hormone estrogen, which is involved in regulating the functions of many cells, begins to decrease. This is associated with insufficient skin hydration, skin laxity, and poor wound healing. After 35 years, the lack of estrogen in the body is especially noticeable. Complete renewal of skin cells at the age of 30–35 years occurs in 26–30 days. To prolong the healthy appearance and condition of new cells, it is necessary to carry out regular facial skin care. Skin of a woman over 40 years old The process of age-related involution is observed. The thickness of the layers of the epidermis and dermis decreases, atrophy of the subcutaneous fatty tissue and small sebaceous glands begins. Connective tissue degeneration occurs, the amount of mucopolysaccharides decreases, which leads to skin dehydration. The depth of the nasolabial folds increases. In women over 40 years old, wrinkles begin to actively appear all over the face: around the eyes, on the forehead, and near the nose. Facial features become angular. The skin becomes drier, denser and tougher, prone to flaking, and pigment spots are often noticeable. The cheeks begin to sag, the first wrinkles on the neck are visible. The skin of the eyelids becomes heavier and folds appear. There are noticeable dark circles under the eyes and crow's feet in the corners of the eyes. If you are overweight, a “double chin” appears. Many women have problems related to hormonal status - hair begins to grow on the upper lip. Microcirculatory disorders lead to the appearance of rosacea, spider veins and telangiectasia. Regeneration is slow. Facial skin care at this age should be regular. It must be covered with special oils and creams so that the tissues receive “recharge” through the skin pores. At the age of 40-45 years, complete skin renewal occurs within 35-40 days. The skin of a woman over 50 years old The cause of the changes is age-related hormonal changes in the woman’s body - menopause. A decrease in estrogen levels in the blood leads to a decrease in skin oiliness, it becomes dry and thin. Its hydration and elasticity deteriorate, and age spots appear. The body lacks vitamins and nutrients. The skin rapidly loses its natural strength and barrier properties and begins to change dramatically. It becomes thinner, the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer on the face decreases. Blood supply deteriorates and oxygen starvation of tissues increases. Due to the lack of estrogen, the activity of the sebaceous glands decreases, and hence the oiliness of the skin. The amount of hyaluronic acid and collagen decreases, lipoatrophy of the face and neck progresses. Regeneration processes slow down; complete renewal of skin cells after 50 years occurs in 56–60 days. Skin of a woman over 60 The process of rapid aging continues until about 60 years of age, and then the skin enters a period of relative stability. The skin becomes pale, dry, thin, and often flakes, which leads to a violation of the barrier and regenerative properties. Changes in the dermal-epidermal junction are pronounced, which are characterized by thinning and duplication of the basement membrane and a decrease in the number of hemidesmosomes. The skin is easily injured and difficult to recover. Its turgor and elasticity decrease, and deep wrinkles appear. In people over 65 years of age, the thickness of the dermis decreases by approximately 20%. Pigment spots and benign neoplasms appear, and vellus hair grows on the cheeks, chin and upper lip. There is a sharpening and change in facial features, which is associated with a reduction in subcutaneous fatty tissue and changes in the skull. Bags and circles appear under the eyes, and horizontal and interbrow wrinkles appear on the forehead. To remove sagging skin of the chin and cheeks at this age, to disguise nasolabial and nasolabial furrows along with the general background of many fine wrinkles, it is strongly recommended to perform regular facial skin care. Skin of a woman over 70 years old After 70 years, the skin becomes thin with a thickened upper stratum corneum, through which subcutaneous fatty tissue shines through, giving it a yellowish tint. The skin is characterized by the least elasticity, numerous deep wrinkles and folds appear. Due to the influence of androgens, the specific density of collagen in the dermis of the skin of men is significantly higher than that of women, which allows men to look younger than their peers. Women have thinner skin, so sensitivity to pain is higher. Female sex hormones estrogen promote an increase in hyaluronic acid in the dermis, which leads to an increase in water content in the skin and the smoothing of fine wrinkles. Causes of age-related skin changes Firstly, changes that occur with age arise as a consequence of an irreversible genetically programmed process. This natural aging is a consequence of passing years and is called chronoaging. In this case, the stratum corneum thickens and the remaining layers of the skin become thinner. The amount of hyaluronic acid produced decreases. The walls of blood capillaries become thin. There is a drooping of the soft tissues of the face under the influence of gravity. As a result of these changes, the skin loses its elasticity and deep wrinkles form. To avoid such age-related consequences, you need to seek help from cosmetology centers that provide comprehensive facial skin care. Secondly, aging is associated with wear and tear of the body due to illness, stress and random events that have negative consequences for health in general and appearance in particular. Internal causes of aging include: • dysfunction of the endocrine system; • decreased secretion of hormones, primarily from the pituitary gland and thyroid gland; • in women – decrease in estrogen; • decreased metabolism; • predominance of decay processes over synthesis processes; • weakened immunity; • microcirculation disturbance. Skin aging caused by internal factors leads to various histological changes in all its layers, including flattening of the interface between the epidermis and dermis, disappearance of dermal papillae, a decrease in the number of melanocytes and Langerhans cells in the epidermis, atrophy of the dermis, a decrease in the number of fibroblasts (9), mast cells , blood vessels in the skin, disappearance of elastic fibers in the subepidermal elaunin fibrous network and atypical depletion and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the dermis. Internal aging factors lead to functional changes in the skin: a decrease in the production of collagen types I and III, a decrease in the rate of epidermal regeneration and melanocyte activity. Thirdly, age-related changes are formed under the influence of numerous harmful factors that we constantly encounter throughout our lives. The skin is thinned and made rougher by the action of exogenous factors: sun, wind, frost, water, UV radiation. It is believed that 70% of skin aging depends not on age, but on the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, which is the main component of sunlight. If you compare the skin on the face with the skin on covered areas of the body, you can see that the changes primarily affected areas not protected by clothing. Skin aging caused by external factors, primarily UV radiation, results in histological changes that differ from those associated with internal factors. It is not surprising that nowadays facial skin care is a pressing task for women all over the world. It should also be noted that skin aging under the influence of internal factors manifests itself in a decrease in elasticity and a decrease in its cellular composition; skin damaged by ultraviolet radiation is characterized by elastosis, hyperproduction of abnormal elastic fibers, an increase in the number of mast cells, histiocytes and fibroblasts. Skin damaged by radiation is usually inflamed, its blood vessels the vessels are dilated and tortuous, the basement membrane is thinned. Although intrinsic and extrinsic aging factors cause different histological changes in the skin, functional impairment is similar for these factors. In skin damaged by radiation and internal mechanisms, there is a decrease in collagen content, melanocyte activity, and the skin’s ability to heal wounds. Based on the above information, we can safely say that facial skin care is an extremely important procedure that helps prolong a woman’s natural beauty. The sooner you begin to take this issue seriously, the longer you will maintain the healthy condition of your skin and its appearance.