Related Products
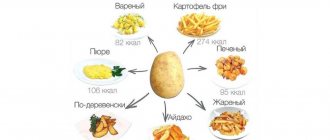
Sweet potatoes (91 cal) Jacket potatoes (82 cal) Red potatoes (70 cal) White potatoes (69 cal) Baked potatoes (93 cal) Roasted boiled potatoes (270 cal) Potato hashbrowns (213 cal) ) Fried Potatoes (168 cal) Raw Potatoes (74 cal) Whole Fried Potatoes (124 cal) Potato Skins (58 cal) Potato Flour (Starch) (357 cal) Potato Pancakes (268 cal) Potato Salad (143 cal) Baked Potatoes (125 cal) Canned Potatoes (55 cal) Frozen Potatoes (77 cal) Potato Casserole (90 cal) Mashed Potatoes (106 cal) Microwaved Potatoes (112 cal) .) Cooked Potatoes (79 cal)
Possible harm from boiled potatoes
Eating potatoes grown with nitrates can be harmful to health . Exceeding the permissible norm of nitrates in the body threatens food poisoning, respiratory failure, and increases the risk of cancer.
The vegetable peel contains solanine , a hemolytic poison that usually accumulates in old peels or when exposed to direct sunlight. It causes nausea, vomiting, dizziness.
Due to the starch content, high doses of boiled potatoes can cause disturbances in the frequency and consistency of stools; in people with intolerance to the product, they can provoke an allergic reaction in the form of rashes, peeling of the skin, itching, and Quincke's edema.
Who should not use it
It is recommended to limit or completely exclude boiled potatoes from the diet for people with allergies to the product, acute urolithiasis, increased gas formation, and constipation.
Composition of nutrients, BJU
Boiled potatoes
| For quantity: 100 grams | ||
| Calories — 84 | Calories in fat - 1 | |
| BJU | ||
| Total fat content | 0.1g | |
| Saturated | 0.03g | |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.04g | |
| Monounsaturated | 0g | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | |
| Total carbohydrate content | 19.11 | |
| Dietary fiber | 2.37g | |
| Sugar | 0.9g | |
| Squirrels | 2.15g | |
| Vitamins and microelements | ||
| A - 0mcg | C - 8.53 mg | |
| B-6 – 0.27 mg | B-12 - 0mcg | |
| D - 0mcg | E - 0.02 mg | |
| Calcium 19mkg | Iron 2.23 mg | |
| Magnesium 24 mg | Zinc 0.34 mg | |
| Potassium 371 mg | Sodium 126 mg | |
Distribution of calories for BJU:Carbohydrates (89%) Fats (1%) Proteins (10%) | ||
Boiled potatoes - benefits for the body
The benefits of boiled potatoes for the body are significant. It is a source of vitamins and minerals that promote health and beauty, prevention of diseases of the heart, blood vessels, liver, kidneys, nervous and digestive systems.
Boiled potatoes are an almost obligatory product in the daily diet . It is often prescribed as a therapeutic food to reduce body weight and cleanse the body of waste and toxins.
About the beneficial properties of other crops:
The health benefits and harms of eggplants
The benefits and harms of radishes for the body
The benefits and harms of beets for the body
The biological value and dietary qualities of the product are determined by the properties of each vitamin in it:
- Vitamin A (beta-carotene). A powerful antioxidant, slows down the aging process, takes part in the formation of new cells, protects the body from colds and genitourinary infections, provides night vision, and is necessary for the full functioning of the immune system.
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine). Supports heart function, the health of the nervous and digestive systems, stimulates the growth of bone and muscle tissue.
- Vitamin B1 (riboflavin). Promotes saturation of blood with oxygen, regulates the activity of the thyroid gland, supports the functioning of the reproductive system, takes an active part in the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- Vitamin B4 (choline). Responsible for neuromuscular transmission, increases brain performance, improves memory, lowers blood and intraocular pressure, slows heart contractions.
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid). Regulates metabolism, helps control weight, stimulates the production of steroid hormones, which makes it a powerful tool for the treatment and prevention of arthritis of various origins, heart disease, and allergic reactions.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). Responsible for the metabolism of proteins and fats, the absorption of unsaturated fatty acids, participates in the processes of hematopoiesis, the synthesis of histamine and hemoglobin, reduces cholesterol levels, and inhibits the aging process.
- Vitamin B9 (folates). Promotes better absorption of iron in the body, affects mood, appetite, and the state of the nervous system; without it, normal growth and development of embryonic tissues is impossible.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Protects a person from viral and cancer diseases, is necessary for the formation of collagen, thereby restoring skin moisture and elasticity, normalizing redox processes.
- Vitamin E (alpha tocopherol). Strengthens the body's defenses, has antioxidant properties, has a beneficial effect on the skin, ensures tissue respiration, and supports the normal activity of the gonads.
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone). Regulates blood clotting processes, prevents the deposition of calcium salts in soft tissues and organs, and reduces the risk of prostate cancer.
- Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid). Participates in the formation of enzymes and lipid metabolism, improves microcirculation, dilates small blood vessels, has detoxification properties, and relieves swelling.
- Betaine . Improves liver function, prevents the risk of breast cancer, protects skin cells from moisture loss, prevents obesity and Alzheimer's disease.
Potatoes - benefits and harm. Description, calorie content and characteristics of potatoes
Recipe Boiled potatoes with butter. Calorie, chemical composition and nutritional value.
Nutritional value and chemical composition of “Boiled potatoes with butter.”
The table shows the nutritional content (calories, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) per 100 grams of edible portion.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Norm** | % of the norm in 100 g | % of the norm in 100 kcal | 100% normal |
| Calorie content | 87.9 kcal | 1684 kcal | 5.2% | 5.9% | 1916 |
| Squirrels | 1.7 g | 76 g | 2.2% | 2.5% | 4471 g |
| Fats | 3.1 g | 56 g | 5.5% | 6.3% | 1806 |
| Carbohydrates | 13.2 g | 219 g | 6% | 6.8% | 1659 g |
| Organic acids | 0.2 g | ~ | |||
| Alimentary fiber | 1.2 g | 20 g | 6% | 6.8% | 1667 g |
| Water | 78.9 g | 2273 g | 3.5% | 4% | 2881 g |
| Ash | 2.582 g | ~ | |||
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin A, RE | 19.8 mcg | 900 mcg | 2.2% | 2.5% | 4545 g |
| Retinol | 0.015 mg | ~ | |||
| beta carotene | 0.029 mg | 5 mg | 0.6% | 0.7% | 17241 g |
| Vitamin B1, thiamine | 0.088 mg | 1.5 mg | 5.9% | 6.7% | 1705 g |
| Vitamin B2, riboflavin | 0.056 mg | 1.8 mg | 3.1% | 3.5% | 3214 g |
| Vitamin B5, pantothenic | 0.259 mg | 5 mg | 5.2% | 5.9% | 1931 |
| Vitamin B6, pyridoxine | 0.259 mg | 2 mg | 13% | 14.8% | 772 g |
| Vitamin B9, folates | 6.897 mcg | 400 mcg | 1.7% | 1.9% | 5800 g |
| Vitamin C, ascorbic acid | 12.07 mg | 90 mg | 13.4% | 15.2% | 746 g |
| Vitamin D, calciferol | 0.05 mcg | 10 mcg | 0.5% | 0.6% | 20000 g |
| Vitamin E, alpha tocopherol, TE | 0.125 mg | 15 mg | 0.8% | 0.9% | 12000 g |
| Vitamin H, biotin | 0.086 mcg | 50 mcg | 0.2% | 0.2% | 58140 g |
| Vitamin RR, NE | 1.5594 mg | 20 mg | 7.8% | 8.9% | 1283 g |
| Niacin | 0.9 mg | ~ | |||
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Potassium, K | 417.53 mg | 2500 mg | 16.7% | 19% | 599 g |
| Calcium, Ca | 16.25 mg | 1000 mg | 1.6% | 1.8% | 6154 g |
| Magnesium, Mg | 17.41 mg | 400 mg | 4.4% | 5% | 2298 g |
| Sodium, Na | 743.54 mg | 1300 mg | 57.2% | 65.1% | 175 g |
| Sera, S | 31.46 mg | 1000 mg | 3.1% | 3.5% | 3179 g |
| Phosphorus, P | 47.6 mg | 800 mg | 6% | 6.8% | 1681 g |
| Chlorine, Cl | 1193.65 mg | 2300 mg | 51.9% | 59% | 193 g |
| Microelements | |||||
| Aluminium, Al | 741.4 mcg | ~ | |||
| Bor, B | 99.1 mcg | ~ | |||
| Vanadium, V | 128.45 mcg | ~ | |||
| Iron, Fe | 0.723 mg | 18 mg | 4% | 4.6% | 2490 g |
| Yod, I | 4.31 mcg | 150 mcg | 2.9% | 3.3% | 3480 g |
| Cobalt, Co | 4.598 mcg | 10 mcg | 46% | 52.3% | 217 g |
| Lithium, Li | 66.379 mcg | ~ | |||
| Manganese, Mn | 0.1517 mg | 2 mg | 7.6% | 8.6% | 1318 g |
| Copper, Cu | 126.18 mcg | 1000 mcg | 12.6% | 14.3% | 793 g |
| Molybdenum, Mo | 9.004 mcg | 70 mcg | 12.9% | 14.7% | 777 g |
| Nickel, Ni | 4.31 mcg | ~ | |||
| Rubidium, Rb | 431 mcg | ~ | |||
| Selenium, Se | 0.259 mcg | 55 mcg | 0.5% | 0.6% | 21236 g |
| Fluorine, F | 37.36 mcg | 4000 mcg | 0.9% | 1% | 10707 g |
| Chromium, Cr | 8.62 mcg | 50 mcg | 17.2% | 19.6% | 580 g |
| Zinc, Zn | 0.3276 mg | 12 mg | 2.7% | 3.1% | 3663 g |
| Digestible carbohydrates | |||||
| Starch and dextrins | 12.414 g | ~ | |||
| Mono- and disaccharides (sugars) | 0.8 g | max 100 g | |||
| Glucose (dextrose) | 0.517 g | ~ | |||
| Sucrose | 0.517 g | ~ | |||
| Fructose | 0.086 g | ~ | |||
| Essential amino acids | 0.634 g | ~ | |||
| Arginine* | 0.087 g | ~ | |||
| Valin | 0.107 g | ~ | |||
| Histidine* | 0.027 g | ~ | |||
| Isoleucine | 0.076 g | ~ | |||
| Leucine | 0.113 g | ~ | |||
| Lysine | 0.118 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine | 0.023 g | ~ | |||
| Methionine + Cysteine | 0.044 g | ~ | |||
| Threonine | 0.085 g | ~ | |||
| Tryptophan | 0.026 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine | 0.086 g | ~ | |||
| Phenylalanine+Tyrosine | 0.167 g | ~ | |||
| Nonessential amino acids | 1.029 g | ~ | |||
| Alanin | 0.085 g | ~ | |||
| Aspartic acid | 0.218 g | ~ | |||
| Glycine | 0.087 g | ~ | |||
| Glutamic acid | 0.231 g | ~ | |||
| Proline | 0.081 g | ~ | |||
| Serin | 0.112 g | ~ | |||
| Tyrosine | 0.079 g | ~ | |||
| Cysteine | 0.02 g | ~ | |||
| Sterols (sterols) | |||||
| Cholesterol | 6.51 mg | max 300 mg | |||
| Saturated fatty acids | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | 1.9 g | max 18.7 g | |||
| 4:0 Oil | 0.103 g | ~ | |||
| 6:0 Kapronovaya | 0.047 g | ~ | |||
| 8:0 Caprylic | 0.025 g | ~ | |||
| 10:0 Kaprinovaya | 0.058 g | ~ | |||
| 12:0 Lauric | 0.066 g | ~ | |||
| 14:0 Miristinovaya | 0.306 g | ~ | |||
| 16:0 Palmitinaya | 0.907 g | ~ | |||
| 18:0 Stearic | 0.274 g | ~ | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.988 g | min 16.8 g | 5.9% | 6.7% | |
| 14:1 Myristoleic | 0.059 g | ~ | |||
| 16:1 Palmitoleic | 0.093 g | ~ | |||
| 18:1 Oleic (omega-9) | 0.828 g | ~ | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.108 g | from 11.2 to 20.6 g | 1% | 1.1% | |
| 18:2 Linolevaya | 0.104 g | ~ | |||
| 18:3 Linolenic | 0.073 g | ~ | |||
| Omega-6 fatty acids | 0.1 g | from 4.7 to 16.8 g | 2.1% | 2.4% |
The energy value of boiled potatoes with butter is 87.9 kcal.
Primary Source: Created in the application by the user. Read more.
** This table shows the average levels of vitamins and minerals for an adult. If you want to know the norms taking into account your gender, age and other factors, then use the “My Healthy Diet” application.
How low-calorie boiled potatoes can help you lose weight
Eating less to lose weight is a common misconception. In fact, the process of weight loss depends on the ratio of consumed and wasted kilocalories per day.
Weight loss occurs successfully when a daily intake of kilocalories is less than the individual threshold for maintaining body weight. With a standard threshold of 1000 kcal per day, you should consume no more than 900 kcal. If more, the weight will increase, much less, too. A nutritionist determines the calorie threshold when individually calculating height, body weight and physical activity.
The potato diet is one of the effective means for losing weight if the recommendations of nutritionists are followed. The calorie content of potatoes boiled in water is very low, so they are an ideal product for a mono-diet. The optimal time for losing weight “on potatoes” is the end of summer. At this time, the market offers various varieties of new potatoes with a maximum content of nutrients and a minimum of starch.
There are several options for the potato diet:
- fast (lasting 3 days);
- 7 days.
The first option is great for fasting days and allows you to lose 1-4 kg of weight. It is not recommended to eat anything other than tubers cooked in water (200-300 g), kefir (or skim milk - 1-2 glasses), greens and plain unboiled water.
The second option involves the following menu:
- Breakfast – a glass of kefir or low-fat milk;
- Lunch – 250 g of unsalted puree in water with a small amount of greens;
- Dinner - an egg and 200 g of boiled root vegetable salad with cucumber, herbs and a small amount of vegetable oil.